Chapter 11 Bayesian Models of Cognition
11.0.1 Introduction
The impressive power of Bayes theorem and Bayesian approaches to modeling has tempted cognitive scientists into exploring how far they could get in thinking the mind and brain as Bayesian machines. The idea is that the mind is a probabilistic machine that updates its beliefs based on the evidence it receives. The human mind constantly receives input from various sources – direct personal experience, social information from others, prior knowledge, and sensory input. A fundamental question in cognitive science is how these disparate pieces of information are combined to produce coherent beliefs about the world. The Bayesian framework offers a powerful approach to modeling this process. Under this framework, the mind is conceptualized as a probabilistic machine that continuously updates its beliefs based on new evidence. This contrasts with rule-based or purely associative models by emphasizing:
Representations of uncertainty: Beliefs are represented as probability distributions, not single values
Optimal integration: Information is combined according to its reliability
Prior knowledge: New evidence is interpreted in light of existing beliefs
In this chapter, we will explore how Bayesian integration can be formalized and used to model cognitive processes. We’ll start with simple models that give equal weight to different information sources, then develop more sophisticated models that allow for differential weighting based on source reliability, and finally consider how beliefs might update over time.
This chapter is not a comprehensive review of Bayesian cognitive modeling, but rather a practical introduction to the topic. We’ll focus on simple models that illustrate key concepts and provide a foundation for more advanced applications.
To go further in your learning check on Bayesian models of cognition check:
Ma, W. J., Kording, K. P., & Goldreich, D. (2023). Bayesian models of perception and action: An introduction. MIT press.
Griffiths, T. L., Chater, N., & Tenenbaum, J. B. (Eds.). (2024). Bayesian models of cognition: reverse engineering the mind. MIT Press.
N. D. Goodman, J. B. Tenenbaum, and The ProbMods Contributors (2016). Probabilistic Models of Cognition (2nd ed.). Retrieved 2025-3-10 from https://probmods.org/
11.1 Learning Objectives
After completing this chapter, you will be able to:
Understand the basic principles of Bayesian information integration
Implement models that combine multiple sources of information in a principled Bayesian way
Fit and evaluate these models using Stan
Differentiate between alternative Bayesian updating schemes
Apply Bayesian cognitive models to decision-making data
11.2 Chapter Roadmap
In this chapter, we will:
Introduce the Bayesian framework for cognitive modeling
Implement a simple Bayesian integration model
Develop and test a weighted Bayesian model that allows for different source reliability
Explore temporal Bayesian updating
Extend our models to multilevel structures that capture individual differences
Compare alternative Bayesian models and evaluate their cognitive implications
11.3 The Bayesian Framework for Cognition
Bayesian models of cognition explore the idea that the mind operates according to principles similar to Bayes’ theorem, combining different sources of evidence to form updated beliefs. Most commonly this is framed in terms of prior beliefs being updated with new evidence to form updated posterior beliefs. Formally:
P(belief | evidence) ∝ P(evidence | belief) × P(belief)
Where:
P(belief | evidence) is the posterior belief after observing evidence
P(evidence | belief) is the likelihood of observing the evidence given a belief
P(belief) is the prior belief before observing evidence
In cognitive terms, this means people integrate new information with existing knowledge, giving more weight to reliable information sources and less weight to unreliable ones. Yet, there is nothing mathematically special about the prior and the likelihood. They are just two sources of information that are combined in a way that is consistent with the rules of probability. Any other combination of information sources can be modeled with the same theorem.
Note that a more traditional formula for Bayes Theorem would be
P(belief | evidence) = [P(evidence | belief) × P(belief)] / P(evidence)
where the product of prior and likelihood is normalized by P(evidence) (bringing it back to a probability scale). That’s why we used a ∝ symbol in the formula above, to indicate that we are not considering the normalization constant, and that the posterior is only proportional (and not exactly equal) to the multiplication of the two sources of information. Nevertheless, this is a first useful approximation of the theorem, which we can build on in the rest of the chapter. ***
11.4 Visualizing Bayesian Updating
To better understand Bayesian updating, let’s create a conceptual diagram:
# Create a visualization of Bayesian updating process
# Function to create Bayesian updating visualization
create_bayesian_updating_diagram <- function() {
# Create example data
# Prior (starting with uniform distribution)
x <- seq(0, 1, by = 0.01)
prior <- dbeta(x, 1, 1)
# Likelihood (evidence suggesting higher probability)
likelihood <- dbeta(x, 7, 3)
# Posterior (combines prior and likelihood)
posterior <- dbeta(x, 8, 4) # 1+7, 1+3
# Create data frame for plotting
plot_data <- data.frame(
x = rep(x, 3),
density = c(prior, likelihood, posterior),
distribution = factor(rep(c("Prior", "Likelihood", "Posterior"), each = length(x)),
levels = c("Prior", "Likelihood", "Posterior"))
)
# Create main plot showing distributions
p1 <- ggplot(plot_data, aes(x = x, y = density, color = distribution, linetype = distribution)) +
geom_line(size = 1.2) +
scale_color_manual(values = c("Prior" = "blue", "Likelihood" = "red", "Posterior" = "purple")) +
scale_linetype_manual(values = c("Prior" = "dashed", "Likelihood" = "dotted", "Posterior" = "solid")) +
labs(title = "Bayesian Updating Process",
subtitle = "Combining prior beliefs with new evidence",
x = "Belief (probability)",
y = "Probability Density",
color = "Distribution",
linetype = "Distribution") +
theme_minimal() +
theme(legend.position = "bottom") +
annotate("text", x = 0.1, y = 0.9, label = "Low certainty\nprior belief", color = "blue", hjust = 0) +
annotate("text", x = 0.8, y = 1.5, label = "New evidence\nsuggests high\nprobability", color = "red", hjust = 1) +
annotate("text", x = 0.65, y = 2.2, label = "Updated belief\ncombines both\nsources", color = "purple", hjust = 0)
# Create flow diagram to illustrate process
flow_data <- data.frame(
x = c(1, 2, 3),
y = c(1, 1, 1),
label = c("Prior\nBelief", "Evidence", "Posterior\nBelief"),
box_color = c("blue", "red", "purple")
)
arrow_data <- data.frame(
x = c(1.3, 2.3),
xend = c(1.7, 2.7),
y = c(1, 1),
yend = c(1, 1)
)
p2 <- ggplot() +
# Add boxes for process stages
geom_rect(data = flow_data, aes(xmin = x - 0.3, xmax = x + 0.3,
ymin = y - 0.3, ymax = y + 0.3,
fill = box_color), color = "black", alpha = 0.3) +
# Add text labels
geom_text(data = flow_data, aes(x = x, y = y, label = label), size = 3.5) +
# Add arrows
geom_segment(data = arrow_data, aes(x = x, y = y, xend = xend, yend = yend),
arrow = arrow(length = unit(0.2, "cm"), type = "closed")) +
# Add the operation being performed
annotate("text", x = 1.5, y = 1.2, label = "×", size = 6) +
annotate("text", x = 2.5, y = 1.2, label = "∝", size = 5) +
# Formatting
scale_fill_manual(values = c("blue", "red", "purple")) +
theme_void() +
theme(legend.position = "none") +
labs(title = "Bayesian Inference Flow")
# Combine plots vertically
combined_plot <- p1 / p2 + plot_layout(heights = c(4, 1))
return(combined_plot)
}
# Generate and display the diagram
create_bayesian_updating_diagram()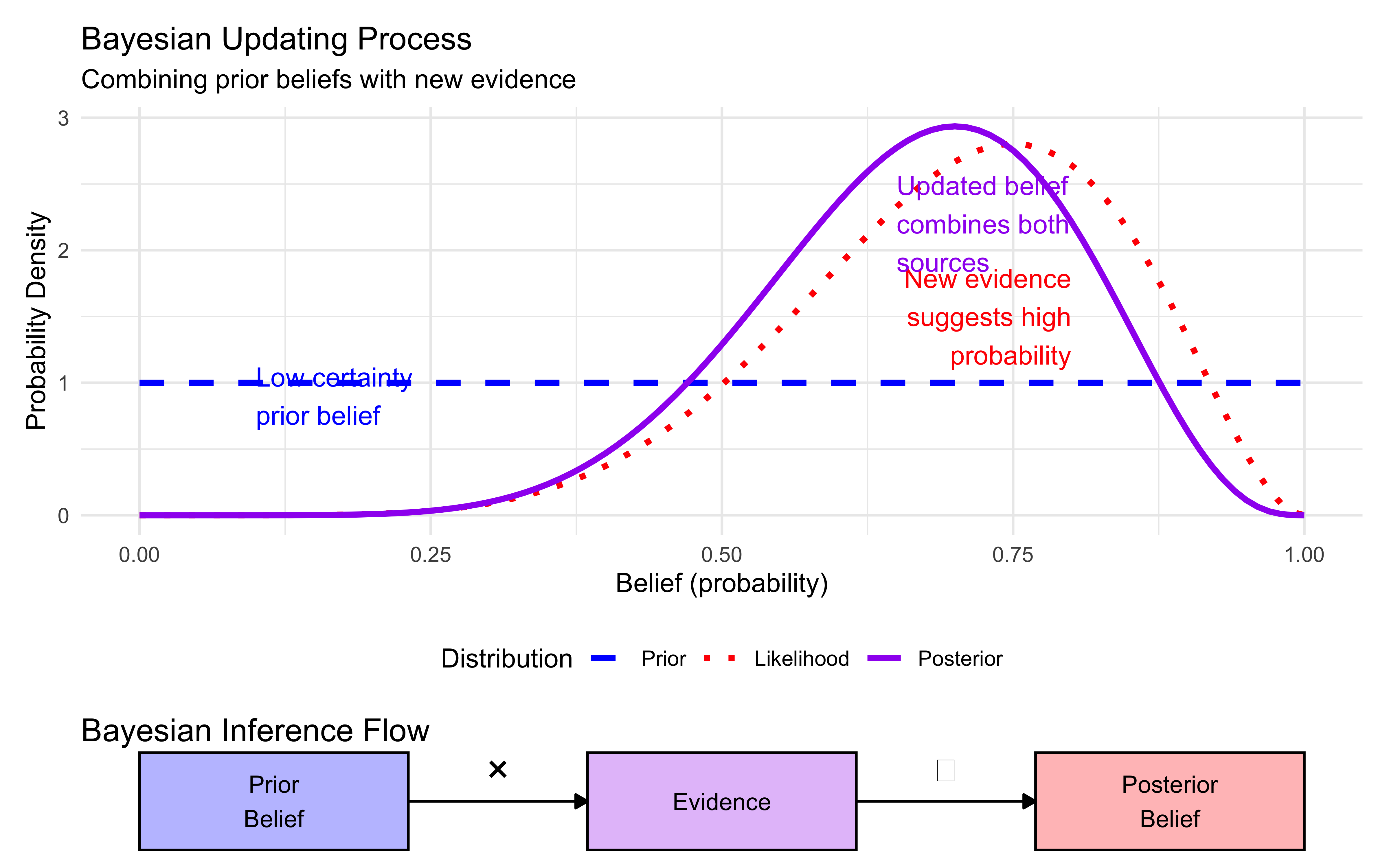
This diagram illustrates the key elements of Bayesian updating:
Prior belief (blue dashed line): Our initial uncertainty about a phenomenon, before seeing evidence
Likelihood (red dotted line): The pattern of evidence we observe
Posterior belief (purple solid line): Our updated belief after combining prior and evidence
Notice how the posterior distribution:
Is narrower than either the prior or likelihood alone (indicating increased certainty)
Sits between the prior and likelihood, but closer to the likelihood (as the evidence was fairly strong)
Has its peak shifted from the prior toward the likelihood (reflecting belief updating)
The bottom diagram shows the algebraic process: we multiply the prior by the likelihood, then normalize to get the posterior belief.
11.5 Bayesian Models in Cognitive Science
Bayesian cognitive models have been successfully applied to a wide range of phenomena:
Perception: How we combine multiple sensory cues (visual, auditory, tactile) to form a unified percept
Learning: How we update our knowledge from observation and instruction
Decision-making: How we weigh different sources of evidence when making choices
Social cognition: How we integrate others’ opinions with our own knowledge
Language: How we disambiguate words and sentences based on context
Psychopathology: How crucial aspects of conditions like schizophrenia and autism can be understood in terms of atypical Bayesian inference (e.g. atypical weights given to different sources of information, or hyper-precise priors or hyper-precise likelihood).
11.7 A Bayesian Integration Model for the Marble Task
In a fully Bayesian approach, participants would:
Use direct evidence to form a belief about the proportion of blue marbles in the jar
Use social evidence to form another belief about the same proportion
Combine these beliefs in a principled way to make their final judgment
11.7.1 Intuitive Explanation Using Beta Distributions
The beta distribution provides an elegant way to represent beliefs about proportions (like the proportion of blue marbles in a jar):
The beta distribution is defined by two parameters, traditionally called α (alpha) and β (beta).
These parameters have an intuitive interpretation: you can think of α as the number of “successes” you’ve observed (e.g., blue marbles) plus 1, and β as the number of “failures” (e.g., red marbles) plus 1.
So a Beta(1,1) distribution represents a uniform belief - no prior knowledge about the proportion.
After observing evidence, you simply add the counts to these parameters:
- If you see 6 blue and 2 red marbles, your updated belief is Beta(1+6, 1+2) = Beta(7, 3)
- This distribution has its peak at 7/(7+3) = 0.7, reflecting your belief that the true proportion is around 70% blue
To combine multiple sources of evidence, you simply add all the counts together:
If direct evidence gives Beta(7, 3) and social evidence suggests Beta(2, 4)
Your combined belief is Beta(7+2, 3+4) = Beta(9, 7)
This has its peak at 9/(9+7) = 0.56, reflecting a compromise between the two sources
The beauty of this approach is that it automatically weights evidence by its strength (amount of data) and properly represents uncertainty through the width of the distribution.
11.8 The Mathematical Model
For our marble task, the Bayesian inference process involves:
11.8.1 Evidence Representation
Direct evidence: Observing blue1 blue marbles and red1 red marbles out of total1 trials
Social evidence: Inferring blue2 blue marbles and red2 red marbles from social information. If we consider only their choice: red corresponds to the sampling of one red marble; blue corresponds to the sampling of one blue marble. If we consider their confidence, we might try to make this correspond to the marbles the sampled: “Clear blue” might imply 8 blue marbles; maybe blue might imply 6 blue and 2 red marbles; “maybe red” might imply 6 red and 2 blue marbles; “clear red” might imply 8 red marbles. Alternatively we can keep it more uncertain and reduce the assumed sample to 0 blue out of 3, 1 blue out of 3, 2 blue marbles out of 3, or 3 blue marbles out of 3. This intrinsically models the added uncertainty in observing the other’s choice and not their samples.
11.8.2 Integration
The integrated belief is represented by a posterior beta distribution:
Beta(α + blue1 + blue2, β + red1 + red2)
Where α and β are prior parameters (typically 1 each for a uniform prior)
11.8.3 Decision
Final choice (blue or red) depends on whether the expected value of this distribution is above 0.5
Confidence depends on the concentration of the distribution
11.8.4 Implementation in R
# Beta-binomial model for Bayesian integration in the marble task
#
# This function implements a Bayesian integration model for combining direct and social evidence
# about the proportion of blue marbles in a jar. It uses the beta-binomial model, which is
# particularly suitable for reasoning about proportions.
#
# Parameters:
# alpha_prior: Prior alpha parameter (conceptually: prior blue marbles + 1)
# beta_prior: Prior beta parameter (conceptually: prior red marbles + 1)
# blue1: Number of blue marbles in direct evidence
# total1: Total marbles in direct evidence
# blue2: Effective blue marbles from social evidence
# total2: Effective total marbles from social evidence
#
# Returns:
# List with posterior parameters and statistics for decision-making
betaBinomialModel <- function(alpha_prior, beta_prior, blue1, total1, blue2, total2) {
# Calculate red marbles for each source
red1 <- total1 - blue1 # Number of red marbles in direct evidence
red2 <- total2 - blue2 # Inferred number of red marbles from social evidence
# The key insight of Bayesian integration: simply add up all evidence counts
# This automatically gives more weight to sources with more data
alpha_post <- alpha_prior + blue1 + blue2 # Posterior alpha (total blues + prior)
beta_post <- beta_prior + red1 + red2 # Posterior beta (total reds + prior)
# Calculate posterior statistics
expected_rate <- alpha_post / (alpha_post + beta_post) # Mean of beta distribution
# Variance has a simple formula for beta distributions
# Lower variance = higher confidence in our estimate
variance <- (alpha_post * beta_post) /
((alpha_post + beta_post)^2 * (alpha_post + beta_post + 1))
# Calculate 95% credible interval using beta quantile functions
# This gives us bounds within which we believe the true proportion lies
ci_lower <- qbeta(0.025, alpha_post, beta_post)
ci_upper <- qbeta(0.975, alpha_post, beta_post)
# Calculate confidence based on variance
# Higher variance = lower confidence; transform to 0-1 scale
confidence <- 1 - (2 * sqrt(variance))
confidence <- max(0, min(1, confidence)) # Bound between 0 and 1
# Make decision based on whether expected rate exceeds 0.5
# If P(blue) > 0.5, choose blue; otherwise choose red
choice <- ifelse(expected_rate > 0.5, "Blue", "Red")
# Return all calculated parameters in a structured list
return(list(
alpha_post = alpha_post,
beta_post = beta_post,
expected_rate = expected_rate,
variance = variance,
ci_lower = ci_lower,
ci_upper = ci_upper,
confidence = confidence,
choice = choice
))
}11.8.5 Simulating Experimental Scenarios
We’ll create a comprehensive set of scenarios by varying both direct evidence (number of blue marbles observed directly) and social evidence (number of blue marbles inferred from social information).
# Set total counts for direct and social evidence
total1 <- 8 # Total marbles in direct evidence
total2 <- 3 # Total evidence units in social evidence
# Create all possible combinations of direct and social evidence
scenarios <- expand_grid(
blue1 = seq(0, 8, 1), # Direct evidence: 0 to 8 blue marbles
blue2 = seq(0, 3, 1) # Social evidence: 0 to 3 blue marbles (confidence levels)
) %>% mutate(
red1 = total1 - blue1, # Calculate red marbles for direct evidence
red2 = total2 - blue2 # Calculate implied red marbles for social evidence
)
# Process all scenarios to generate summary statistics
sim_data <- map_dfr(1:nrow(scenarios), function(i) {
# Extract scenario parameters
blue1 <- scenarios$blue1[i]
red1 <- scenarios$red1[i]
blue2 <- scenarios$blue2[i]
red2 <- scenarios$red2[i]
# Calculate Bayesian integration using our model
result <- betaBinomialModel(1, 1, blue1, total1, blue2, total2)
# Return summary data for this scenario
tibble(
blue1 = blue1,
red1 = red1,
blue2 = blue2,
red2 = red2,
expected_rate = result$expected_rate,
variance = result$variance,
ci_lower = result$ci_lower,
ci_upper = result$ci_upper,
choice = result$choice,
confidence = result$confidence
)
})
# Convert social evidence to meaningful labels for better visualization
sim_data$social_evidence <- factor(sim_data$blue2,
levels = c(0, 1, 2, 3),
labels = c("Clear Red", "Maybe Red", "Maybe Blue", "Clear Blue"))11.8.6 Visualizing Bayesian Integration
Let’s examine how expected proportion and uncertainty vary across different evidence combinations:
# Create two plot panels to visualize model behavior across all evidence combinations
p1 <- ggplot(sim_data, aes(x = blue1, y = expected_rate, color = social_evidence, group = social_evidence)) +
# Add credible intervals to show uncertainty
geom_ribbon(aes(ymin = ci_lower, ymax = ci_upper, fill = social_evidence), alpha = 0.2, color = NA) +
geom_line(size = 1) +
geom_point(size = 3) +
geom_hline(yintercept = 0.5, linetype = "dashed", color = "gray50") +
scale_x_continuous(breaks = 0:8) +
scale_color_brewer(palette = "Set1") +
scale_fill_brewer(palette = "Set1") +
labs(title = "Bayesian Integration of Direct and Social Evidence",
subtitle = "Expected proportion with 95% credible intervals",
x = "Number of Blue Marbles in Direct Sample (out of 8)",
y = "Expected Proportion of Blue Marbles",
color = "Social Evidence",
fill = "Social Evidence") +
theme_bw() +
coord_cartesian(ylim = c(0, 1))
# Display plot
p1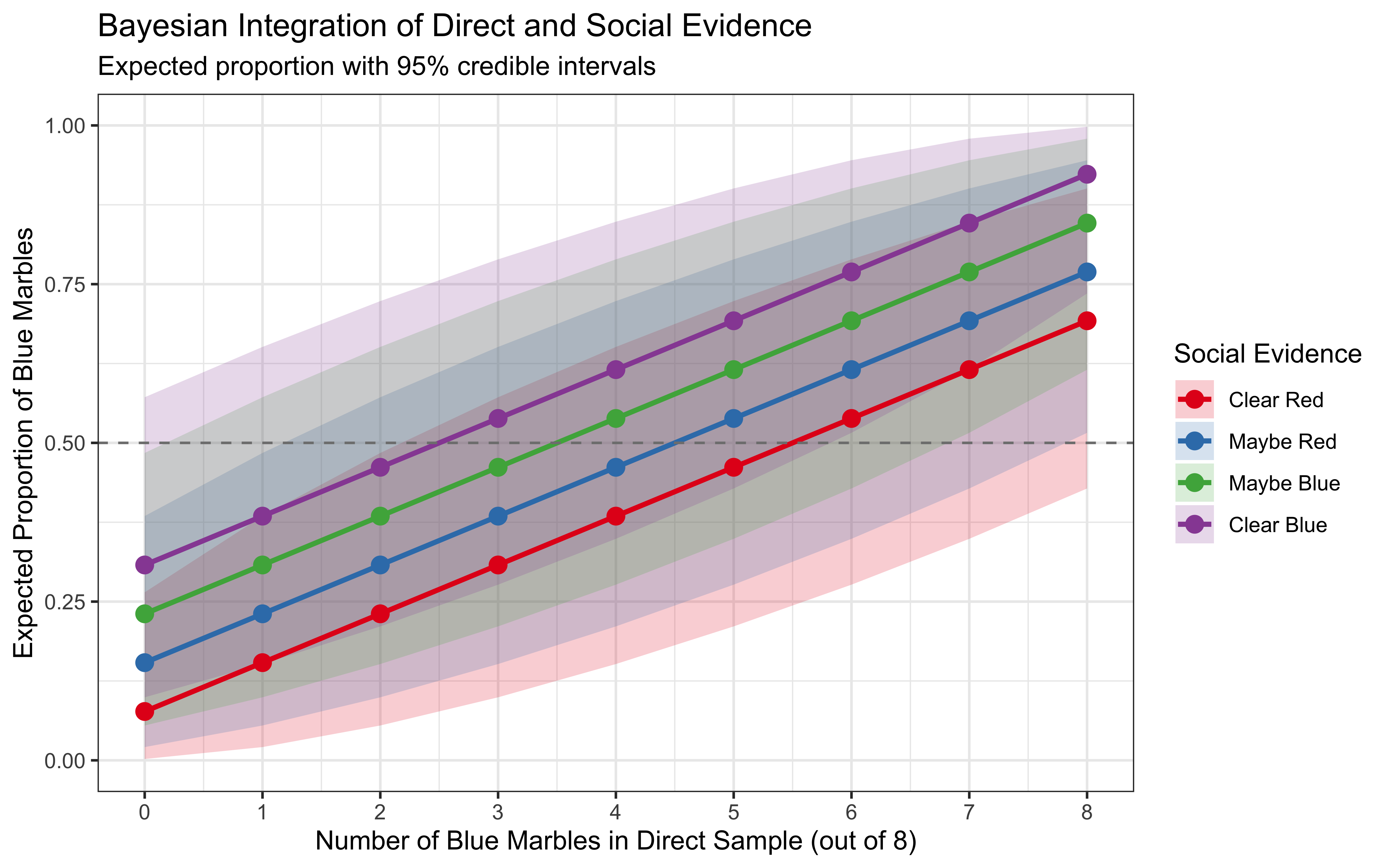
A few notes about the plot:
Evidence integration: The expected proportion of blue marbles (top plot) varies with both direct and social evidence. I would normally expect a non-linear interaction: when direct evidence is ambiguous (e.g., 4 blue out of 8), social evidence should have a stronger effect on the final belief. However, the effect is subtle if any.
Evidence Interaction: It may be hard to see, but the influence of social evidence is strongest when direct evidence is ambiguous (around 4 blue marbles) and weakest at the extremes (0 or 8 blue marbles). This reflects the Bayesian property that stronger evidence dominates weaker evidence.
Credible intervals: The 95% credible intervals (shaded regions) show our uncertainty about the true proportion. These intervals narrow with more evidence, indicating increased confidence in our estimates. This is better seen in the lower plot than in the upper one. Notice how the variance is highest when direct evidence is ambiguous (around 4 blue marbles) and lowest at the extremes (as they combine congruent evidence from both sources).
11.9 Examining Belief Distributions for Selected Scenarios
While the summary statistics give us a high-level view, examining the full posterior distributions provides deeper insight into how evidence is combined. Let’s visualize the complete probability distributions for a selected subset of scenarios:
# Function to generate Beta distributions for all components of a Bayesian model
# This function returns the prior, likelihood, and posterior distributions
# for a given scenario of blue and red marbles
simpleBayesianModel_f <- function(blue1, red1, blue2, red2) {
# Prior parameters (uniform prior)
alpha_prior <- 1
beta_prior <- 1
# Calculate parameters for each distribution
# Direct evidence distribution
alpha_direct <- alpha_prior + blue1
beta_direct <- beta_prior + red1
# Social evidence distribution
alpha_social <- alpha_prior + blue2
beta_social <- beta_prior + red2
# Posterior distribution (combined evidence)
alpha_post <- alpha_prior + blue1 + blue2
beta_post <- beta_prior + red1 + red2
# Create a grid of theta values (possible proportions of blue marbles)
theta <- seq(0.001, 0.999, length.out = 200)
# Calculate densities for each distribution
prior_density <- dbeta(theta, alpha_prior, beta_prior)
direct_density <- dbeta(theta, alpha_direct, beta_direct)
social_density <- dbeta(theta, alpha_social, beta_social)
posterior_density <- dbeta(theta, alpha_post, beta_post)
# Return dataframe with all distributions
return(data.frame(
theta = theta,
prior = prior_density,
direct = direct_density,
social = social_density,
posterior = posterior_density
))
}
# Select a few representative scenarios
selected_scenarios <- expand_grid(
blue1 = c(1, 4, 7), # Different levels of direct evidence
blue2 = c(0, 1, 2, 3) # Different levels of social evidence
)
# Generate distributions for each scenario
distribution_data <- do.call(rbind, lapply(1:nrow(selected_scenarios), function(i) {
blue1 <- selected_scenarios$blue1[i]
blue2 <- selected_scenarios$blue2[i]
# Generate distributions
dist_df <- simpleBayesianModel_f(blue1, total1 - blue1, blue2, total2 - blue2)
# Add scenario information
dist_df$blue1 <- blue1
dist_df$blue2 <- blue2
dist_df$social_evidence <- factor(blue2,
levels = c(0, 1, 2, 3),
labels = c("Clear Red", "Maybe Red", "Maybe Blue", "Clear Blue"))
return(dist_df)
}))
# Modify the plotting function
p_evidence_combination <- ggplot(distribution_data) +
# Prior distribution with clear emphasis
geom_line(aes(x = theta, y = prior), color = "gray50", linetype = "solid", size = 0.5) +
# Posterior distribution with consistent coloring
geom_area(aes(x = theta, y = posterior),
fill = "purple",
alpha = 0.3) +
geom_line(aes(x = theta, y = posterior),
color = "purple",
size = 1.2) +
# Direct and social evidence distributions
geom_line(aes(x = theta, y = direct, color = "Direct Evidence"),
size = 1,
alpha = 0.7,
linetype = "dashed") +
geom_line(aes(x = theta, y = social, color = "Social Evidence"),
size = 1,
alpha = 0.7,
linetype = "dashed") +
# Facet by direct and social evidence levels
facet_grid(blue2 ~ blue1,
labeller = labeller(
blue1 = function(x) paste("Direct: ", x, " Blue"),
blue2 = function(x) paste("Social: ", x, " Blue")
)) +
# Aesthetics
scale_color_manual(values = c(
"Direct Evidence" = "blue",
"Social Evidence" = "red"
)) +
# Labels and theme
labs(
title = "Bayesian Evidence Integration: Distribution Combination",
subtitle = "Merging direct and social evidence into a posterior belief",
x = "Proportion of Blue Marbles",
y = "Probability Density",
color = "Evidence Type"
) +
theme_minimal() +
theme(
legend.position = "bottom",
strip.text = element_text(size = 8),
axis.text = element_text(size = 6)
)
# Display the plot
print(p_evidence_combination)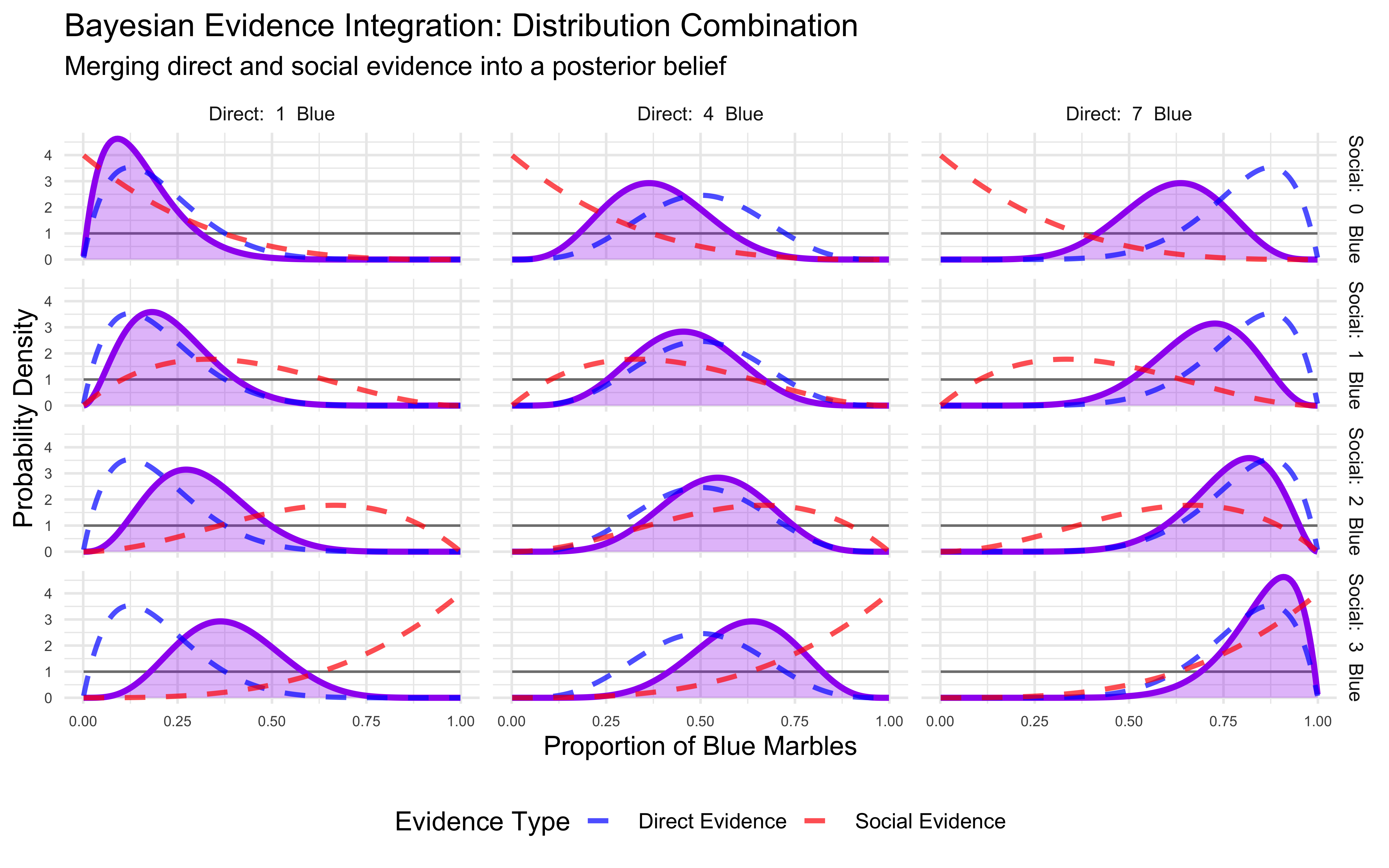
This comprehensive visualization shows how the different probability distributions interact:
Prior distribution (gray line): Our initial uniform belief about the proportion of blue marbles.
Direct evidence distribution (blue dashed line): Belief based solely on our direct observation of marbles. Notice how it becomes more concentrated with more extreme evidence (e.g., 1 or 7 blue marbles).
Social evidence distribution (red dashed line): Belief based solely on social information. This is generally less concentrated than the direct evidence distribution since it’s based on lower evidence (0-3 vs. 0-8).
Posterior distribution (purple area): The final belief that results from combining all information sources. Notice how it tends to lie between the direct and social evidence distributions, but is typically narrower than either, reflecting increased certainty from combining information, unless the evidence is in conflict.
11.10 Weighted Bayesian Integration
In real cognitive systems, people often weight information sources differently based on their reliability or relevance. Let’s implement a weighted Bayesian model that allows for differential weighting of evidence sources.
11.10.1 The Mathematical Model
Our weighted Bayesian integration model extends the simple model by introducing weight parameters for each information source:
Start with prior: Beta(α₀, β₀)
Observe direct evidence: k₁ blue marbles out of n₁ total
Observe social evidence: k₂ blue marbles out of n₂ total
Apply weights: w₁ for direct evidence, w₂ for social evidence
Posterior: Beta(α₀ + w₁·k₁ + w₂·k₂, β₀ + w₁·(n₁-k₁) + w₂·(n₂-k₂))
The weights represent the degree to which each information source influences the final belief. A weight of 2.0 means you treat that evidence as if you had observed twice as many marbles as you actually did (as more reliable than what the current evidence would warrant), while a weight of 0.5 means you treat it as half as informative. From a cognitive perspective, they might reflect judgments about reliability, relevance, or attentional focus.
11.10.2 Implementation
# Weighted Beta-Binomial model for evidence integration
#
# This function extends our basic model by allowing different weights for each
# evidence source. This can represent differences in perceived reliability,
# attention, or individual cognitive tendencies.
#
# Parameters:
# alpha_prior, beta_prior: Prior parameters (typically 1,1 for uniform prior)
# blue1, total1: Direct evidence (blue marbles and total)
# blue2, total2: Social evidence (blue signals and total)
# weight_direct, weight_social: Relative weights for each evidence source
#
# Returns:
# List with model results and statistics
weightedBetaBinomial <- function(alpha_prior, beta_prior,
blue1, total1,
blue2, total2,
weight_direct, weight_social) {
# Calculate red marbles for each source
red1 <- total1 - blue1 # Number of red marbles in direct evidence
red2 <- total2 - blue2 # Number of red signals in social evidence
# Apply weights to evidence (this is the key step)
# Weighting effectively scales the "sample size" of each information source
weighted_blue1 <- blue1 * weight_direct # Weighted blue count from direct evidence
weighted_red1 <- red1 * weight_direct # Weighted red count from direct evidence
weighted_blue2 <- blue2 * weight_social # Weighted blue count from social evidence
weighted_red2 <- red2 * weight_social # Weighted red count from social evidence
# Calculate posterior parameters by adding weighted evidence
alpha_post <- alpha_prior + weighted_blue1 + weighted_blue2 # Posterior alpha parameter
beta_post <- beta_prior + weighted_red1 + weighted_red2 # Posterior beta parameter
# Calculate statistics from posterior beta distribution
expected_rate <- alpha_post / (alpha_post + beta_post) # Mean of beta distribution
# Calculate variance (lower variance = higher confidence)
variance <- (alpha_post * beta_post) /
((alpha_post + beta_post)^2 * (alpha_post + beta_post + 1))
# Calculate 95% credible interval
ci_lower <- qbeta(0.025, alpha_post, beta_post)
ci_upper <- qbeta(0.975, alpha_post, beta_post)
# Calculate decision and confidence
decision <- ifelse(rbinom(1, 1, expected_rate) == 1, "Blue", "Red") # Decision based on most likely color
confidence <- 1 - (2 * sqrt(variance)) # Confidence based on certainty
confidence <- max(0, min(1, confidence)) # Bound between 0 and 1
# Return all calculated parameters in a structured list
return(list(
alpha_post = alpha_post,
beta_post = beta_post,
expected_rate = expected_rate,
variance = variance,
ci_lower = ci_lower,
ci_upper = ci_upper,
decision = decision,
confidence = confidence
))
}11.10.3 Visualizing Weighted Bayesian Integration
Let’s create a comprehensive visualization showing how different weights affect belief formation:
# Create improved visualization using small multiples
weighted_belief_plot <- function() {
# Define grid of parameters to visualize
w1_values <- seq(0, 2, by = 0.2) # Weight for source 1
w2_values <- seq(0, 2, by = 0.2) # Weight for source 2
source1_values <- seq(0, 8, by = 1) # Source 1 values
source2_values <- seq(0, 3, by = 1) # Source 2 values
# Generate data
plot_data <- expand_grid(
w1 = w1_values,
w2 = w2_values,
Source1 = source1_values,
Source2 = source2_values
) %>%
mutate(
belief = pmap_dbl(list(w1, w2, Source1, Source2), function(w1, w2, s1, s2) {
# Calculate Beta parameters
alpha_prior <- 1
beta_prior <- 1
alpha_post <- alpha_prior + w1 * s1 + w2 * s2
beta_post <- beta_prior + w1 * (8 - s1) + w2*(3 - s2)
# Return expected value
alpha_post / (alpha_post + beta_post)
})
)
# Create visualization
p <- ggplot(plot_data, aes(x = Source1, y = belief, color = Source2, group = Source2)) +
geom_line() +
facet_grid(w1 ~ w2, labeller = labeller(
w1 = function(x) paste("w1 =", x),
w2 = function(x) paste("w2 =", x)
)) +
scale_color_viridis_c(option = "plasma") +
labs(
title = "Weighted Bayesian Integration of Two Evidence Sources",
x = "Direct Evidence (Blue Marbles)",
y = "Belief in the next pick being a blue marble",
color = "Social Evidence (Blue Marbles)"
) +
theme_minimal() +
theme(
strip.background = element_rect(fill = "gray90"),
strip.text = element_text(size = 10, face = "bold"),
panel.grid.minor = element_blank(),
panel.border = element_rect(color = "black", fill = NA)
)
return(p)
}
# Generate and display the plot
weighted_belief_plot()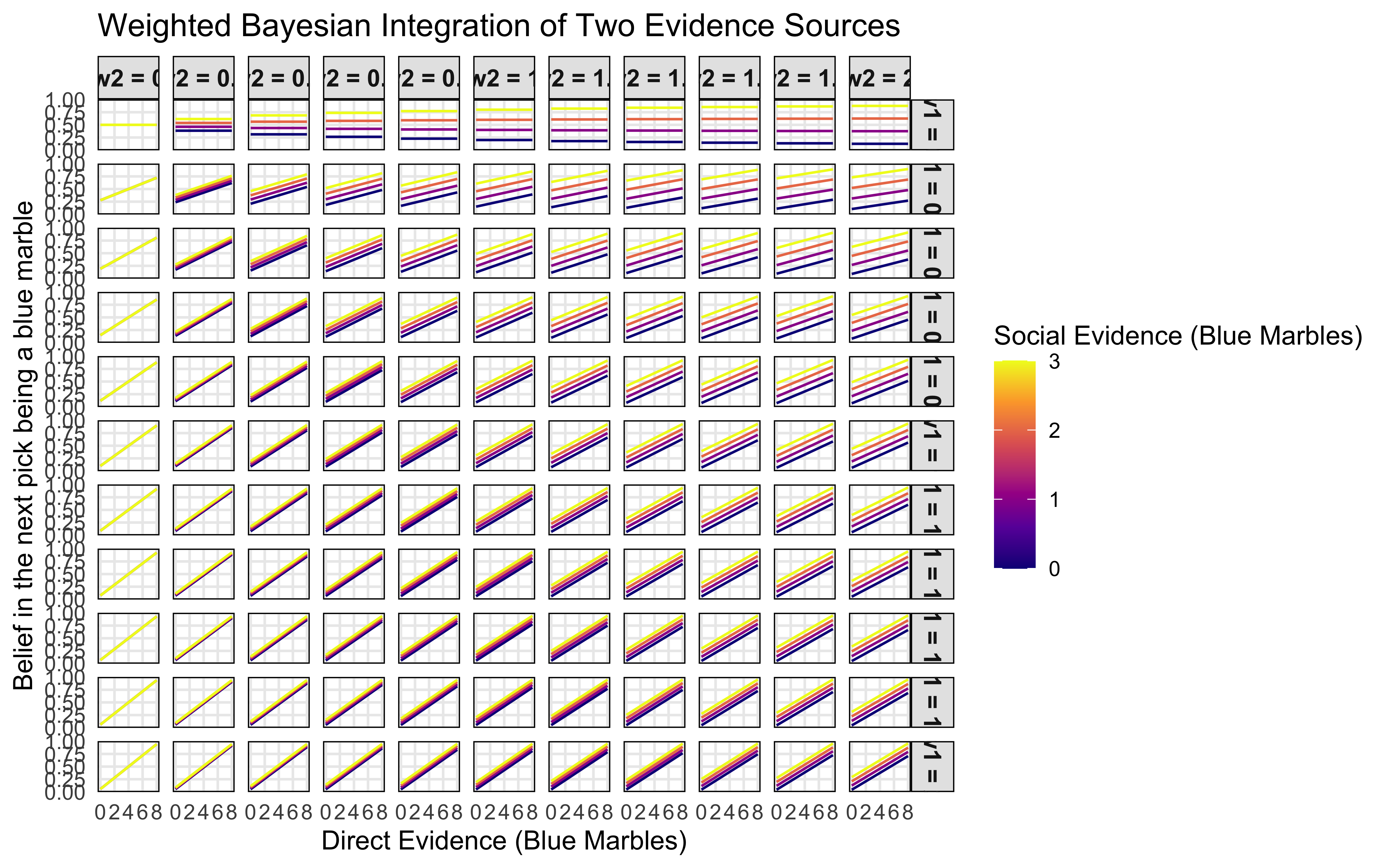
The visualization showcases weighted Bayesian integration:
First, when both weights (w1 and w2) are low (top left panels), beliefs remain moderate regardless of the evidence values, representing high uncertainty. As weights increase (moving right and down), beliefs become more extreme, showing increased confidence in the integrated evidence.
Second, the slope of the lines indicates the relative influence of each source. Steeper slopes (bottom right panels) demonstrate that Source1 has stronger influence on belief when both weights are high, while the spacing between lines shows the impact of Source2.
Third, when weights are asymmetric (e.g., high w1 and low w2), the belief is dominated by the source with the higher weight, essentially ignoring evidence from the other source. This illustrates how selective attention to certain evidence sources can be modeled as differential weighting in a Bayesian framework.
11.10.4 Resolving Conflicting Evidence
To further understand how weighted Bayesian integration resolves conflicts between evidence sources, let’s examine two specific conflict scenarios:
# Define conflict scenarios
scenario1 <- list(blue1 = 7, total1 = 8, blue2 = 0, total2 = 3) # Direct: blue, Social: red
scenario2 <- list(blue1 = 5, total1 = 8, blue2 = 0, total2 = 3) # Direct: red, Social: blue
# Create function to evaluate scenarios across weight combinations
evaluate_conflict <- function(scenario) {
weight_grid <- expand_grid(
weight_direct = seq(0, 2, by = 0.2),
weight_social = seq(0, 2, by = 0.2)
)
# Calculate results for each weight combination
results <- pmap_dfr(weight_grid, function(weight_direct, weight_social) {
result <- weightedBetaBinomial(
1, 1,
scenario$blue1, scenario$total1,
scenario$blue2, scenario$total2,
weight_direct, weight_social
)
tibble(
weight_direct = weight_direct,
weight_social = weight_social,
expected_rate = result$expected_rate,
decision = result$decision
)
})
return(results)
}
# Calculate results
conflict1_results <- evaluate_conflict(scenario1)
conflict2_results <- evaluate_conflict(scenario2)
# Create visualizations
p1 <- ggplot(conflict1_results, aes(x = weight_direct, y = weight_social)) +
geom_tile(aes(fill = expected_rate)) +
geom_contour(aes(z = expected_rate), breaks = 0.5, color = "black", size = 1) +
scale_fill_gradient2(
low = "red", mid = "white", high = "blue",
midpoint = 0.5, limits = c(0, 1)
) +
labs(
title = "Scenario 1: Strong Direct Evidence for Blue (7 out of 8) \nvs. Strong Social Evidence for Red (0/3)",
subtitle = "Black line shows decision boundary (expected rate = 0.5)",
x = "Weight for Direct Evidence",
y = "Weight for Social Evidence",
fill = "Expected\nRate"
) +
theme_minimal() +
coord_fixed()
p2 <- ggplot(conflict2_results, aes(x = weight_direct, y = weight_social)) +
geom_tile(aes(fill = expected_rate)) +
geom_contour(aes(z = expected_rate), breaks = 0.5, color = "black", size = 1) +
scale_fill_gradient2(
low = "red", mid = "white", high = "blue",
midpoint = 0.5, limits = c(0, 1)
) +
labs(
title = "Scenario 1: Weak Direct Evidence for Blue (5 out of 8) \nvs. Strong Social Evidence for Red (0/3)",
subtitle = "Black line shows decision boundary (expected rate = 0.5)",
x = "Weight for Direct Evidence",
y = "Weight for Social Evidence",
fill = "Expected\nRate"
) +
theme_minimal() +
coord_fixed()
# Display plots
p1 / p2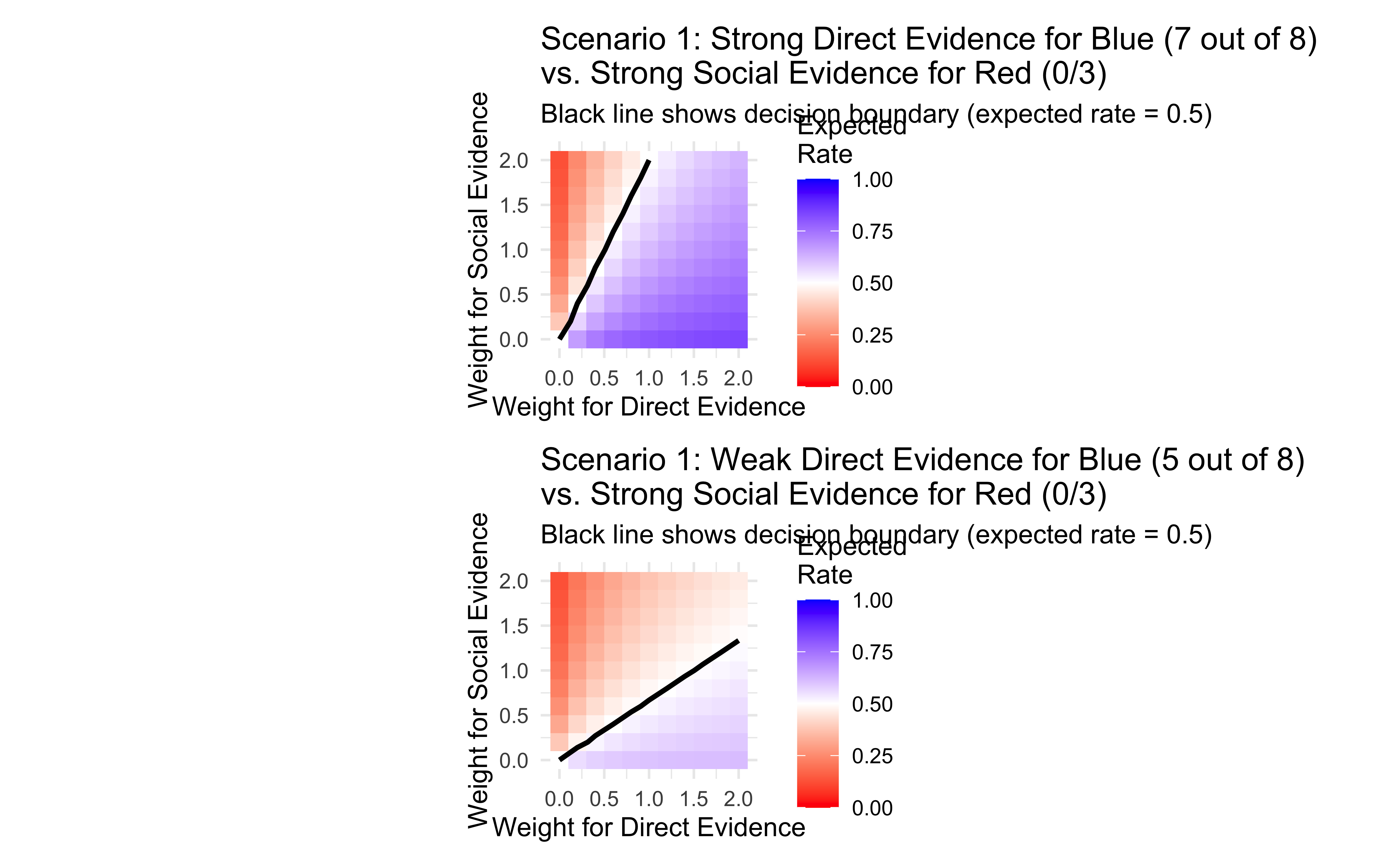
These visualizations illustrate how different weight combinations resolve conflicts between evidence sources:
Decision boundary: The black line represents combinations of weights that lead to equal evidence for red and blue (expected rate = 0.5). Weight combinations above this line lead to a “blue” decision, while those below lead to a “red” decision.
Relative evidence strength: The slope of the decision boundary reflects the relative strength of the evidence sources. A steeper slope indicates that direct evidence is stronger relative to social evidence.
Individual differences: Different individuals might give different weights to evidence sources, leading to different decisions even when faced with identical evidence. This provides a mechanistic explanation for individual variation in decision-making.
11.11 Common Misinterpretations
11.11.1 Weight Interpretation
Weights effectively scale the relative importance of each source of evidence. A weight of 0 means ignoring that evidence source entirely. A weight of 1 means treating the evidence as observed, at face value. Weights above 1 amplify the evidence, while weights below 1 dampen it. A negative weight would make the agent invert the direction of the evidence (if more evidence for red, they’d tend to pick blue). Remember that weights moderate the evidence, so a strong weight doesn’t guarantee a strong influence if the evidence itself is weak.
11.11.2 Integration vs. Averaging
Bayesian integration is not simply the averaging of evidence across sources, because it naturally includes how precise the evidence is (how narrow the distribution). Normally, this would happen when we multiply the distributions involved. The Beta-Binomial model handles this automatically by incorporating sample sizes (the n of marbles).
11.11.3 Interpreting Confidence
There is something tricky in this model when it comes to confidence. We can say that a belief that the next sample is going to be blue with a 0.8 (average) probability more confident than one with a 0.6 (average) probability. We can also say that a belief that the next sample is going to be blue with a 0.8 (95% CIs 0.5-1) probability is less confident than a belief with a 0.6 (95% CIs 0.55-0.65) probability. We need to keep these two aspects separate. The first one is about the average probability, the second one is about the uncertainty around that average probability. In the code above we only call the second confidence and use entropy of the posterior distribution to quantify it.
11.12 Simulating Agents with Different Evidence Weighting Strategies
To prepare for our model fitting, we’ll simulate three distinct agents:
Balanced Agent: This agent treats both direct and social evidence at face value, applying equal weights (w_direct = 1.0, w_social = 1.0). This represents an unbiased integration of information.
Self-Focused Agent: This agent overweights their own direct evidence (w_direct = 1.5) while underweighting social evidence (w_social = 0.5). This represents someone who trusts their own observations more than information from others.
Socially-Influenced Agent: This agent does the opposite, overweighting social evidence (w_social = 2.0) while underweighting their own direct evidence (w_direct = 0.7). This might represent someone who is highly responsive to social information.
Let’s generate decisions for these three agents in an experiment exposing them to all possible evidence combinations and visualize how their different weighting strategies affect their beliefs and choices.
# Simulation of agents with different weighting strategies
# This code generates decisions for three agents with different approaches to weighting evidence
# Define our three agent types with their respective weights
agents <- tibble(
agent_type = c("Balanced", "Self-Focused", "Socially-Influenced"),
weight_direct = c(1.0, 1.5, 0.7), # Weight for direct evidence
weight_social = c(1.0, 0.5, 2.0) # Weight for social evidence
)
# Create all possible evidence combinations
# Direct evidence: 0-8 blue marbles out of 8 total
# Social evidence: 0-3 signals (representing confidence levels)
evidence_combinations <- expand_grid(
blue1 = 0:8, # Direct evidence: number of blue marbles seen
blue2 = 0:3 # Social evidence: strength of blue evidence
) %>% mutate(
total1 = 8, # Total marbles in direct evidence
total2 = 3 # Total strength units in social evidence
)
generate_agent_decisions <- function(weight_direct, weight_social, evidence_df, n_samples = 5) {
# Create a data frame that repeats each evidence combination n_samples times
repeated_evidence <- evidence_df %>%
slice(rep(1:n(), each = n_samples)) %>%
# Add a sample_id to distinguish between repetitions of the same combination
group_by(blue1, blue2, total1, total2) %>%
mutate(sample_id = 1:n()) %>%
ungroup()
# Apply our weighted Bayesian model to each evidence combination
decisions <- pmap_dfr(repeated_evidence, function(blue1, blue2, total1, total2, sample_id) {
# Calculate Bayesian integration with the agent's specific weights
result <- weightedBetaBinomial(
alpha_prior = 1, beta_prior = 1,
blue1 = blue1, total1 = total1,
blue2 = blue2, total2 = total2,
weight_direct = weight_direct,
weight_social = weight_social
)
# Return key decision metrics
tibble(
sample_id = sample_id,
blue1 = blue1,
blue2 = blue2,
total1 = total1,
total2 = total2,
expected_rate = result$expected_rate, # Probability the next marble is blue
choice = result$decision, # Final decision (Blue or Red)
choice_binary = ifelse(result$decision == "Blue", 1, 0),
confidence = result$confidence # Confidence in decision
)
})
return(decisions)
}
# When generating data for weighted Bayesian model simulation
simulation_results <- map_dfr(1:nrow(agents), function(i) {
# Extract this agent's parameters
agent_data <- agents[i, ]
# Generate decisions for this agent with multiple samples
decisions <- generate_agent_decisions(
agent_data$weight_direct,
agent_data$weight_social,
evidence_combinations,
n_samples = 5 # Generate 5 samples per evidence combination
)
# Add agent identifier
decisions$agent_type <- agent_data$agent_type
return(decisions)
})
# Add descriptive labels for visualization
simulation_results <- simulation_results %>%
mutate(
# Create descriptive labels for social evidence
social_evidence = factor(
blue2,
levels = 0:3,
labels = c("Clear Red", "Maybe Red", "Maybe Blue", "Clear Blue")
),
# Create factor for agent type to control plotting order
agent_type = factor(
agent_type,
levels = c("Balanced", "Self-Focused", "Socially-Influenced")
)
)
# Let's examine a sample of the generated data
head(simulation_results)## # A tibble: 6 × 11
## sample_id blue1 blue2 total1 total2 expected_rate choice choice_binary confidence
## <int> <int> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <chr> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 1 0 0 8 3 0.0769 Red 0 0.858
## 2 2 0 0 8 3 0.0769 Red 0 0.858
## 3 3 0 0 8 3 0.0769 Red 0 0.858
## 4 4 0 0 8 3 0.0769 Red 0 0.858
## 5 5 0 0 8 3 0.0769 Red 0 0.858
## 6 1 0 1 8 3 0.154 Red 0 0.807
## # ℹ 2 more variables: agent_type <fct>, social_evidence <fct>Now let’s create visualizations to compare how these different agents make decisions based on the same evidence:
# Visualization 1: Expected probability across evidence combinations
p1 <- ggplot(simulation_results,
aes(x = blue1, y = expected_rate, color = social_evidence, group = social_evidence)) +
# Draw a line for each social evidence level
geom_line(size = 1) +
# Add points to show discrete evidence combinations
geom_point(size = 2) +
# Add a reference line at 0.5 (decision boundary)
geom_hline(yintercept = 0.5, linetype = "dashed", color = "gray50") +
# Facet by agent type
facet_wrap(~ agent_type, ncol = 1) +
# Customize colors and labels
scale_color_brewer(palette = "Set1") +
scale_x_continuous(breaks = 0:8) +
labs(
title = "How Different Agents Integrate Evidence",
subtitle = "Expected probability of blue marble across evidence combinations",
x = "Number of Blue Marbles in Direct Sample (out of 8)",
y = "Expected Probability of Blue",
color = "Social Evidence"
) +
theme_bw() +
theme(legend.position = "bottom")
# Visualization 2: Decision boundaries for each agent
# Create a simplified dataset showing just the decision (Blue/Red)
decision_data <- simulation_results %>%
mutate(decision_value = ifelse(choice == "Blue", 1, 0))
p2 <- ggplot(decision_data, aes(x = blue1, y = blue2)) +
# Create tiles colored by decision
geom_tile(aes(fill = choice)) +
# Add decision boundary contour line
stat_contour(aes(z = decision_value), breaks = 0.5, color = "black", size = 1) +
# Facet by agent type
facet_wrap(~ agent_type) +
# Customize colors and labels
scale_fill_manual(values = c("Red" = "firebrick", "Blue" = "royalblue")) +
scale_x_continuous(breaks = 0:8) +
scale_y_continuous(breaks = 0:3) +
labs(
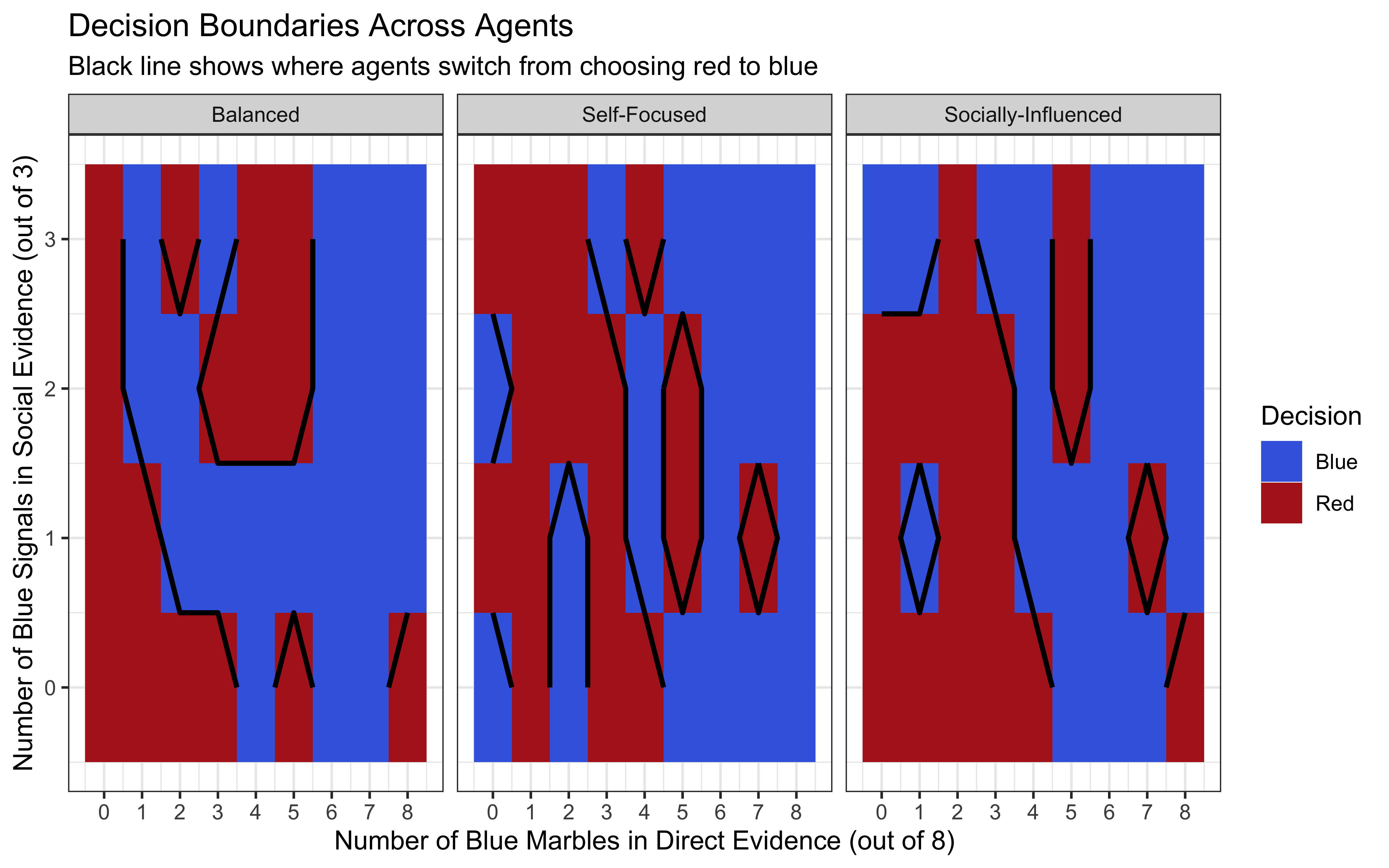
title = "Decision Boundaries Across Agents",
subtitle = "Black line shows where agents switch from choosing red to blue",
x = "Number of Blue Marbles in Direct Evidence (out of 8)",
y = "Number of Blue Signals in Social Evidence (out of 3)",
fill = "Decision"
) +
theme_bw()
# Visualization 3: Confidence levels
p3 <- ggplot(simulation_results, aes(x = blue1, y = confidence, color = social_evidence, group = social_evidence)) +
geom_line(size = 1) +
geom_point(size = 2) +
facet_wrap(~ agent_type, ncol = 1) +
scale_color_brewer(palette = "Set1") +
scale_x_continuous(breaks = 0:8) +
labs(
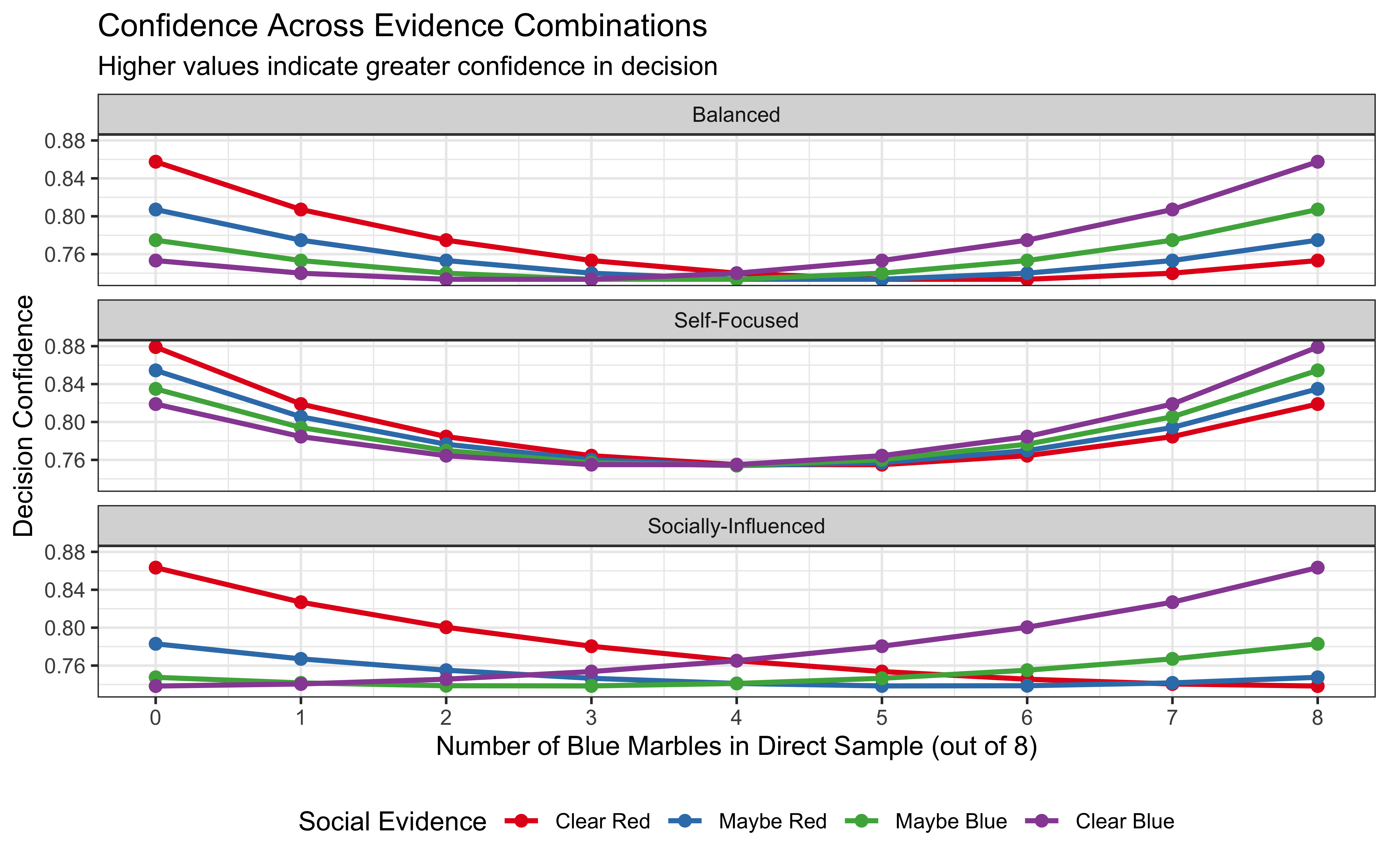
title = "Confidence Across Evidence Combinations",
subtitle = "Higher values indicate greater confidence in decision",
x = "Number of Blue Marbles in Direct Sample (out of 8)",
y = "Decision Confidence",
color = "Social Evidence"
) +
theme_bw() +
theme(legend.position = "bottom")
# Display the visualizations
p1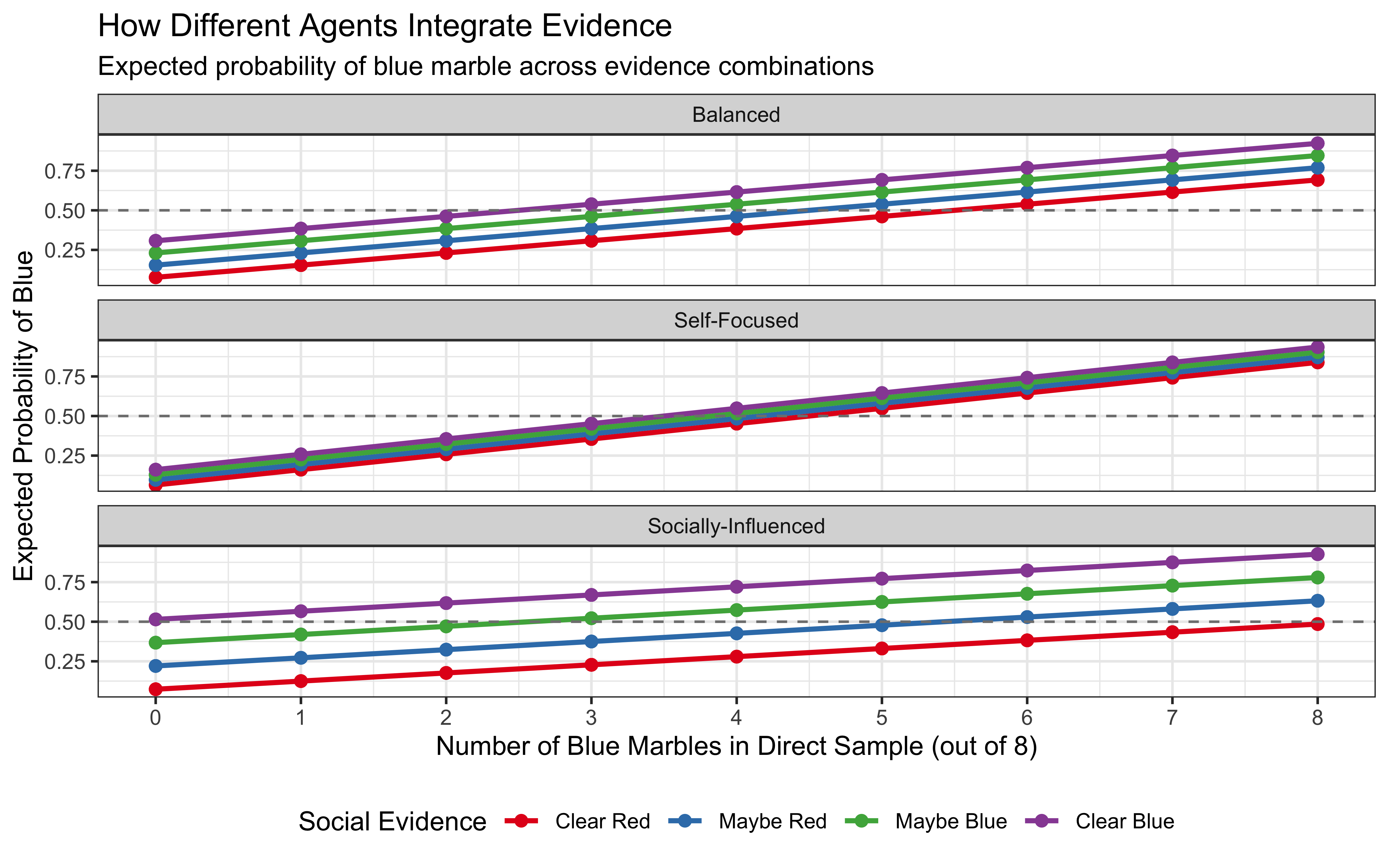
11.13 Key Observations from the Simulation
Our simulation highlights several important aspects of Bayesian evidence integration with different weighting strategies:
Evidence Thresholds: The decision boundaries (Visualization 2) clearly show how much evidence each agent requires to switch from choosing red to blue. The Self-Focused agent needs less direct evidence when social evidence supports blue, compared to the Socially-Influenced agent.
Influence of Social Evidence: In the first visualization, we can observe how the lines for different social evidence levels are spaced. For the Socially-Influenced agent, these lines are widely spaced, indicating that social evidence strongly affects their beliefs. For the Self-Focused agent, the lines are closer together, showing less impact from social evidence.
Confidence Patterns: The third visualization reveals how confidence varies across evidence combinations and agent types. All agents are most confident when evidence is strong and consistent across sources, but they differ in how they handle conflicting evidence.
Decision Regions: The Self-Focused agent has a larger region where they choose blue based primarily on direct evidence, while the Socially-Influenced agent has more regions where social evidence can override moderate direct evidence.
These patterns highlight the profound impact that evidence weighting can have on decision-making, even when agents are all using the same underlying Bayesian integration mechanism. In the next section, we’ll implement these agents in Stan to perform more sophisticated parameter estimation.
Now, let’s define our Stan models to implement: a simple bayesian agent (equivalent to assuming both weights to be 1); and a weighted bayesian agent (explicitly inferring weights for direct and social evidence).
# Simple Beta-Binomial Stan model (no weights)
SimpleAgent_stan <- "
// Bayesian integration model relying on a beta-binomial distribution
// to preserve all uncertainty
// All evidence is taken at face value (equal weights)
data {
int<lower=1> N; // Number of decisions
array[N] int<lower=0, upper=1> choice; // Choices (0=red, 1=blue)
array[N] int<lower=0> blue1; // Direct evidence (blue marbles)
array[N] int<lower=0> total1; // Total direct evidence (total marbles)
array[N] int<lower=0> blue2; // Social evidence (blue signals)
array[N] int<lower=0> total2; // Total social evidence (total signals)
}
parameters{
real<lower = 0> alpha_prior; // Prior alpha parameter
real<lower = 0> beta_prior; // Prior beta parameter
}
model {
target += lognormal_lpdf(alpha_prior | 0, 1); // Prior on alpha_prior, the agent bias towards blue
target += lognormal_lpdf(beta_prior | 0, 1); // Prior on beta_prior, the agent bias towards red
// Each observation is a separate decision
for (i in 1:N) {
// Calculate Beta parameters for posterior belief distribution
real alpha_post = alpha_prior + blue1[i] + blue2[i];
real beta_post = beta_prior + (total1[i] - blue1[i]) + (total2[i] - blue2[i]);
// Use beta_binomial distribution which integrates over all possible values
// of the rate parameter weighted by their posterior probability
target += beta_binomial_lpmf(choice[i] | 1, alpha_post, beta_post);
}
}
generated quantities {
// Log likelihood for model comparison
vector[N] log_lik;
// Prior and posterior predictive checks
array[N] int prior_pred_choice;
array[N] int posterior_pred_choice;
for (i in 1:N) {
// For prior predictions, use uniform prior (Beta(1,1))
prior_pred_choice[i] = beta_binomial_rng(1, 1, 1);
// For posterior predictions, use integrated evidence
real alpha_post = alpha_prior + blue1[i] + blue2[i];
real beta_post = beta_prior + (total1[i] - blue1[i]) + (total2[i] - blue2[i]);
// Generate predictions using the complete beta-binomial model
posterior_pred_choice[i] = beta_binomial_rng(1, alpha_post, beta_post);
// Log likelihood calculation using beta-binomial
log_lik[i] = beta_binomial_lpmf(choice[i] | 1, alpha_post, beta_post);
}
}
"
# Weighted Beta-Binomial Stan model
WeightedAgent_stan <- "
data {
int<lower=1> N; // Number of decisions
array[N] int<lower=0, upper=1> choice; // Choices (0=red, 1=blue)
array[N] int<lower=0> blue1; // Direct evidence (blue marbles)
array[N] int<lower=0> total1; // Total direct evidence
array[N] int<lower=0> blue2; // Social evidence (blue signals)
array[N] int<lower=0> total2; // Total social evidence
}
parameters {
real<lower = 0> alpha_prior; // Prior alpha parameter
real<lower = 0> beta_prior; // Prior beta parameter
real<lower=0> total_weight; // Total influence of all evidence
real<lower=0, upper=1> weight_prop; // Proportion of weight for direct evidence
}
transformed parameters {
real<lower=0> weight_direct = total_weight * weight_prop;
real<lower=0> weight_social = total_weight * (1 - weight_prop);
}
model {
// Priors
target += lognormal_lpdf(alpha_prior | 0, 1); // Prior on alpha_prior
target += lognormal_lpdf(beta_prior | 0, 1); // Prior on beta_prior
target += lognormal_lpdf(total_weight | .8, .4); // Centered around 2 with reasonable spread and always positive
target += beta_lpdf(weight_prop | 1, 1); // Uniform prior on proportion
// Each observation is a separate decision
for (i in 1:N) {
// For this specific decision:
real weighted_blue1 = blue1[i] * weight_direct;
real weighted_red1 = (total1[i] - blue1[i]) * weight_direct;
real weighted_blue2 = blue2[i] * weight_social;
real weighted_red2 = (total2[i] - blue2[i]) * weight_social;
// Calculate Beta parameters for this decision
real alpha_post = alpha_prior + weighted_blue1 + weighted_blue2;
real beta_post = beta_prior + weighted_red1 + weighted_red2;
// Use beta_binomial distribution to integrate over the full posterior
target += beta_binomial_lpmf(choice[i] | 1, alpha_post, beta_post);
}
}
generated quantities {
// Log likelihood and predictions
vector[N] log_lik;
array[N] int posterior_pred_choice;
array[N] int prior_pred_choice;
// Sample the agent's preconceptions
real alpha_prior_prior = lognormal_rng(0, 1);
real beta_prior_prior = lognormal_rng(0, 1);
// Sample from priors for the reparameterized model
real<lower = 0> total_weight_prior = lognormal_rng(.8, .4);
real weight_prop_prior = beta_rng(1, 1);
// Derive the implied direct and social weights from the prior samples
real weight_direct_prior = total_weight_prior * weight_prop_prior;
real weight_social_prior = total_weight_prior * (1 - weight_prop_prior);
// Posterior predictions and log-likelihood
for (i in 1:N) {
// Posterior predictions using the weighted evidence
real weighted_blue1 = blue1[i] * weight_direct;
real weighted_red1 = (total1[i] - blue1[i]) * weight_direct;
real weighted_blue2 = blue2[i] * weight_social;
real weighted_red2 = (total2[i] - blue2[i]) * weight_social;
real alpha_post = alpha_prior + weighted_blue1 + weighted_blue2;
real beta_post = beta_prior + weighted_red1 + weighted_red2;
// Log likelihood using beta_binomial
log_lik[i] = beta_binomial_lpmf(choice[i] | 1, alpha_post, beta_post);
// Generate predictions from the full posterior
posterior_pred_choice[i] = beta_binomial_rng(1, alpha_post, beta_post);
// Prior predictions using the prior-derived weights
real prior_weighted_blue1 = blue1[i] * weight_direct_prior;
real prior_weighted_red1 = (total1[i] - blue1[i]) * weight_direct_prior;
real prior_weighted_blue2 = blue2[i] * weight_social_prior;
real prior_weighted_red2 = (total2[i] - blue2[i]) * weight_social_prior;
real alpha_prior_preds = alpha_prior + prior_weighted_blue1 + prior_weighted_blue2;
real beta_prior_preds = beta_prior + prior_weighted_red1 + prior_weighted_red2;
// Generate predictions from the prior
prior_pred_choice[i] = beta_binomial_rng(1, alpha_prior, beta_prior);
}
}
"
# Write the models to files
write_stan_file(
SimpleAgent_stan,
dir = "stan/",
basename = "W10 _beta_binomial.stan"
)## [1] "/Users/au209589/Dropbox/Teaching/AdvancedCognitiveModeling23_book/stan/W10 _beta_binomial.stan"## [1] "/Users/au209589/Dropbox/Teaching/AdvancedCognitiveModeling23_book/stan/W10 _weighted_beta_binomial.stan"# Prepare simulation data for Stan fitting
# Convert 'Blue' and 'Red' choices to binary format (1 for Blue, 0 for Red)
sim_data_for_stan <- simulation_results %>%
mutate(
choice_binary = as.integer(choice == "Blue"),
total1 = 8, # Total marbles in direct evidence (constant)
total2 = 3 # Total signals in social evidence (constant)
)
# Split data by agent type
balanced_data <- sim_data_for_stan %>% filter(agent_type == "Balanced")
self_focused_data <- sim_data_for_stan %>% filter(agent_type == "Self-Focused")
socially_influenced_data <- sim_data_for_stan %>% filter(agent_type == "Socially-Influenced")
# Function to prepare data for Stan
prepare_stan_data <- function(df) {
list(
N = nrow(df),
choice = df$choice_binary,
blue1 = df$blue1,
total1 = df$total1,
blue2 = df$blue2,
total2 = df$total2
)
}
# Prepare Stan data for each agent
stan_data_balanced <- prepare_stan_data(balanced_data)
stan_data_self_focused <- prepare_stan_data(self_focused_data)
stan_data_socially_influenced <- prepare_stan_data(socially_influenced_data)
# Compile the Stan models
file_simple <- file.path("stan/W10 _beta_binomial.stan")
file_weighted <- file.path("stan/W10 _weighted_beta_binomial.stan")
# Check if we need to regenerate simulation results
if (regenerate_simulations) {
# Compile models
mod_simple <- cmdstan_model(file_simple, cpp_options = list(stan_threads = TRUE))
mod_weighted <- cmdstan_model(file_weighted, cpp_options = list(stan_threads = TRUE))
# Fit simple model to each agent's data
fit_simple_balanced <- mod_simple$sample(
data = stan_data_balanced,
seed = 123,
chains = 2,
parallel_chains = 2,
threads_per_chain = 1,
iter_warmup = 1000,
iter_sampling = 1000,
refresh = 0 # Set to 500 or so to see progress
)
fit_simple_self_focused <- mod_simple$sample(
data = stan_data_self_focused,
seed = 124,
chains = 2,
parallel_chains = 2,
threads_per_chain = 1,
iter_warmup = 1000,
iter_sampling = 1000,
refresh = 0
)
fit_simple_socially_influenced <- mod_simple$sample(
data = stan_data_socially_influenced,
seed = 125,
chains = 2,
parallel_chains = 2,
threads_per_chain = 1,
iter_warmup = 1000,
iter_sampling = 1000,
refresh = 0
)
# Fit weighted model to each agent's data
fit_weighted_balanced <- mod_weighted$sample(
data = stan_data_balanced,
seed = 124,
chains = 2,
parallel_chains = 2,
threads_per_chain = 1,
iter_warmup = 1000,
iter_sampling = 1000,
refresh = 0
)
fit_weighted_self_focused <- mod_weighted$sample(
data = stan_data_self_focused,
seed = 127,
chains = 2,
parallel_chains = 2,
threads_per_chain = 1,
iter_warmup = 1000,
iter_sampling = 1000,
refresh = 0
)
fit_weighted_socially_influenced <- mod_weighted$sample(
data = stan_data_socially_influenced,
seed = 128,
chains = 2,
parallel_chains = 2,
threads_per_chain = 1,
iter_warmup = 1000,
iter_sampling = 1000,
refresh = 0
)
# Save model fits for future use
fit_simple_balanced$save_object("simmodels/fit_simple_balanced.rds")
fit_simple_self_focused$save_object("simmodels/fit_simple_self_focused.rds")
fit_simple_socially_influenced$save_object("simmodels/fit_simple_socially_influenced.rds")
fit_weighted_balanced$save_object("simmodels/fit_weighted_balanced.rds")
fit_weighted_self_focused$save_object("simmodels/fit_weighted_self_focused.rds")
fit_weighted_socially_influenced$save_object("simmodels/fit_weighted_socially_influenced.rds")
cat("Generated and saved new model fits\n")
} else {
# Load existing model fits
fit_simple_balanced <- readRDS("simmodels/fit_simple_balanced.rds")
fit_simple_self_focused <- readRDS("simmodels/fit_simple_self_focused.rds")
fit_simple_socially_influenced <- readRDS("simmodels/fit_simple_socially_influenced.rds")
fit_weighted_balanced <- readRDS("simmodels/fit_weighted_balanced.rds")
fit_weighted_self_focused <- readRDS("simmodels/fit_weighted_self_focused.rds")
fit_weighted_socially_influenced <- readRDS("simmodels/fit_weighted_socially_influenced.rds")
cat("Loaded existing model fits\n")
}## Loaded existing model fits11.14 Model Quality Checks
11.14.1 Overview
Model quality checks are crucial for understanding how well our Bayesian models capture the underlying data-generating process. We’ll use three primary techniques:
- Prior Predictive Checks
- Posterior Predictive Checks
- Prior-Posterior Update Visualization
# Function to create trace and rank plots for a model
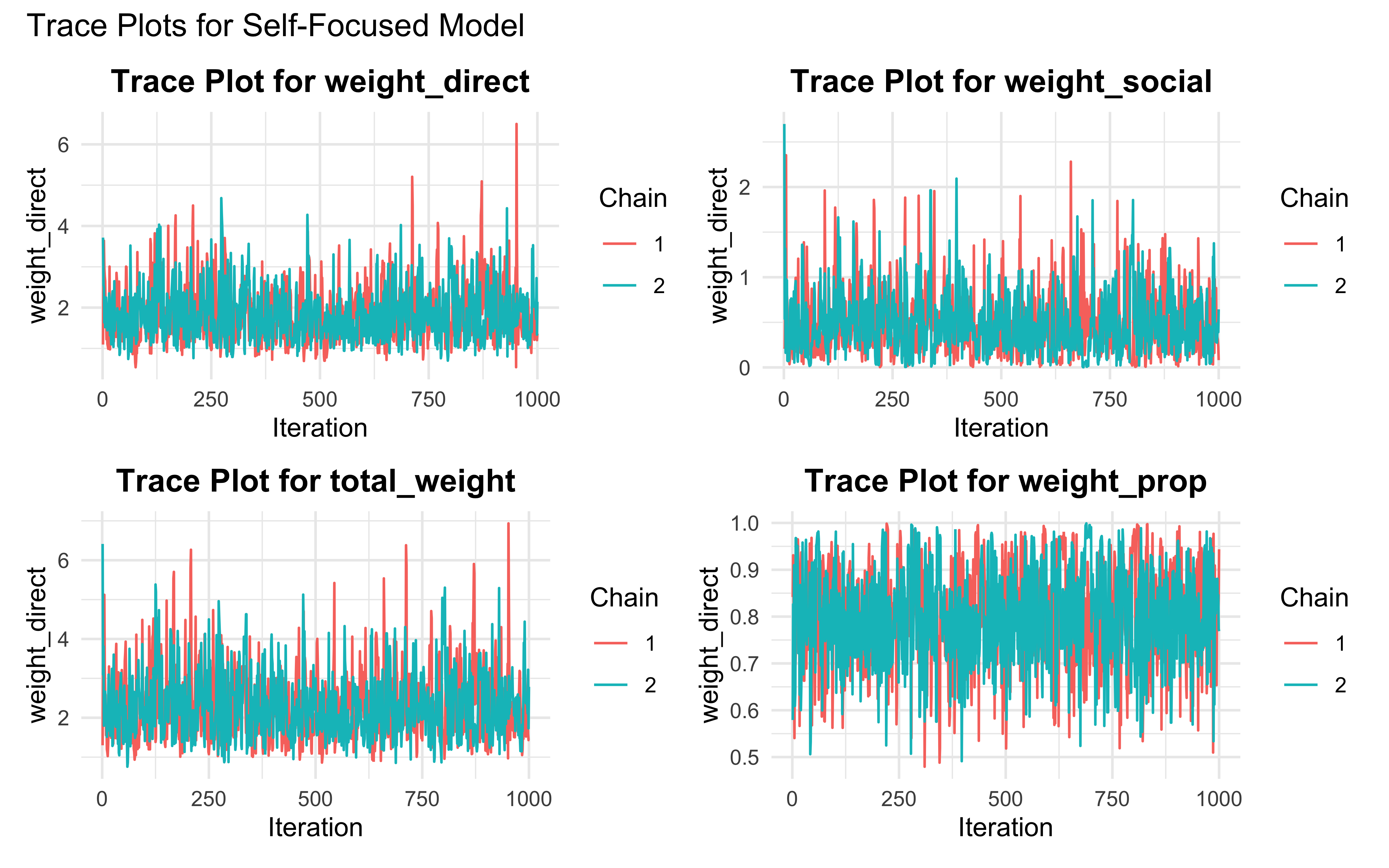
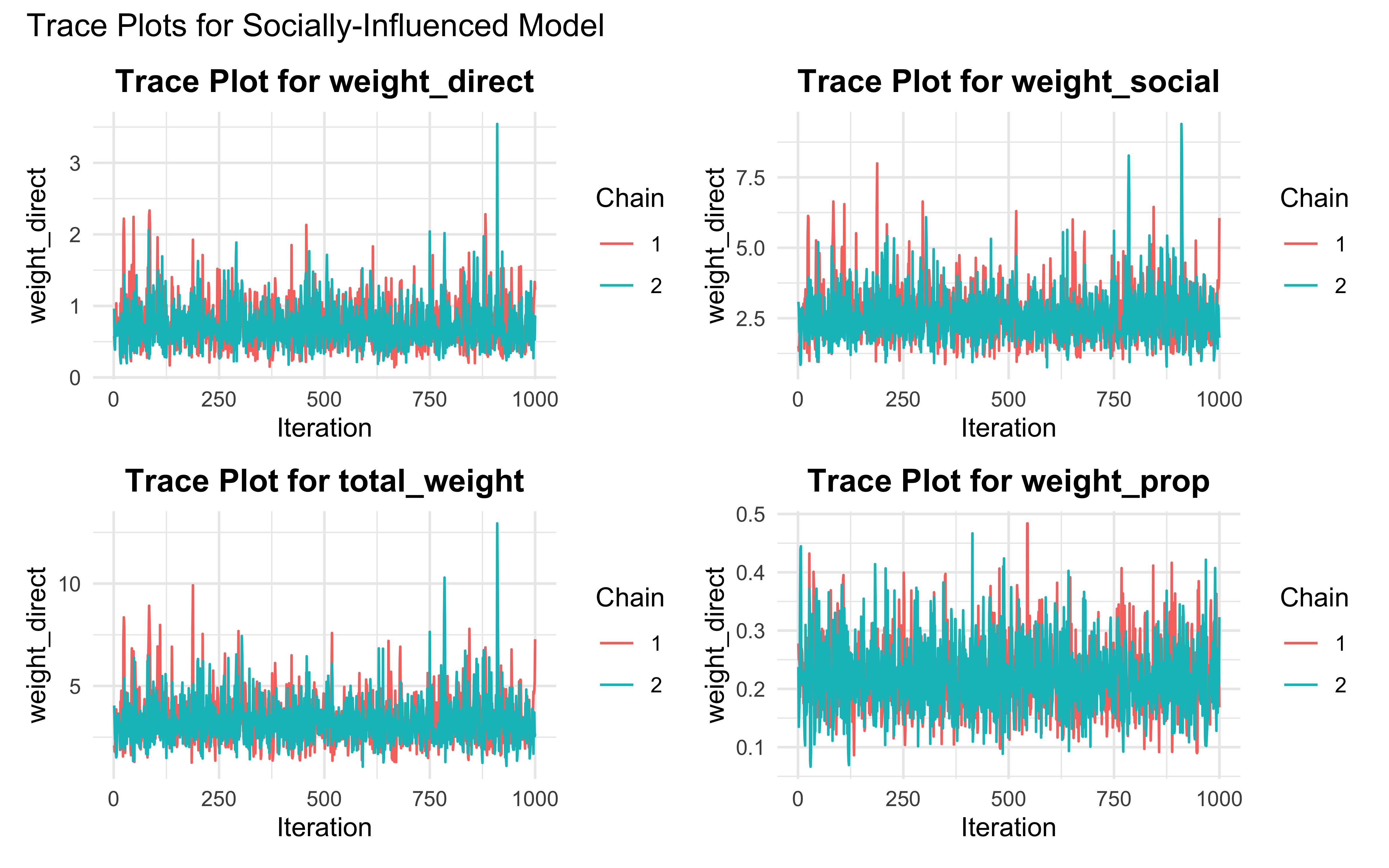
create_diagnostic_plots <- function(fit, model_name) {
# Extract posterior draws
draws <- as_draws_df(fit$draws())
trace_data <- data.frame(
Iteration = rep(1:(nrow(draws)/length(unique(draws$.chain))),
length(unique(draws$.chain))),
Chain = draws$.chain,
weight_direct = draws$weight_direct,
weight_social = draws$weight_social,
total_weight = draws$total_weight,
weight_prop = draws$weight_prop
)
# Create trace plot
trace_plot1 <- ggplot(trace_data, aes(x = Iteration, y = weight_direct, color = factor(Chain))) +
geom_line() +
labs(title = paste("Trace Plot for weight_direct"),
x = "Iteration",
y = "weight_direct",
color = "Chain") +
theme_minimal() +
theme(plot.title = element_text(hjust = 0.5, face = "bold"))
trace_plot2 <- ggplot(trace_data, aes(x = Iteration, y = weight_social, color = factor(Chain))) +
geom_line() +
labs(title = paste("Trace Plot for weight_social"),
x = "Iteration",
y = "weight_direct",
color = "Chain") +
theme_minimal() +
theme(plot.title = element_text(hjust = 0.5, face = "bold"))
trace_plot3 <- ggplot(trace_data, aes(x = Iteration, y = total_weight, color = factor(Chain))) +
geom_line() +
labs(title = paste("Trace Plot for total_weight"),
x = "Iteration",
y = "weight_direct",
color = "Chain") +
theme_minimal() +
theme(plot.title = element_text(hjust = 0.5, face = "bold"))
trace_plot4 <- ggplot(trace_data, aes(x = Iteration, y = weight_prop, color = factor(Chain))) +
geom_line() +
labs(title = paste("Trace Plot for weight_prop"),
x = "Iteration",
y = "weight_direct",
color = "Chain") +
theme_minimal() +
theme(plot.title = element_text(hjust = 0.5, face = "bold"))
# Combine plots using patchwork
combined_trace_plot <- (trace_plot1 + trace_plot2) / (trace_plot3 + trace_plot4) +
plot_annotation(title = paste("Trace Plots for", model_name))
# Return the plots
return(combined_trace_plot)
}
# Generate diagnostic plots for each model
create_diagnostic_plots(fit_weighted_balanced, "Balanced Model")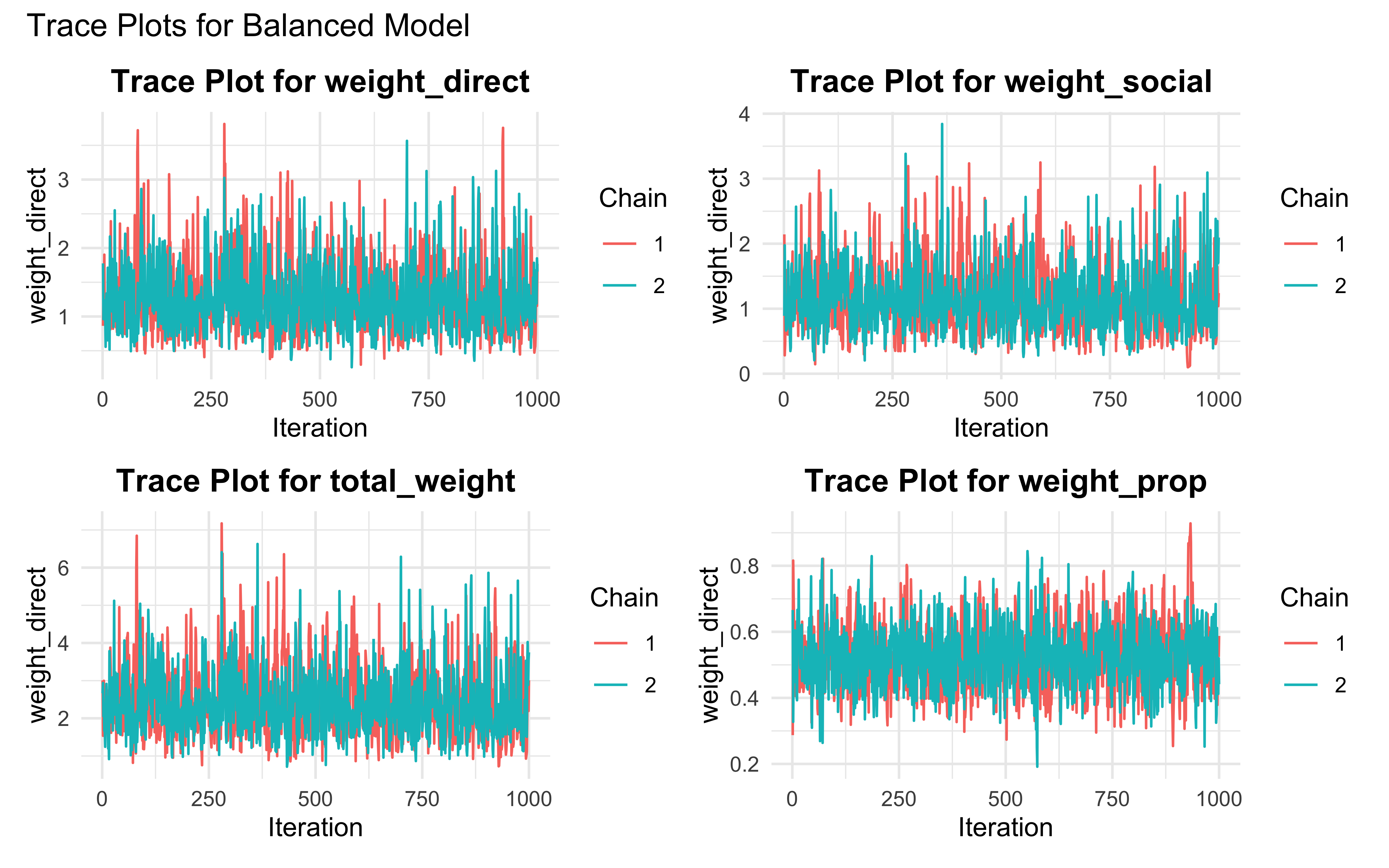
11.14.2 Prior and Posterior Predictive Checks
Prior predictive checks help us understand what our model assumes about the world before seeing any data. They answer the question: “What kind of data would we expect to see if we only used our prior beliefs?” Posterior predictive checks are the same, but after having seen the data. This helps us assess whether the model can generate data that looks similar to our observed data.
plot_predictive_checks <- function(stan_fit,
simulation_results,
model_name = "Simple Balanced",
param_name = "prior_pred_choice") {
# Extract predictive samples
pred_samples <- stan_fit$draws(param_name, format = "data.frame")
# Get the number of samples and observations
n_samples <- nrow(pred_samples)
n_obs <- ncol(pred_samples) - 3 # Subtract chain, iteration, and draw columns
# Convert to long format
long_pred <- pred_samples %>%
dplyr::select(-.chain, -.iteration, -.draw) %>% # Remove metadata columns
pivot_longer(
cols = everything(),
names_to = "obs_id",
values_to = "choice"
) %>%
mutate(obs_id = parse_number(obs_id)) # Extract observation number
# Join with the original simulation data to get evidence levels
# First, add an observation ID to the simulation data
sim_with_id <- simulation_results %>%
mutate(obs_id = row_number())
# Join predictions with evidence levels
long_pred_with_evidence <- long_pred %>%
left_join(
sim_with_id %>% dplyr::select(obs_id, blue1, blue2),
by = "obs_id"
)
# Summarize proportion of 1s per evidence combination
pred_summary <- long_pred_with_evidence %>%
group_by(blue1, blue2) %>%
summarize(
proportion = mean(choice, na.rm = TRUE),
n = n(),
se = sqrt((proportion * (1 - proportion)) / n), # Binomial SE
lower = proportion - 1.96 * se,
upper = proportion + 1.96 * se,
.groups = "drop"
)
# Generate title based on parameter name
title <- ifelse(param_name == "prior_pred_choice",
paste0("Prior Predictive Check for ", model_name),
paste0("Posterior Predictive Check for ", model_name))
# Create plot
ggplot(pred_summary, aes(x = blue1, y = proportion, color = factor(blue2), group = blue2)) +
geom_line() +
geom_point() +
geom_ribbon(aes(ymin = lower, ymax = upper, fill = factor(blue2)), alpha = 0.2, color = NA) +
ylim(0, 1) +
labs(title = title,
x = "Direct Evidence (Blue Marbles)",
y = "Proportion of Choice = Blue",
color = "Social Evidence",
fill = "Social Evidence") +
theme_minimal()
}
# Generate all plots
prior_simple_balanced <- plot_predictive_checks(fit_simple_balanced, simulation_results, "Simple Balanced", "prior_pred_choice")
prior_simple_self_focused <- plot_predictive_checks(fit_simple_self_focused, simulation_results, "Simple Self Focused", "prior_pred_choice")
prior_simple_socially_influenced <- plot_predictive_checks(fit_simple_socially_influenced, simulation_results, "Simple Socially Influenced", "prior_pred_choice")
#prior_weighted_balanced <- plot_predictive_checks(fit_weighted_balanced, simulation_results, "Weighted Balanced", "prior_pred_choice")
#prior_weighted_self_focused <- plot_predictive_checks(fit_weighted_self_focused, simulation_results, "Weighted Self Focused", "prior_pred_choice")
#prior_weighted_socially_influenced <- plot_predictive_checks(fit_weighted_socially_influenced, simulation_results, "Weighted Socially Influenced", "prior_pred_choice")
posterior_simple_balanced <- plot_predictive_checks(fit_simple_balanced, simulation_results, "Simple Balanced", "posterior_pred_choice")
posterior_simple_self_focused <- plot_predictive_checks(fit_simple_self_focused, simulation_results, "Simple Self Focused", "posterior_pred_choice")
posterior_simple_socially_influenced <- plot_predictive_checks(fit_simple_socially_influenced, simulation_results, "Simple Socially Influenced", "posterior_pred_choice")
posterior_weighted_balanced <- plot_predictive_checks(fit_weighted_balanced, simulation_results, "Weighted Balanced", "posterior_pred_choice")
posterior_weighted_self_focused <- plot_predictive_checks(fit_weighted_self_focused, simulation_results, "Weighted Self Focused", "posterior_pred_choice")
posterior_weighted_socially_influenced <- plot_predictive_checks(fit_weighted_socially_influenced, simulation_results, "Weighted Socially Influenced", "posterior_pred_choice")
# Arrange Prior Predictive Checks in a Grid
prior_grid <- (prior_simple_balanced + prior_simple_self_focused + prior_simple_socially_influenced) +#/ (prior_weighted_balanced + prior_weighted_self_focused + prior_weighted_socially_influenced) +
plot_annotation(title = "Prior Predictive Checks")
# Arrange Posterior Predictive Checks in a Grid
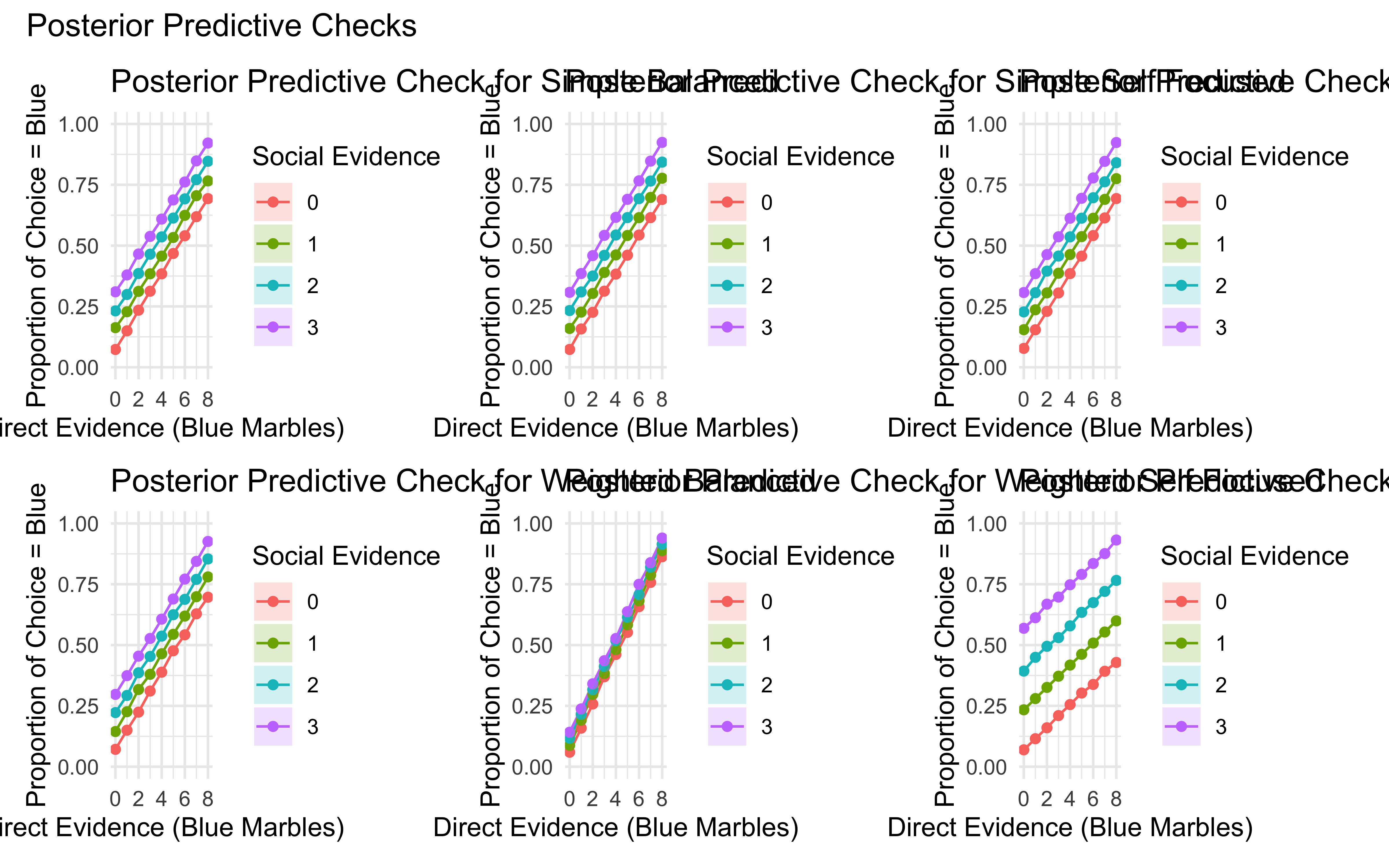
posterior_grid <- (posterior_simple_balanced + posterior_simple_self_focused + posterior_simple_socially_influenced) /
(posterior_weighted_balanced + posterior_weighted_self_focused + posterior_weighted_socially_influenced) +
plot_annotation(title = "Posterior Predictive Checks")
# Display the grids
print(prior_grid)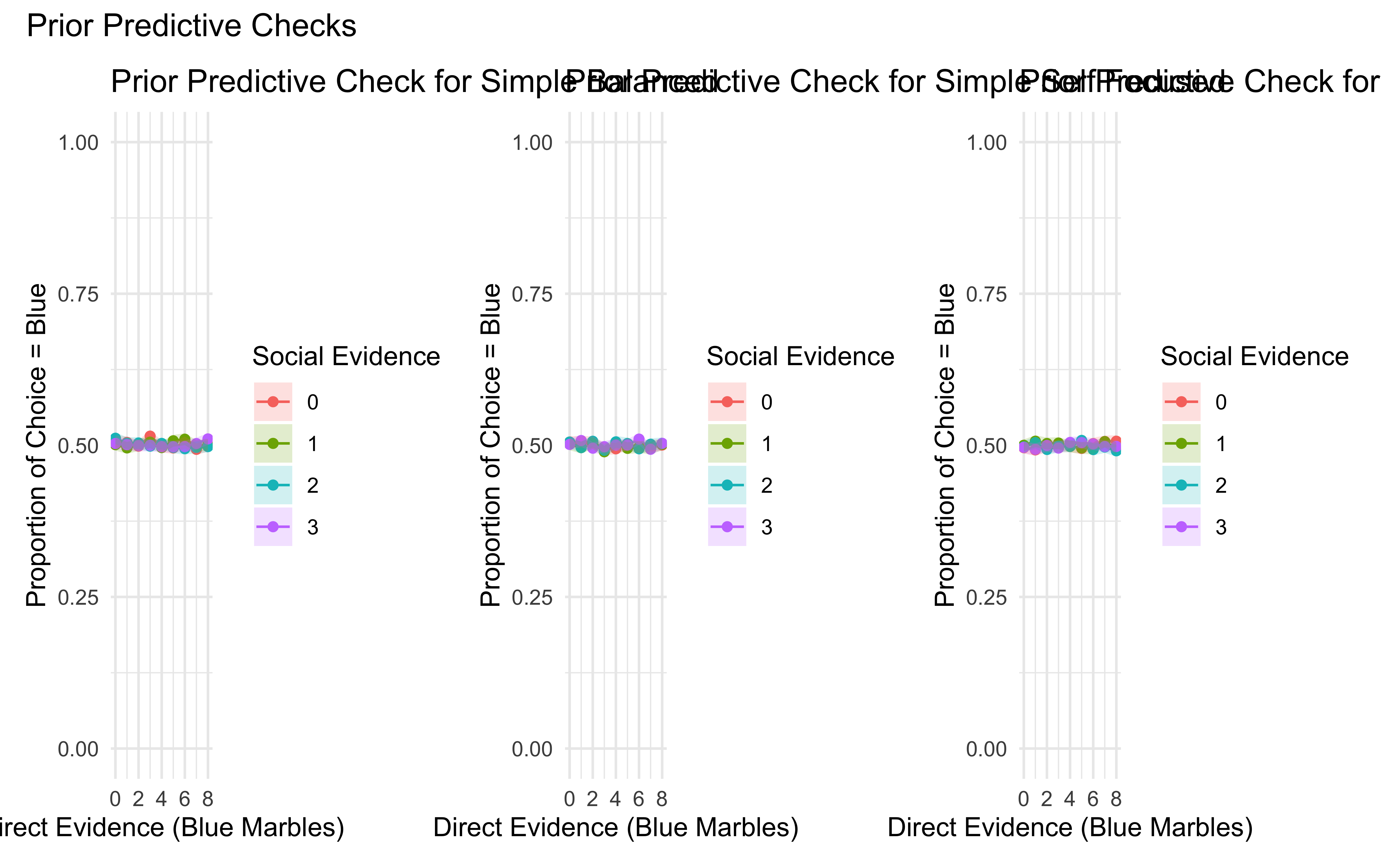
11.15 Prior-Posterior Update Visualization
This visualization shows how our beliefs change after observing data, comparing the prior and posterior distributions for key parameters.
# Function to plot prior-posterior updates for reparameterized model
plot_reparameterized_updates <- function(fit_list, true_params_list, model_names) {
# Create dataframe for posterior values
posterior_df <- tibble()
# Process each model
for (i in seq_along(fit_list)) {
fit <- fit_list[[i]]
model_name <- model_names[i]
# Extract posterior draws
draws_df <- as_draws_df(fit$draws())
# Check which parameterization is used (old or new)
if (all(c("total_weight", "weight_prop") %in% names(draws_df))) {
# New parameterization - extract parameters directly
temp_df <- tibble(
model_name = model_name,
parameter = "total_weight",
value = draws_df$total_weight,
distribution = "Posterior"
)
posterior_df <- bind_rows(posterior_df, temp_df)
temp_df <- tibble(
model_name = model_name,
parameter = "weight_prop",
value = draws_df$weight_prop,
distribution = "Posterior"
)
posterior_df <- bind_rows(posterior_df, temp_df)
# Also calculate the derived parameters for comparison with true values
temp_df <- tibble(
model_name = model_name,
parameter = "weight_direct",
value = draws_df$total_weight * draws_df$weight_prop,
distribution = "Posterior (derived)"
)
posterior_df <- bind_rows(posterior_df, temp_df)
temp_df <- tibble(
model_name = model_name,
parameter = "weight_social",
value = draws_df$total_weight * (1 - draws_df$weight_prop),
distribution = "Posterior (derived)"
)
posterior_df <- bind_rows(posterior_df, temp_df)
} else if (all(c("weight_direct", "weight_social") %in% names(draws_df))) {
# Old parameterization - extract and calculate equivalent new parameters
temp_df <- tibble(
model_name = model_name,
parameter = "weight_direct",
value = draws_df$weight_direct,
distribution = "Posterior"
)
posterior_df <- bind_rows(posterior_df, temp_df)
temp_df <- tibble(
model_name = model_name,
parameter = "weight_social",
value = draws_df$weight_social,
distribution = "Posterior"
)
posterior_df <- bind_rows(posterior_df, temp_df)
# Calculate the equivalent new parameters
total_weight <- draws_df$weight_direct + draws_df$weight_social
weight_prop <- draws_df$weight_direct / total_weight
temp_df <- tibble(
model_name = model_name,
parameter = "total_weight",
value = total_weight,
distribution = "Posterior (derived)"
)
posterior_df <- bind_rows(posterior_df, temp_df)
temp_df <- tibble(
model_name = model_name,
parameter = "weight_prop",
value = weight_prop,
distribution = "Posterior (derived)"
)
posterior_df <- bind_rows(posterior_df, temp_df)
} else {
warning(paste("Unknown parameterization in model", model_name))
}
}
# Generate prior samples based on recommended priors for new parameterization
prior_df <- tibble()
for (i in seq_along(model_names)) {
model_name <- model_names[i]
# Number of prior samples to match posterior
n_samples <- 2000
# Generate prior samples - gamma(2,1) for total_weight and beta(1,1) for weight_prop
total_weight_prior <- rgamma(n_samples, shape = 2, rate = 1)
weight_prop_prior <- rbeta(n_samples, 1, 1)
# For the new parameterization
temp_df <- tibble(
model_name = model_name,
parameter = "total_weight",
value = total_weight_prior,
distribution = "Prior"
)
prior_df <- bind_rows(prior_df, temp_df)
temp_df <- tibble(
model_name = model_name,
parameter = "weight_prop",
value = weight_prop_prior,
distribution = "Prior"
)
prior_df <- bind_rows(prior_df, temp_df)
# Calculate derived parameters for the old parameterization
weight_direct_prior <- total_weight_prior * weight_prop_prior
weight_social_prior <- total_weight_prior * (1 - weight_prop_prior)
temp_df <- tibble(
model_name = model_name,
parameter = "weight_direct",
value = weight_direct_prior,
distribution = "Prior (derived)"
)
prior_df <- bind_rows(prior_df, temp_df)
temp_df <- tibble(
model_name = model_name,
parameter = "weight_social",
value = weight_social_prior,
distribution = "Prior (derived)"
)
prior_df <- bind_rows(prior_df, temp_df)
}
# Combine prior and posterior
combined_df <- bind_rows(prior_df, posterior_df)
# Convert true parameter values
true_values_df <- map2_dfr(true_params_list, model_names, function(params, model_name) {
# Extract original parameters
weight_direct <- params$weight_direct
weight_social <- params$weight_social
# Calculate new parameterization
total_weight <- weight_direct + weight_social
weight_prop <- weight_direct / total_weight
tibble(
model_name = model_name,
parameter = c("weight_direct", "weight_social", "total_weight", "weight_prop"),
value = c(weight_direct, weight_social, total_weight, weight_prop)
)
})
# Create plots for different parameter sets
# 1. New parameterization (total_weight and weight_prop)
p1 <- combined_df %>%
filter(parameter %in% c("total_weight", "weight_prop")) %>%
ggplot(aes(x = value, fill = distribution, color = distribution)) +
geom_density(alpha = 0.3, linewidth = 1.2) +
facet_grid(model_name ~ parameter, scales = "free") +
scale_fill_manual(values = c("Prior" = "#E63946",
"Prior (derived)" = "#E67946",
"Posterior" = "#1D3557",
"Posterior (derived)" = "#1D5587")) +
scale_color_manual(values = c("Prior" = "#E63946",
"Prior (derived)" = "#E67946",
"Posterior" = "#1D3557",
"Posterior (derived)" = "#1D5587")) +
geom_vline(data = true_values_df %>% filter(parameter %in% c("total_weight", "weight_prop")),
aes(xintercept = value),
color = "#2A9D8F", linetype = "dashed", linewidth = 1.2) +
labs(title = "Prior vs. Posterior: New Parameterization",
subtitle = "Green dashed lines indicate true parameter values",
x = "Parameter Value",
y = "Density",
fill = "Distribution",
color = "Distribution") +
theme_minimal(base_size = 14) +
theme(legend.position = "top")
# 2. Original parameterization (weight_direct and weight_social)
p2 <- combined_df %>%
filter(parameter %in% c("weight_direct", "weight_social")) %>%
ggplot(aes(x = value, fill = distribution, color = distribution)) +
geom_density(alpha = 0.3, linewidth = 1.2) +
facet_grid(model_name ~ parameter, scales = "free") +
scale_fill_manual(values = c("Prior" = "#E63946",
"Prior (derived)" = "#E67946",
"Posterior" = "#1D3557",
"Posterior (derived)" = "#1D5587")) +
scale_color_manual(values = c("Prior" = "#E63946",
"Prior (derived)" = "#E67946",
"Posterior" = "#1D3557",
"Posterior (derived)" = "#1D5587")) +
geom_vline(data = true_values_df %>% filter(parameter %in% c("weight_direct", "weight_social")),
aes(xintercept = value),
color = "#2A9D8F", linetype = "dashed", linewidth = 1.2) +
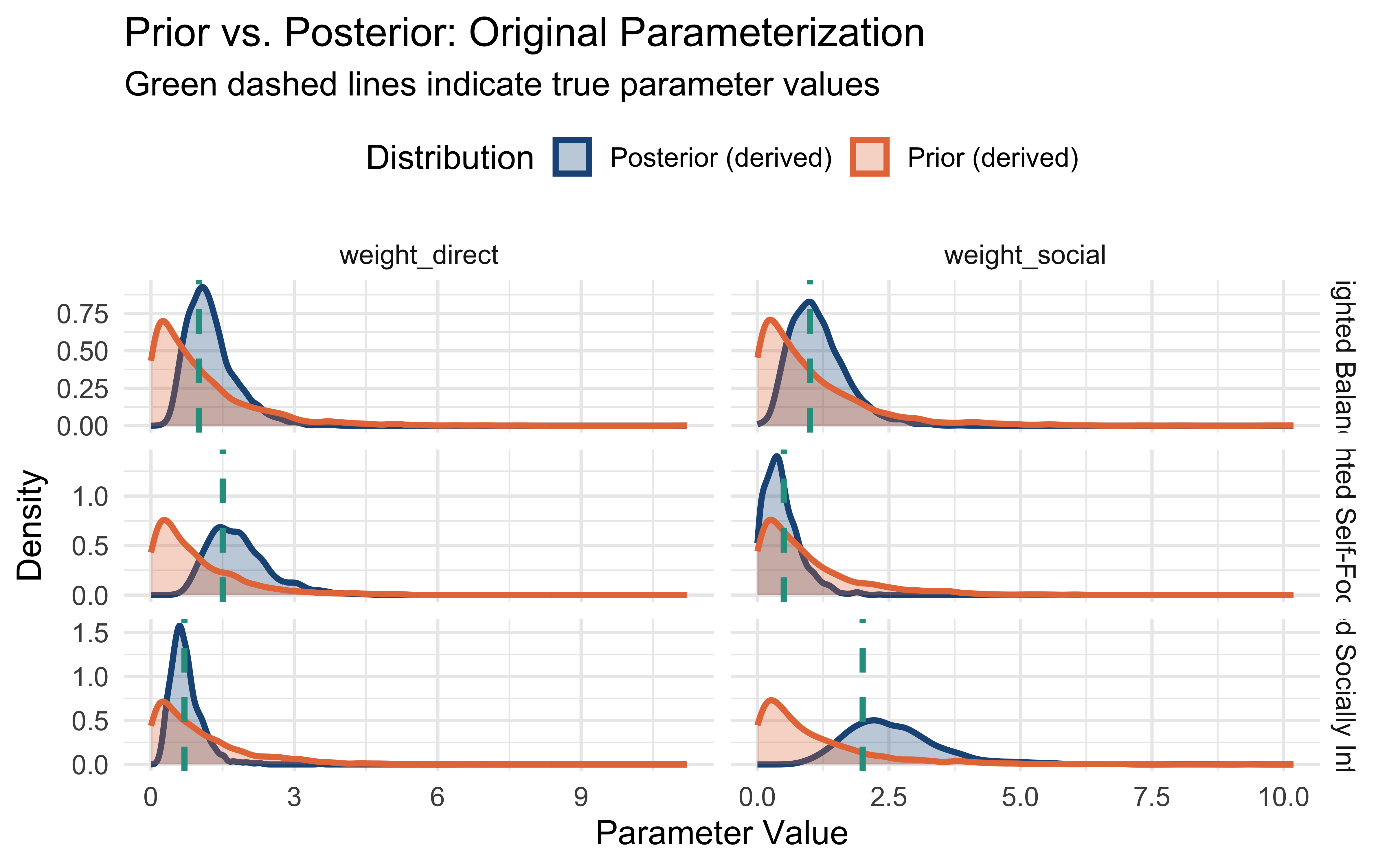
labs(title = "Prior vs. Posterior: Original Parameterization",
subtitle = "Green dashed lines indicate true parameter values",
x = "Parameter Value",
y = "Density",
fill = "Distribution",
color = "Distribution") +
theme_minimal(base_size = 14) +
theme(legend.position = "top")
# Return both plots
return(list(new_params = p1, old_params = p2))
}
fit_list <- list(
fit_weighted_balanced,
fit_weighted_self_focused,
fit_weighted_socially_influenced
)
true_params_list <- list(
list(weight_direct = 1, weight_social = 1),
list(weight_direct = 1.5, weight_social = 0.5),
list(weight_direct = 0.7, weight_social = 2)
)
model_names <- c("Weighted Balanced", "Weighted Self-Focused", "Weighted Socially Influenced")
# Generate the plots
plots <- plot_reparameterized_updates(fit_list, true_params_list, model_names)
# Display the plots
print(plots$new_params)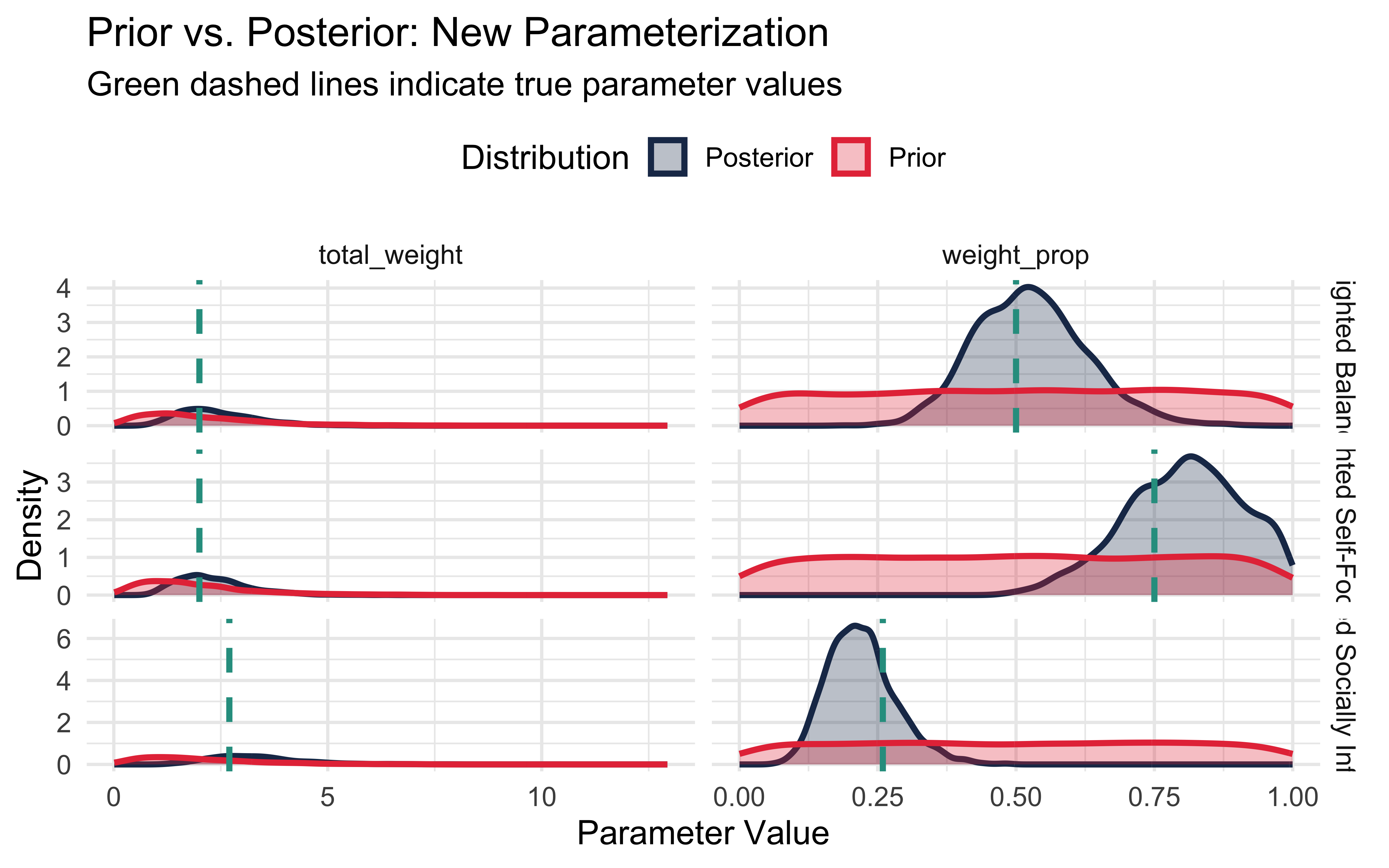
11.16 Parameter recovery
## Parameter recovery
# Set random seed for reproducibility
set.seed(123)
## Set up parallel processing
future::plan(multisession, workers = parallel::detectCores() - 1)
# Define parameter grid for thorough testing
weight_values <- c(0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, 1, 1.2, 1.4, 1.6, 1.8, 2)
n_trials <- c(1, 2, 3, 4, 5) # Number of times full combination of levels is repeated
# Create a grid of all parameter combinations to test
param_grid <- expand_grid(w1 = weight_values, w2 = weight_values, trials = n_trials)
# Define evidence combinations
evidence_combinations <- expand_grid(
blue1 = 0:8, # Direct evidence: number of blue marbles seen
blue2 = 0:3, # Social evidence: strength of blue evidence
total1 = 8, # Total marbles in direct evidence (constant)
total2 = 3 # Total strength units in social evidence (constant)
)
# Function to generate decisions across all evidence combinations for a given agent
generate_agent_decisions <- function(weight_direct, weight_social, evidence_df, n_samples = 5) {
# Create a data frame that repeats each evidence combination n_samples times
repeated_evidence <- evidence_df %>%
slice(rep(1:n(), each = n_samples)) %>%
# Add a sample_id to distinguish between repetitions of the same combination
group_by(blue1, blue2, total1, total2) %>%
mutate(sample_id = 1:n()) %>%
ungroup()
# Apply our weighted Bayesian model to each evidence combination
decisions <- pmap_dfr(repeated_evidence, function(blue1, blue2, total1, total2, sample_id) {
# Calculate Bayesian integration with the agent's specific weights
result <- weightedBetaBinomial(
alpha_prior = 1, beta_prior = 1,
blue1 = blue1, total1 = total1,
blue2 = blue2, total2 = total2,
weight_direct = weight_direct,
weight_social = weight_social
)
# Return key decision metrics
tibble(
sample_id = sample_id,
blue1 = blue1,
blue2 = blue2,
total1 = total1,
total2 = total2,
expected_rate = result$expected_rate, # Probability the next marble is blue
choice = result$decision, # Final decision (Blue or Red)
choice_binary = ifelse(result$decision == "Blue", 1, 0),
confidence = result$confidence # Confidence in decision
)
})
return(decisions)
}
# Function to prepare Stan data
prepare_stan_data <- function(df) {
list(
N = nrow(df),
choice = df$choice_binary,
blue1 = df$blue1,
total1 = df$total1,
blue2 = df$blue2,
total2 = df$total2
)
}
# Compile the Stan model
file_weighted <- file.path("stan/W10 _weighted_beta_binomial.stan")
mod_weighted <- cmdstan_model(file_weighted, cpp_options = list(stan_threads = TRUE))
# Function to fit model using cmdstanr
fit_model <- function(data) {
stan_data <- prepare_stan_data(data)
fit <- mod_weighted$sample(
data = stan_data,
seed = 126,
chains = 2,
parallel_chains = 2,
threads_per_chain = 1,
iter_warmup = 1000,
iter_sampling = 1000,
refresh = 0
)
return(fit)
}
# Run simulations and model fitting in parallel
results <- param_grid %>%
mutate(
# Generate synthetic data for each parameter combination
data = future_pmap(list(w1, w2, trials), function(w1, w2, t) {
generate_agent_decisions(w1, w2, evidence_combinations, t)
}, .options = furrr_options(seed = TRUE)),
# Fit model to each dataset
fit = future_map(data, fit_model, .progress = TRUE)
)## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.4 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.4 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.4 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 1.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 1.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 1.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.4 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.4 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.4 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.9 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.9 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.9 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.1 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 1.0 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 1.0 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 1.0 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.2 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.4 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.4 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.9 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.9 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.9 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.4 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.4 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.4 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 1 finished in 0.9 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 1.0 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 1.0 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 1.0 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.2 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.4 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.4 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.4 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.6 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 1.0 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 1.1 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 1.0 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.2 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.4 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.4 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.6 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 1 finished in 0.9 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.9 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.4 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 2 finished in 0.9 seconds.
## Chain 1 finished in 0.9 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.9 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.1 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.9 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.9 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.9 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.4 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.4 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.9 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.9 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.9 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.4 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.4 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.6 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.9 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.9 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.9 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.4 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.4 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.6 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 1.0 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 1.0 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 1.0 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.2 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.4 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.4 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.4 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.9 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 1.0 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.9 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.2 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.4 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.4 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.4 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.4 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.9 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 1.0 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.9 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.9 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.9 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.4 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.4 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.4 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.6 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 1.0 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 1.0 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 1.0 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.1 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.4 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.4 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.9 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.9 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.9 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.6 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.4 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.4 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.4 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.6 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.9 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.9 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.9 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.4 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.4 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.4 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.6 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.9 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.9 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.9 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.4 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 1.0 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 1.0 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 1.0 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.2 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.4 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 2 finished in 0.9 seconds.
## Chain 1 finished in 1.0 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 1.0 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.1 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.9 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.9 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.9 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 2 finished in 0.9 seconds.
## Chain 1 finished in 1.0 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.9 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.4 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.4 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.4 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.6 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.9 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.9 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.9 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.4 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 1 finished in 0.9 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.9 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.9 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.9 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.9 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.1 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.4 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.9 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.9 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.9 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.4 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.4 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.4 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.4 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.4 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.4 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.6 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 2 finished in 0.9 seconds.
## Chain 1 finished in 1.0 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.9 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.1 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.4 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.9 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.9 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.4 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.9 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 1.0 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.9 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.1 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.4 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.4 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.4 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.6 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.9 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.9 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.9 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.4 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.4 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.6 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.4 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.4 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.4 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.9 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 2 finished in 0.9 seconds.
## Chain 1 finished in 1.0 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 1.0 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.1 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.4 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.6 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 1.0 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 1.0 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 1.0 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.2 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.9 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.9 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.9 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.4 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.4 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.4 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.4 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 1 finished in 0.9 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.9 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.4 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.4 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.9 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.4 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.4 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.6 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.4 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.9 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.9 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.1 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.4 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.4 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.4 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.9 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.9 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.9 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.9 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.9 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.9 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.4 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 1.1 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 1.0 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 1.0 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.2 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.6 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 1.0 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 1.1 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 1.0 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.2 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.9 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.9 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.9 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.2 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.4 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.4 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.6 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.4 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 2 finished in 0.9 seconds.
## Chain 1 finished in 1.0 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.9 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.1 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.4 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.4 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.6 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.9 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.9 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.4 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.4 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.9 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.9 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.1 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.4 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.4 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.4 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.4 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.4 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.9 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.9 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.9 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.4 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.4 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.4 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 1 finished in 0.9 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.9 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.4 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.6 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.9 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.9 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 1 finished in 0.9 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 2 finished in 0.9 seconds.
## Chain 1 finished in 1.0 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.9 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.1 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.4 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.4 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.4 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.9 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.6 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.6 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.4 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.9 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.4 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.4 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.6 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.4 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.4 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.4 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.6 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.4 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.4 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.9 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.1 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.4 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.4 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.4 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.9 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.9 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.4 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.6 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.9 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.9 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.4 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.6 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.4 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.4 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.4 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.9 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.4 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.9 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.9 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.4 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.4 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.4 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.4 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.4 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.9 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 1.0 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 1.0 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.1 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.4 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.4 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.4 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.6 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.4 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.4 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.6 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.4 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.4 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.4 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.9 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.9 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.9 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.4 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.6 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 2 finished in 0.9 seconds.
## Chain 1 finished in 1.0 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 1.0 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.1 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.4 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.4 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.4 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.9 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.9 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.4 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.9 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.9 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.9 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.6 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.9 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.1 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.6 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.9 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.9 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.9 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.6 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.9 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.9 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.9 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.9 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.4 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.4 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 1.0 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 1.0 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 1.0 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.2 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.4 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.4 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.4 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.4 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.6 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.6 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.6 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.9 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.9 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.9 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.6 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.4 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.6 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.9 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.9 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.9 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.1 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 1 finished in 0.4 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.4 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.4 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.4 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 1.0 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.9 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.1 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.4 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.6 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.4 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.4 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.4 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.4 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.4 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.4 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.4 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.4 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.4 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.4 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.4 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.1 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.9 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.9 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.9 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.4 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.4 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.4 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.4 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 1 finished in 0.9 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.4 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.4 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.6 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.4 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.4 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.4 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.6 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.6 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.4 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.6 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.6 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.9 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.1 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.9 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.9 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.2 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.4 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.4 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.4 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.1 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.4 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.2 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.4 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 1 finished in 0.4 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.3 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.3 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.7 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.7 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.7 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.8 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.9 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 1.0 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.2 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.2 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.2 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.3 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.4 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.3 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.4 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.5 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.5 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.5 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.5 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.6 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.6 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.6 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.6 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.7 seconds.
##
## Running MCMC with 2 parallel chains, with 1 thread(s) per chain...
##
## Chain 1 finished in 0.8 seconds.
## Chain 2 finished in 0.8 seconds.
##
## Both chains finished successfully.
## Mean chain execution time: 0.8 seconds.
## Total execution time: 0.9 seconds.# Extract both old and new parameterization results
results <- results %>%
mutate(
# First extract parameters in the new parameterization
total_weight_est = map_dbl(fit, ~mean(as_draws_df(.x$draws())$total_weight)),
weight_prop_est = map_dbl(fit, ~mean(as_draws_df(.x$draws())$weight_prop)),
# Calculate the traditional parameters from the new parameterization
weight_direct_est = total_weight_est * weight_prop_est,
weight_social_est = total_weight_est * (1 - weight_prop_est),
# Calculate the true parameters in the new parameterization
true_total_weight = w1 + w2,
true_weight_prop = w1 / (w1 + w2),
# Also extract uncertainty estimates
total_weight_sd = map_dbl(fit, ~sd(as_draws_df(.x$draws())$total_weight)),
weight_prop_sd = map_dbl(fit, ~sd(as_draws_df(.x$draws())$weight_prop)),
weight_direct_sd = map_dbl(fit, function(x) {
draws <- as_draws_df(x$draws())
sd(draws$total_weight * draws$weight_prop)
}),
weight_social_sd = map_dbl(fit, function(x) {
draws <- as_draws_df(x$draws())
sd(draws$total_weight * (1 - draws$weight_prop))
})
)
# Create functions to visualize parameter recovery for both parameterizations
plot_recovery_original <- function(results_df) {
# Visualize direct weight recovery
p1 <- results_df %>%
ggplot(aes(x = w1, y = weight_direct_est, color = factor(trials))) +
geom_point() +
geom_errorbar(aes(ymin = weight_direct_est - weight_direct_sd,
ymax = weight_direct_est + weight_direct_sd),
width = 0.1, alpha = 0.5) +
geom_abline(slope = 1, intercept = 0, linetype = "dashed") +
facet_wrap(~ w2, labeller = labeller(w2 = function(x) paste("Social Weight =", x))) +
labs(title = "Direct Weight Parameter Recovery",
x = "True Direct Weight",
y = "Estimated Direct Weight",
color = "Number of\nTrials per\nCondition") +
theme_minimal() +
theme(legend.position = "right")
# Visualize social weight recovery
p2 <- results_df %>%
ggplot(aes(x = w2, y = weight_social_est, color = factor(trials))) +
geom_point() +
geom_errorbar(aes(ymin = weight_social_est - weight_social_sd,
ymax = weight_social_est + weight_social_sd),
width = 0.1, alpha = 0.5) +
geom_abline(slope = 1, intercept = 0, linetype = "dashed") +
facet_wrap(~ w1, labeller = labeller(w1 = function(x) paste("Direct Weight =", x))) +
labs(title = "Social Weight Parameter Recovery",
x = "True Social Weight",
y = "Estimated Social Weight",
color = "Number of\nTrials per\nCondition") +
theme_minimal() +
theme(legend.position = "right")
return(list(direct = p1, social = p2))
}
plot_recovery_new <- function(results_df) {
# Visualize total weight recovery
# First, create discrete categories for weight proportion to avoid using continuous variable in facet_wrap
results_with_categories <- results_df %>%
filter(true_total_weight > 0) %>% # Avoid division by zero issues
mutate(weight_prop_cat = cut(true_weight_prop,
breaks = c(0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1.0),
labels = c("0-0.25", "0.25-0.5", "0.5-0.75", "0.75-1.0"),
include.lowest = TRUE))
p1 <- results_with_categories %>%
ggplot(aes(x = true_total_weight, y = total_weight_est, color = factor(trials))) +
geom_point() +
geom_errorbar(aes(ymin = total_weight_est - total_weight_sd,
ymax = total_weight_est + total_weight_sd),
width = 0.1, alpha = 0.5) +
geom_abline(slope = 1, intercept = 0, linetype = "dashed") +
facet_wrap(~ weight_prop_cat, labeller = labeller(
weight_prop_cat = function(x) paste("Weight Proportion =", x)
)) +
labs(title = "Total Weight Parameter Recovery",
x = "True Total Weight",
y = "Estimated Total Weight",
color = "Number of\nTrials per\nCondition") +
theme_minimal() +
theme(legend.position = "right")
# Visualize weight proportion recovery
# Create discrete categories for total weight
results_with_categories <- results_df %>%
filter(true_total_weight > 0) %>% # Avoid division by zero issues
mutate(total_weight_cat = cut(true_total_weight,
breaks = c(0, 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0),
labels = c("0-0.5", "0.5-1.0", "1.0-1.5", "1.5-2.0"),
include.lowest = TRUE))
p2 <- results_with_categories %>%
ggplot(aes(x = true_weight_prop, y = weight_prop_est, color = factor(trials))) +
geom_point() +
geom_errorbar(aes(ymin = weight_prop_est - weight_prop_sd,
ymax = weight_prop_est + weight_prop_sd),
width = 0.01, alpha = 0.5) +
geom_abline(slope = 1, intercept = 0, linetype = "dashed") +
facet_wrap(~ total_weight_cat, labeller = labeller(
total_weight_cat = function(x) paste("Total Weight =", x)
)) +
labs(title = "Weight Proportion Parameter Recovery",
x = "True Weight Proportion",
y = "Estimated Weight Proportion",
color = "Number of\nTrials per\nCondition") +
theme_minimal() +
theme(legend.position = "right")
return(list(total = p1, prop = p2))
}
# Generate plots
original_recovery_plots <- plot_recovery_original(results)
new_recovery_plots <- plot_recovery_new(results)
# Display plots for new parameterization
new_recovery_plots$total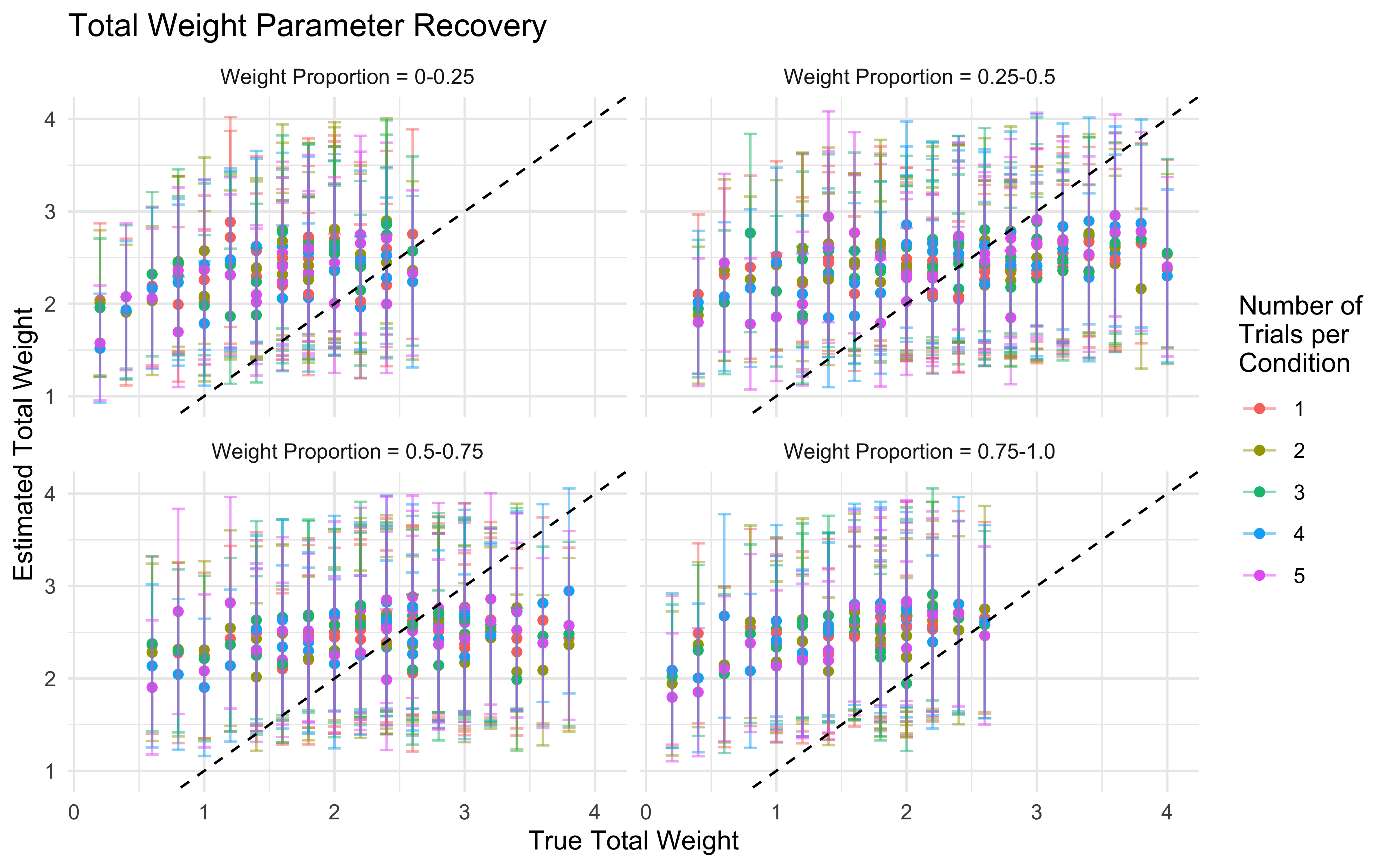
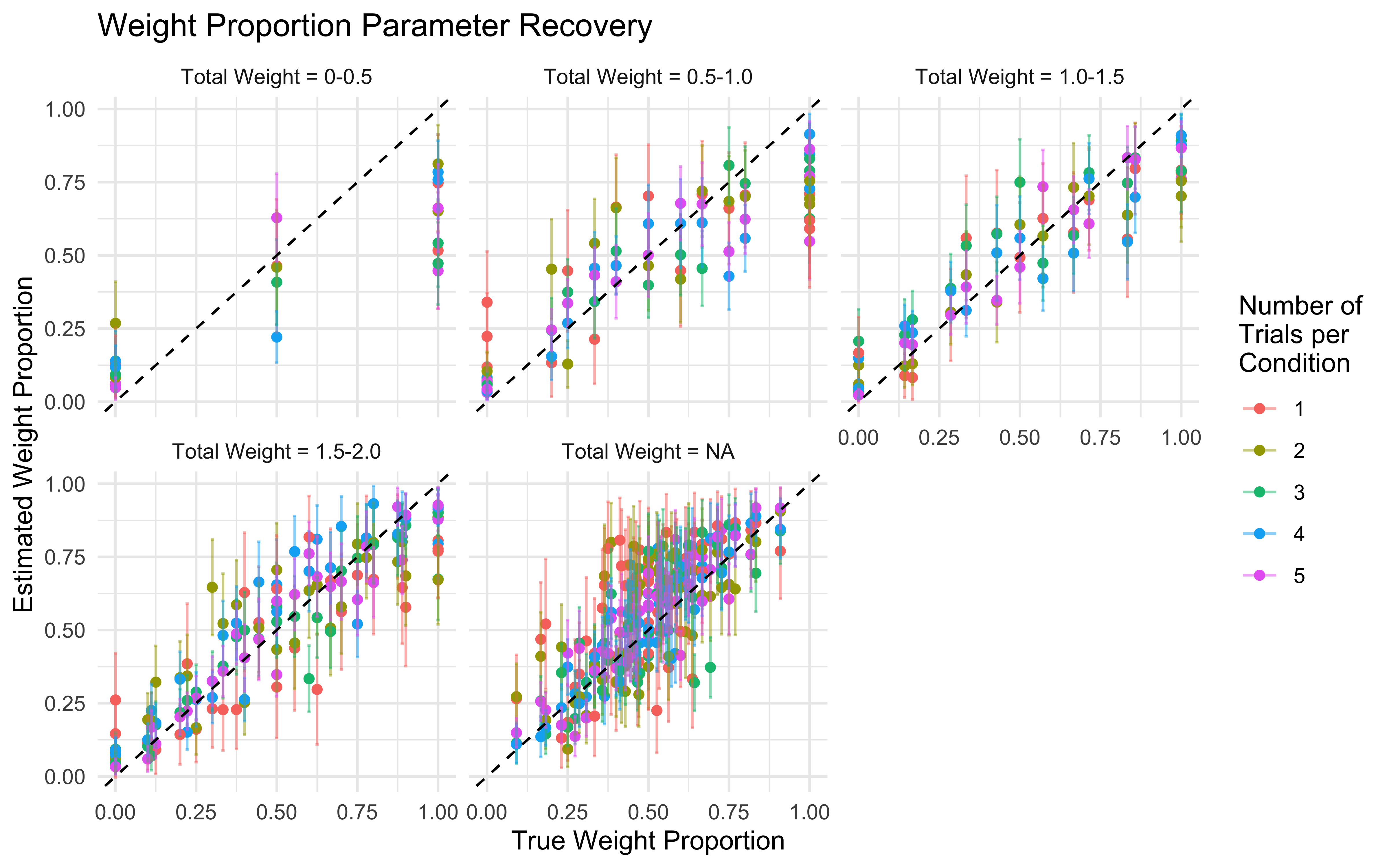
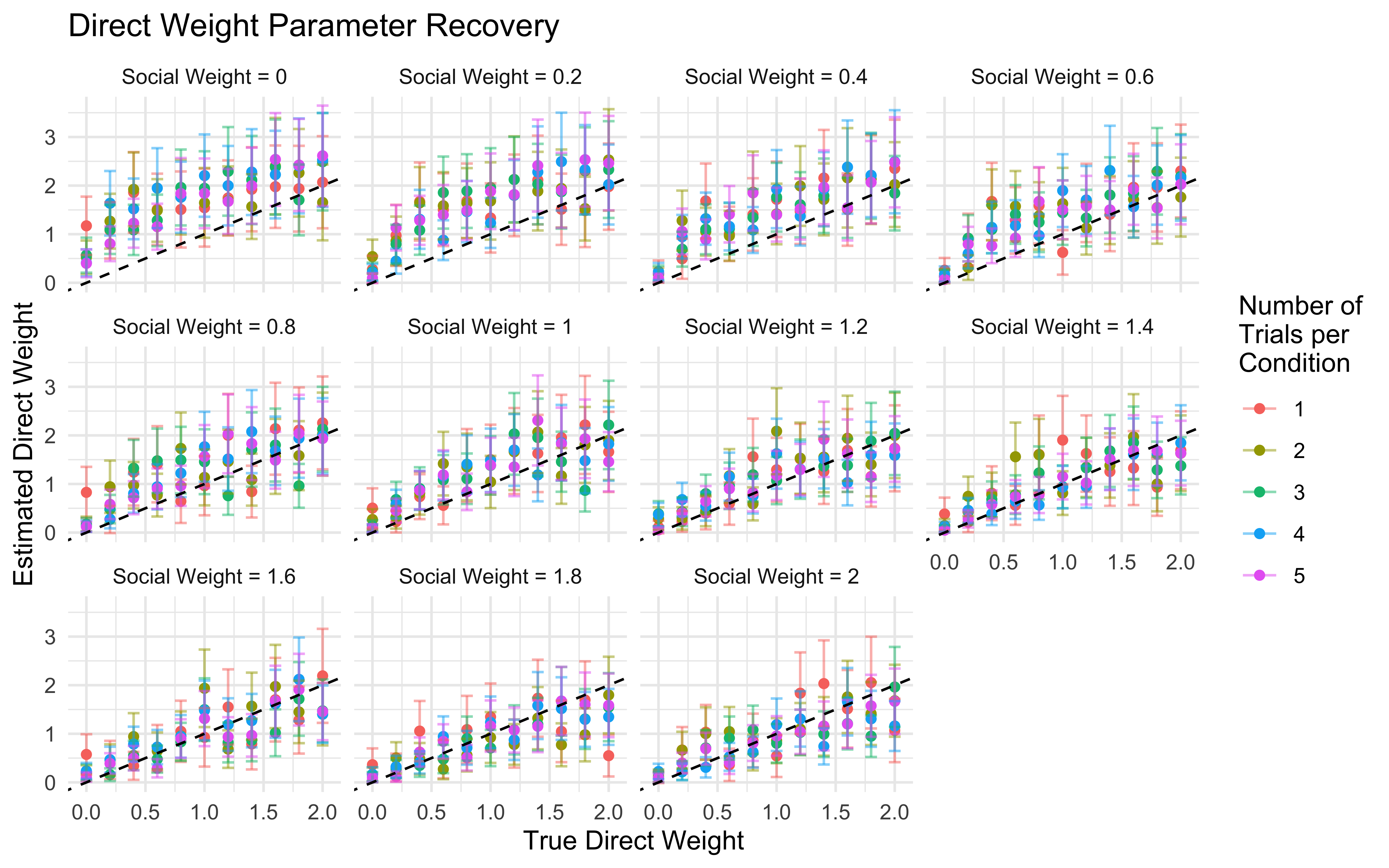
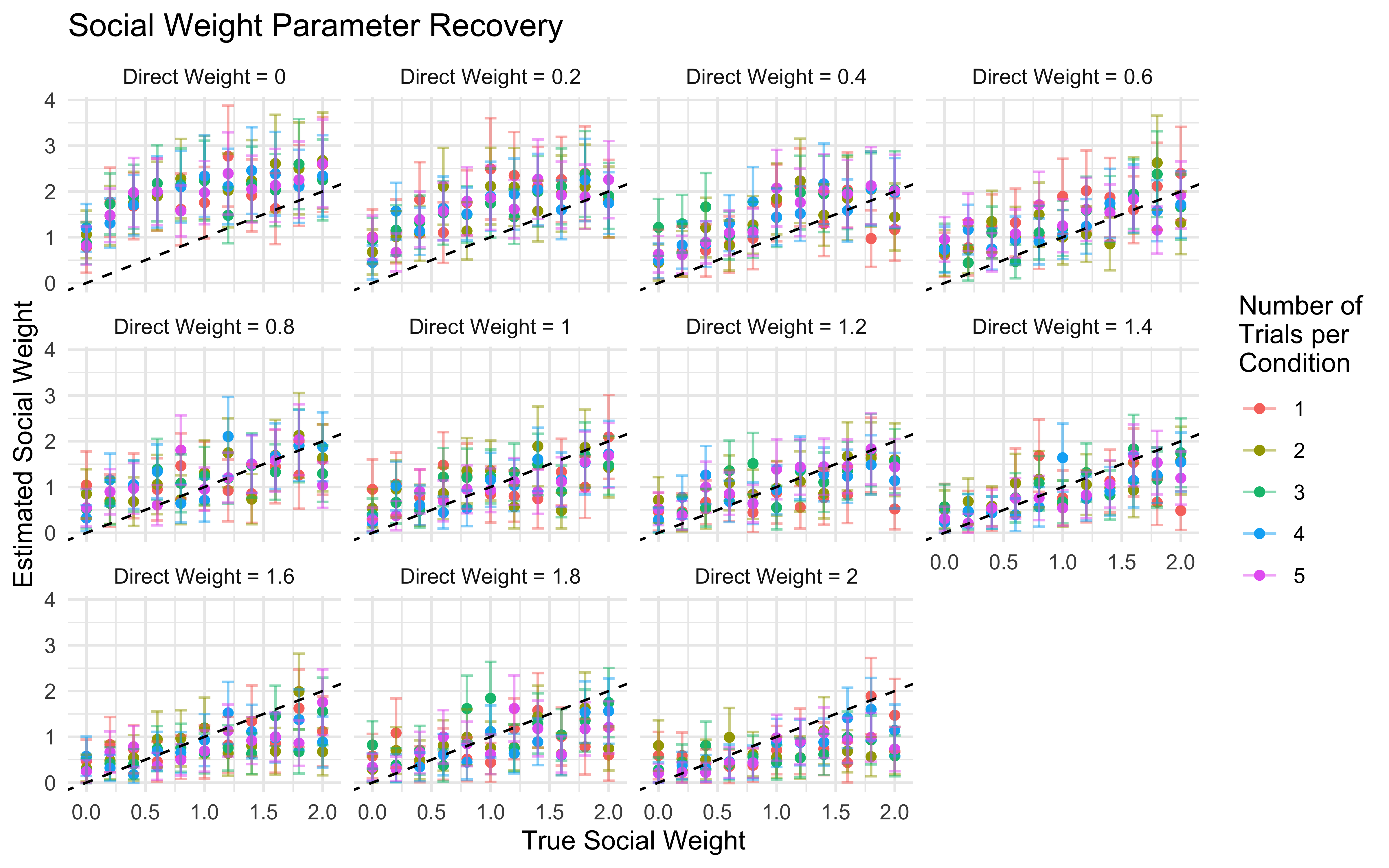
# Analysis of recovery quality by parameter combination
recovery_summary <- results %>%
mutate(
# Calculate error metrics for original parameterization
error_direct = abs(weight_direct_est - w1),
error_social = abs(weight_social_est - w2),
rel_error_direct = ifelse(w1 > 0, error_direct / w1, NA),
rel_error_social = ifelse(w2 > 0, error_social / w2, NA),
# Calculate error metrics for new parameterization
error_total = abs(total_weight_est - true_total_weight),
error_prop = abs(weight_prop_est - true_weight_prop),
rel_error_total = ifelse(true_total_weight > 0, error_total / true_total_weight, NA),
rel_error_prop = ifelse(true_weight_prop > 0, error_prop / true_weight_prop, NA)
) %>%
group_by(trials) %>%
summarize(
mean_error_direct = mean(error_direct, na.rm = TRUE),
mean_error_social = mean(error_social, na.rm = TRUE),
mean_rel_error_direct = mean(rel_error_direct, na.rm = TRUE),
mean_rel_error_social = mean(rel_error_social, na.rm = TRUE),
mean_error_total = mean(error_total, na.rm = TRUE),
mean_error_prop = mean(error_prop, na.rm = TRUE),
mean_rel_error_total = mean(rel_error_total, na.rm = TRUE),
mean_rel_error_prop = mean(rel_error_prop, na.rm = TRUE),
.groups = "drop"
)
# Display summary table
knitr::kable(recovery_summary,
digits = 3,
caption = "Parameter Recovery Quality by Number of Trials")| trials | mean_error_direct | mean_error_social | mean_rel_error_direct | mean_rel_error_social | mean_error_total | mean_error_prop | mean_rel_error_total | mean_rel_error_prop |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.436 | 0.560 | 0.652 | 0.833 | 0.784 | 0.151 | 0.774 | 0.339 |
| 2 | 0.431 | 0.524 | 0.742 | 0.742 | 0.795 | 0.126 | 0.768 | 0.315 |
| 3 | 0.404 | 0.487 | 0.627 | 0.740 | 0.780 | 0.102 | 0.764 | 0.211 |
| 4 | 0.389 | 0.442 | 0.611 | 0.736 | 0.740 | 0.097 | 0.719 | 0.208 |
| 5 | 0.350 | 0.451 | 0.569 | 0.666 | 0.721 | 0.087 | 0.690 | 0.184 |
# Create a summary visualization showing how recovery improves with more trials
p_summary <- recovery_summary %>%
pivot_longer(
cols = starts_with("mean_"),
names_to = "metric",
values_to = "value"
) %>%
mutate(
parameter_type = case_when(
grepl("direct", metric) ~ "Direct Weight",
grepl("social", metric) ~ "Social Weight",
grepl("total", metric) ~ "Total Weight",
grepl("prop", metric) ~ "Weight Proportion"
),
error_type = case_when(
grepl("rel_error", metric) ~ "Relative Error",
TRUE ~ "Absolute Error"
)
) %>%
ggplot(aes(x = trials, y = value, color = parameter_type, linetype = error_type)) +
geom_line(size = 1) +
geom_point(size = 3) +
facet_wrap(~ error_type, scales = "free_y") +
labs(
title = "Parameter Recovery Improvement with Increased Trials",
x = "Number of Trials per Evidence Combination",
y = "Mean Error",
color = "Parameter",
linetype = "Error Type"
) +
theme_minimal()
p_summary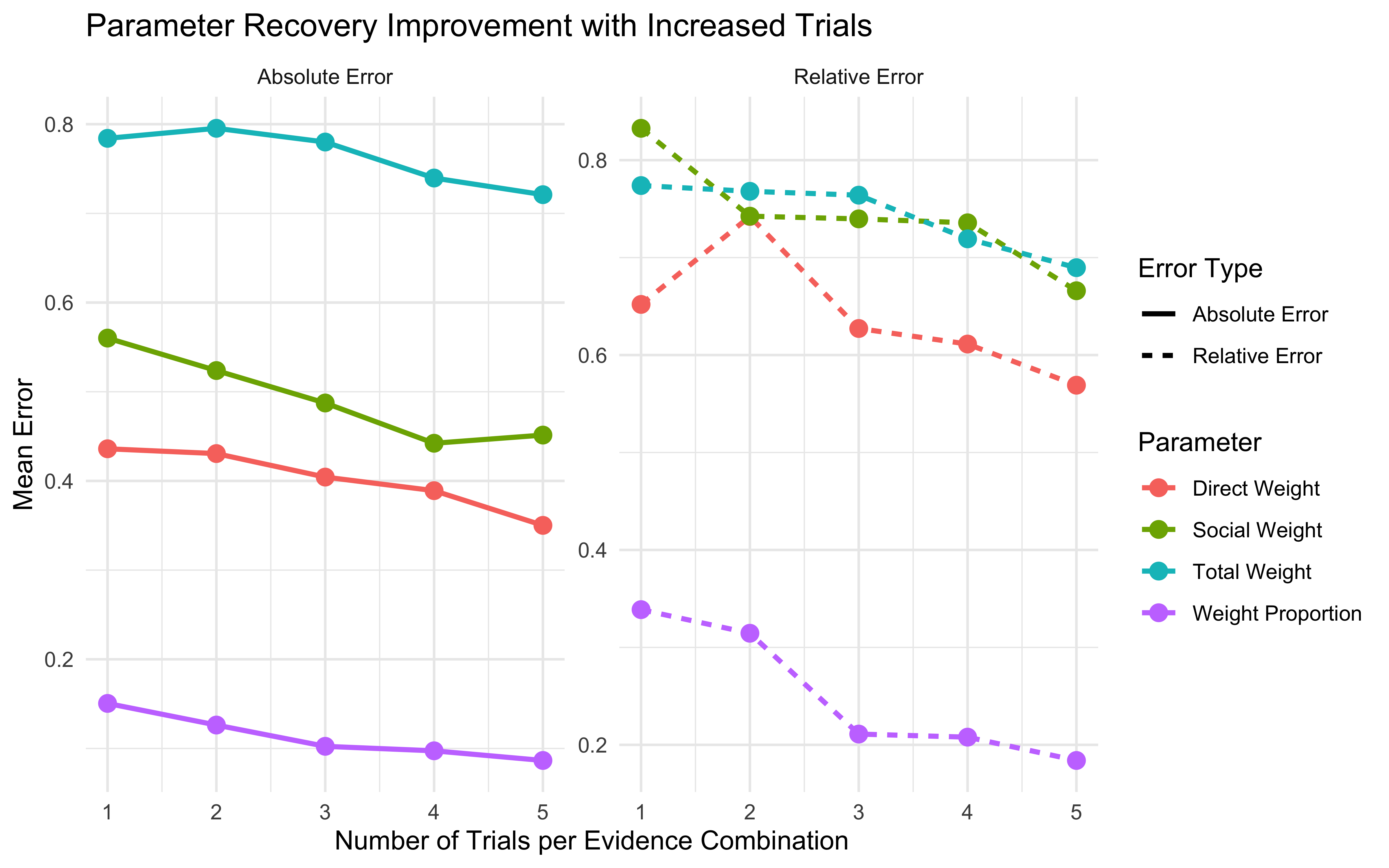
11.18 Leave-One-Out Cross-Validation and Model Comparison
In this section, we’ll explore how to compare the simple Bayesian agent (where weights are equal) and the weighted Bayesian agent (where weights can differ) using Leave-One-Out Cross-Validation (LOO-CV). We’ll leverage the models we’ve already fitted to our three simulated agent types: Balanced, Self-Focused, and Socially-Influenced.
11.18.1 Understanding LOO Cross-Validation in Bayesian Framework
LOO-CV is a powerful method for model comparison that estimates how well a model will predict new, unseen data. At its core, LOO-CV works by:
- Leaving out one observation at a time
- Fitting the model on all remaining observations
- Predicting the left-out observation using that model
- Repeating for all observations and aggregating the results
In a Bayesian context, exact LOO-CV would require refitting our model N times (where N is the number of observations), which is computationally expensive. Instead, we use Pareto-Smoothed Importance Sampling (PSIS-LOO), which approximates LOO-CV from a single model fit.
The key insight of PSIS-LOO is that we can use importance sampling to approximate how the posterior would change if an observation were removed:
\[p(\theta | y_{-i}) \approx \frac{p(\theta | y)}{p(y_i | \theta)} \propto \frac{p(\theta | y)}{p(y_i | \theta)}\]
where \(p(\theta | y_{-i})\) is the posterior without observation \(i\), and \(p(\theta | y)\) is the full posterior.
11.18.2 Step-by-Step Implementation of LOO-CV
Let’s apply LOO-CV to compare our models across the three scenarios.
# Load the loo package
library(loo)
# Function to extract log-likelihood and compute LOO
compute_loo <- function(model_fit) {
# Extract log-likelihood values
log_lik <- model_fit$draws("log_lik", format = "matrix")
# Compute LOO-CV using PSIS
loo_result <- loo(log_lik)
return(loo_result)
}
# Compute LOO for each model and scenario
loo_simple_balanced <- compute_loo(fit_simple_balanced)
loo_simple_self_focused <- compute_loo(fit_simple_self_focused)
loo_simple_socially_influenced <- compute_loo(fit_simple_socially_influenced)
loo_weighted_balanced <- compute_loo(fit_weighted_balanced)
loo_weighted_self_focused <- compute_loo(fit_weighted_self_focused)
loo_weighted_socially_influenced <- compute_loo(fit_weighted_socially_influenced)11.18.3 Understanding PSIS-LOO Diagnostics
Before we compare models, it’s important to check the reliability of our LOO estimates. PSIS-LOO provides diagnostics through the Pareto k values:
# Function to check Pareto k diagnostics
check_pareto_k <- function(loo_result, model_name) {
# Extract Pareto k values
pareto_k <- loo_result$diagnostics$pareto_k
# Count problematic k values
n_k_high <- sum(pareto_k > 0.7)
n_k_medium <- sum(pareto_k > 0.5 & pareto_k <= 0.7)
# Proportion of problematic observations
prop_problematic <- (n_k_high + n_k_medium) / length(pareto_k)
# Create diagnostic summary
summary_df <- tibble(
model = model_name,
total_obs = length(pareto_k),
k_high = n_k_high,
k_medium = n_k_medium,
prop_problematic = prop_problematic,
reliability = case_when(
prop_problematic == 0 ~ "Excellent",
prop_problematic < 0.05 ~ "Good",
prop_problematic < 0.1 ~ "Fair",
TRUE ~ "Poor"
)
)
return(summary_df)
}
# Check diagnostics for all models
diagnostics <- bind_rows(
check_pareto_k(loo_simple_balanced, "Simple - Balanced"),
check_pareto_k(loo_simple_self_focused, "Simple - Self-Focused"),
check_pareto_k(loo_simple_socially_influenced, "Simple - Socially-Influenced"),
check_pareto_k(loo_weighted_balanced, "Weighted - Balanced"),
check_pareto_k(loo_weighted_self_focused, "Weighted - Self-Focused"),
check_pareto_k(loo_weighted_socially_influenced, "Weighted - Socially-Influenced")
)
# Display diagnostics table
knitr::kable(diagnostics,
digits = 3,
caption = "PSIS-LOO Reliability Diagnostics")| model | total_obs | k_high | k_medium | prop_problematic | reliability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simple - Balanced | 180 | 180 | 0 | 1 | Poor |
| Simple - Self-Focused | 180 | 180 | 0 | 1 | Poor |
| Simple - Socially-Influenced | 180 | 180 | 0 | 1 | Poor |
| Weighted - Balanced | 180 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Excellent |
| Weighted - Self-Focused | 180 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Excellent |
| Weighted - Socially-Influenced | 180 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Excellent |
11.18.4 Model Comparison for Each Scenario
Now we can compare the models within each scenario:
# Function to compare models and create visualization
compare_scenario_models <- function(loo_simple, loo_weighted, scenario_name) {
# Compare models
comparison <- loo_compare(loo_simple, loo_weighted)
# Calculate model weights
weights <- loo_model_weights(list(
"Simple Bayesian" = loo_simple,
"Weighted Bayesian" = loo_weighted
))
# Print comparison
cat("\nModel comparison for", scenario_name, "scenario:\n")
print(comparison)
# Print weights
cat("\nModel weights for", scenario_name, "scenario:\n")
print(weights)
# Create comparison dataframe
comparison_df <- as.data.frame(comparison)
comparison_df$model <- rownames(comparison_df)
rownames(comparison_df) <- NULL
comparison_df$scenario <- scenario_name
# Create weights dataframe
weights_df <- tibble(
model = names(weights),
weight = as.numeric(weights),
scenario = scenario_name
)
# Return both dataframes
return(list(comparison = comparison_df, weights = weights_df))
}
# Perform comparisons for each scenario
balanced_comparison <- compare_scenario_models(
loo_simple_balanced, loo_weighted_balanced, "Balanced"
)##
## Model comparison for Balanced scenario:
## elpd_diff se_diff
## model1 0.0 0.0
## model2 -1.0 0.3
##
## Model weights for Balanced scenario:
## Method: stacking
## ------
## weight
## Simple Bayesian 1.000
## Weighted Bayesian 0.000self_focused_comparison <- compare_scenario_models(
loo_simple_self_focused, loo_weighted_self_focused, "Self-Focused"
)##
## Model comparison for Self-Focused scenario:
## elpd_diff se_diff
## model2 0.0 0.0
## model1 -3.1 2.6
##
## Model weights for Self-Focused scenario:
## Method: stacking
## ------
## weight
## Simple Bayesian 0.085
## Weighted Bayesian 0.915socially_influenced_comparison <- compare_scenario_models(
loo_simple_socially_influenced, loo_weighted_socially_influenced, "Socially-Influenced"
)##
## Model comparison for Socially-Influenced scenario:
## elpd_diff se_diff
## model2 0.0 0.0
## model1 -6.2 3.5
##
## Model weights for Socially-Influenced scenario:
## Method: stacking
## ------
## weight
## Simple Bayesian 0.000
## Weighted Bayesian 1.00011.18.5 Visualizing the Comparison Results
Let’s create informative visualizations to better understand the comparison results:
# Plot ELPD differences
p1 <- ggplot(all_comparisons,
aes(x = model, y = elpd_diff, fill = model)) +
geom_col() +
geom_errorbar(aes(ymin = elpd_diff - se_diff,
ymax = elpd_diff + se_diff),
width = 0.2) +
facet_wrap(~ scenario, scales = "free_y") +
labs(
title = "Model Comparison via LOO-CV",
subtitle = "Higher ELPD difference is better; error bars show ±1 SE",
x = NULL,
y = "ELPD Difference"
) +
scale_fill_brewer(palette = "Set1") +
theme_minimal() +
theme(legend.position = "bottom")
# Plot model weights
p2 <- ggplot(all_weights,
aes(x = model, y = weight, fill = model)) +
geom_col() +
geom_text(aes(label = scales::percent(weight, accuracy = 0.1)),
vjust = -0.5, size = 4) +
facet_wrap(~ scenario) +
labs(
title = "Model Weights Based on LOO-CV",
subtitle = "Higher weights indicate better predictive performance",
x = NULL,
y = "Model Weight"
) +
scale_fill_brewer(palette = "Set1") +
theme_minimal() +
theme(legend.position = "bottom") +
ylim(0, 1)
# Display plots
p1 + p2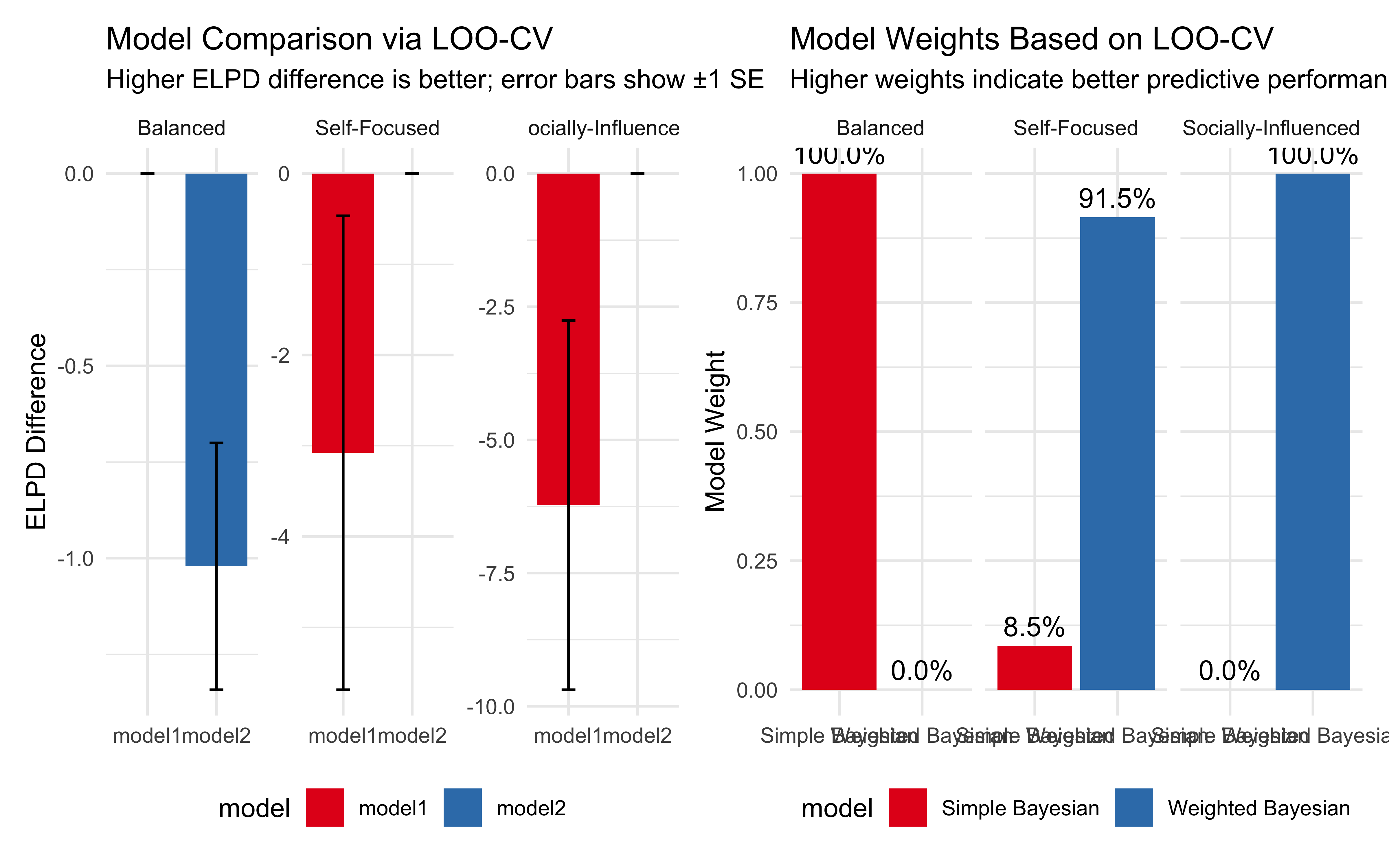
# Create a summary table of results
summary_table <- all_weights %>%
pivot_wider(names_from = model, values_from = weight) %>%
mutate(
winning_model = case_when(
`Simple Bayesian` > `Weighted Bayesian` ~ "Simple Bayesian",
`Weighted Bayesian` > `Simple Bayesian` ~ "Weighted Bayesian",
TRUE ~ "Tie"
),
weight_difference = abs(`Simple Bayesian` - `Weighted Bayesian`),
evidence_strength = case_when(
weight_difference < 0.1 ~ "Weak",
weight_difference < 0.3 ~ "Moderate",
weight_difference < 0.6 ~ "Strong",
TRUE ~ "Very Strong"
)
)
# Display summary table
knitr::kable(summary_table,
digits = 3,
caption = "Summary of Model Comparison Results")| scenario | Simple Bayesian | Weighted Bayesian | winning_model | weight_difference | evidence_strength |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Balanced | 1.000 | 0.000 | Simple Bayesian | 1.00 | Very Strong |
| Self-Focused | 0.085 | 0.915 | Weighted Bayesian | 0.83 | Very Strong |
| Socially-Influenced | 0.000 | 1.000 | Weighted Bayesian | 1.00 | Very Strong |
11.18.6 Understanding the Results
Now let’s take a deeper look at what these LOO comparisons tell us:
11.18.6.1 1. Balanced Agent Scenario
In the Balanced Agent scenario (where both direct and social evidence are weighted equally), we expect the simple Bayesian model to perform well, since it assumes equal weights by design. If our LOO comparison shows the weighted model doesn’t provide much advantage, this confirms our expectations - the additional complexity of differential weighting isn’t justified when the true process gives equal weight to evidence sources.
11.18.6.2 2. Self-Focused Agent Scenario
For the Self-Focused Agent (who overweights direct evidence and underweights social evidence), we expect the weighted Bayesian model to outperform the simple model. If the LOO comparison shows a substantial advantage for the weighted model, it suggests that capturing the differential weighting of evidence is important for predicting this agent’s behavior.
11.18.7 The Mathematics Behind LOO-CV
Let’s look at the mathematical foundations of LOO-CV to better understand what’s happening:
Log Predictive Density: For each observation \(i\), the log predictive density is:
\[\log p(y_i | y_{-i}) = \log \int p(y_i | \theta) p(\theta | y_{-i}) d\theta\]
This represents how well we can predict observation \(i\) using a model trained on all other observations.
PSIS-LOO Approximation: Since we don’t want to refit our model for each observation, we use importance sampling:
\[\log p(y_i | y_{-i}) \approx \log \frac{\sum_{j=1}^S w_i^j p(y_i | \theta^j)}{\sum_{j=1}^S w_i^j}\]
where \(w_i^j \propto \frac{1}{p(y_i | \theta^j)}\) are importance weights and \(\theta^j\) are samples from the full posterior.
Expected Log Predictive Density (ELPD): The overall measure of model predictive accuracy is:
\[\text{ELPD} = \sum_{i=1}^N \log p(y_i | y_{-i})\]
Higher ELPD values indicate better predictive performance.
11.18.8 Examining Pointwise Contributions to LOO
To understand where model differences arise, we can look at the pointwise contributions to LOO:
# Extract pointwise values
pointwise_balanced <- tibble(
observation = 1:length(loo_simple_balanced$pointwise[,"elpd_loo"]),
simple = loo_simple_balanced$pointwise[,"elpd_loo"],
weighted = loo_weighted_balanced$pointwise[,"elpd_loo"],
difference = weighted - simple,
scenario = "Balanced"
)
pointwise_self_focused <- tibble(
observation = 1:length(loo_simple_self_focused$pointwise[,"elpd_loo"]),
simple = loo_simple_self_focused$pointwise[,"elpd_loo"],
weighted = loo_weighted_self_focused$pointwise[,"elpd_loo"],
difference = weighted - simple,
scenario = "Self-Focused"
)
pointwise_socially_influenced <- tibble(
observation = 1:length(loo_simple_socially_influenced$pointwise[,"elpd_loo"]),
simple = loo_simple_socially_influenced$pointwise[,"elpd_loo"],
weighted = loo_weighted_socially_influenced$pointwise[,"elpd_loo"],
difference = weighted - simple,
scenario = "Socially-Influenced"
)
# Combine pointwise data
all_pointwise <- bind_rows(
pointwise_balanced,
pointwise_self_focused,
pointwise_socially_influenced
)
# Plot pointwise differences
ggplot(all_pointwise, aes(x = observation, y = difference)) +
geom_col(aes(fill = difference > 0)) +
geom_hline(yintercept = 0, linetype = "dashed") +
facet_wrap(~ scenario, scales = "free_x") +
scale_fill_manual(values = c("TRUE" = "green4", "FALSE" = "firebrick"),
name = "Weighted Better?") +
labs(
title = "Pointwise Differences in ELPD Between Models",
subtitle = "Green bars indicate observations where the weighted model performs better",
x = "Observation",
y = "ELPD Difference (Weighted - Simple)"
) +
theme_minimal() +
theme(legend.position = "bottom")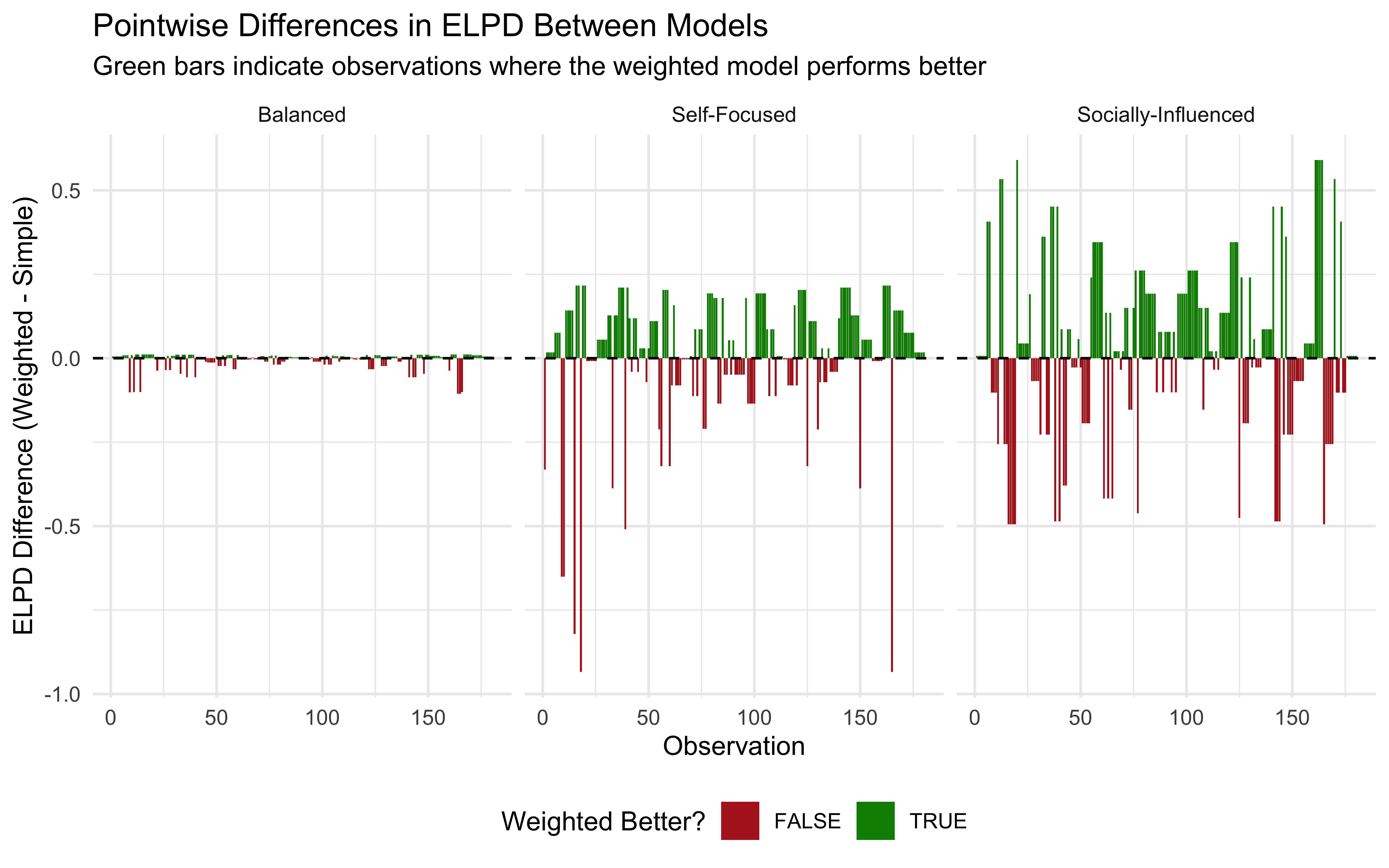
11.19 Multilevel Bayesian Models
In the previous sections, we explored how individuals integrate direct and social evidence using Bayesian principles. However, our models assumed that all individuals use the same weighting strategy. In reality, people vary in how they weigh different sources of information - some may trust their own observations more, while others may be more influenced by social information.
Multilevel (hierarchical) models allow us to capture this individual variation while still leveraging the commonalities across individuals. They offer several advantages:
- They model individual differences explicitly
- They improve parameter estimation for individuals with limited data
- They allow us to examine correlations between individual parameters
- They provide population-level insights about general tendencies
In this section, we’ll develop multilevel versions of both our simple beta-binomial and weighted beta-binomial models.
11.19.1 Simulating Data from Multiple Agents
First, let’s simulate a population of agents with varying evidence-weighting parameters:
# Simulation parameters
n_agents <- 20 # Number of agents per model
n_trials_per_agent <- 36 # Number of evidence combinations per agent
# Define population parameters for simple model (equal weights with varying scaling)
simple_population_scaling_mean <- 1.0 # Mean scaling factor (log-scale)
simple_population_scaling_sd <- 0.3 # SD of scaling factor (log-scale)
# Define population parameters for weighted model
weighted_population_scaling_mean <- 1.5 # Mean scaling factor (log-scale)
weighted_population_scaling_sd <- 0.3 # SD of scaling factor (log-scale)
weighted_population_ratio_mean <- 1 # Mean weight ratio (log-scale, 0 = equal weights)
weighted_population_ratio_sd <- 0.5 # SD of weight ratio (log-scale)
# Generate agent parameters for simple model
simple_agents <- tibble(
agent_id = 1:n_agents,
model_type = "simple",
# Generate log-normal scaling factors
log_scaling = rnorm(n_agents, simple_population_scaling_mean, simple_population_scaling_sd),
scaling_factor = exp(log_scaling),
# For simple model, weight ratio is always 1 (equal weights)
weight_ratio = rep(1, n_agents),
# Calculate the actual weights
weight_direct = scaling_factor * weight_ratio / (1 + weight_ratio),
weight_social = scaling_factor / (1 + weight_ratio)
)
# Generate agent parameters for weighted model
weighted_agents <- tibble(
agent_id = n_agents + (1:n_agents), # Continue numbering from simple agents
model_type = "weighted",
# Generate log-normal scaling factors
log_scaling = rnorm(n_agents, weighted_population_scaling_mean, weighted_population_scaling_sd),
scaling_factor = exp(log_scaling),
# Generate log-normal weight ratios
log_weight_ratio = rnorm(n_agents, weighted_population_ratio_mean, weighted_population_ratio_sd),
weight_ratio = exp(log_weight_ratio),
# Calculate the actual weights
weight_direct = scaling_factor * weight_ratio / (1 + weight_ratio),
weight_social = scaling_factor / (1 + weight_ratio)
)
# Combine agent parameters
all_agents <- bind_rows(simple_agents, weighted_agents)
# Print summary of agent parameters
agent_summary <- all_agents %>%
group_by(model_type) %>%
summarize(
n = n(),
mean_scaling = mean(scaling_factor),
sd_scaling = sd(scaling_factor),
mean_ratio = mean(weight_ratio),
sd_ratio = sd(weight_ratio),
mean_direct = mean(weight_direct),
sd_direct = sd(weight_direct),
mean_social = mean(weight_social),
sd_social = sd(weight_social)
)
print(agent_summary)## # A tibble: 2 × 10
## model_type n mean_scaling sd_scaling mean_ratio sd_ratio mean_direct sd_direct
## <chr> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 simple 20 2.94 0.878 1 0 1.47 0.439
## 2 weighted 20 4.56 1.08 3.28 1.67 3.37 0.881
## # ℹ 2 more variables: mean_social <dbl>, sd_social <dbl># Create all possible evidence combinations
evidence_combinations <- expand_grid(
blue1 = 0:8, # Direct evidence: 0-8 blue marbles out of 8
blue2 = 0:3, # Social evidence: 0-3 blue signals out of 3
total1 = 8, # Total marbles in direct evidence (constant)
total2 = 3 # Total signals in social evidence (constant)
)
# Function to generate agent decisions based on their parameters
generate_agent_decisions <- function(agent_data, evidence_df, n_samples = 5) {
# Extract agent parameters
agent_id <- agent_data$agent_id
model_type <- agent_data$model_type
weight_direct <- agent_data$weight_direct
weight_social <- agent_data$weight_social
# Create a data frame that repeats each evidence combination n_samples times
repeated_evidence <- evidence_df %>%
slice(rep(1:n(), each = n_samples)) %>%
group_by(blue1, blue2, total1, total2) %>%
mutate(sample_id = 1:n()) %>%
ungroup()
# Generate decisions for each evidence combination
decisions <- pmap_dfr(repeated_evidence, function(blue1, blue2, total1, total2, sample_id) {
# Calculate weighted evidence
weighted_blue1 <- blue1 * weight_direct
weighted_red1 <- (total1 - blue1) * weight_direct
weighted_blue2 <- blue2 * weight_social
weighted_red2 <- (total2 - blue2) * weight_social
# Calculate Beta parameters
alpha_post <- 1 + weighted_blue1 + weighted_blue2
beta_post <- 1 + weighted_red1 + weighted_red2
# Expected probability
expected_rate <- alpha_post / (alpha_post + beta_post)
# Make choice
choice <- rbinom(1, 1, expected_rate)
# Return decision data
tibble(
agent_id = agent_id,
model_type = model_type,
sample_id = sample_id,
blue1 = blue1,
blue2 = blue2,
total1 = total1,
total2 = total2,
expected_rate = expected_rate,
choice = choice,
# Include true parameter values for reference
true_weight_direct = weight_direct,
true_weight_social = weight_social,
true_weight_ratio = weight_direct / weight_social,
true_scaling_factor = weight_direct + weight_social
)
})
return(decisions)
}
# Generate decisions for all agents
multilevel_sim_data <- map_dfr(1:nrow(all_agents), function(i) {
generate_agent_decisions(all_agents[i, ], evidence_combinations)
})
# Add descriptive labels
multilevel_sim_data <- multilevel_sim_data %>%
mutate(
social_evidence = factor(
blue2,
levels = 0:3,
labels = c("Clear Red", "Weak Red", "Weak Blue", "Clear Blue")
)
)
# Visualize decision patterns for selected agents
# Take a sample of agents from each model type
selected_simple_agents <- sample(unique(simple_agents$agent_id), 3)
selected_weighted_agents <- sample(unique(weighted_agents$agent_id), 3)
selected_agents <- c(selected_simple_agents, selected_weighted_agents)
# Create plot
decision_plot <- multilevel_sim_data %>%
filter(agent_id %in% selected_agents) %>%
ggplot(aes(x = blue1, y = expected_rate, color = social_evidence, group = social_evidence)) +
geom_line(size = 1) +
geom_point(size = 2) +
geom_hline(yintercept = 0.5, linetype = "dashed", color = "gray50") +
facet_wrap(~ model_type + agent_id, ncol = 3) +
labs(
title = "Decision Patterns: Simple vs. Weighted Integration",
subtitle = "Simple model shows parallel curves (equal weights), weighted model shows varying influence of social evidence",
x = "Blue Marbles in Direct Evidence (out of 8)",
y = "Probability of Choosing Blue",
color = "Social Evidence"
) +
theme_bw() +
theme(legend.position = "bottom")
# Display plot
print(decision_plot)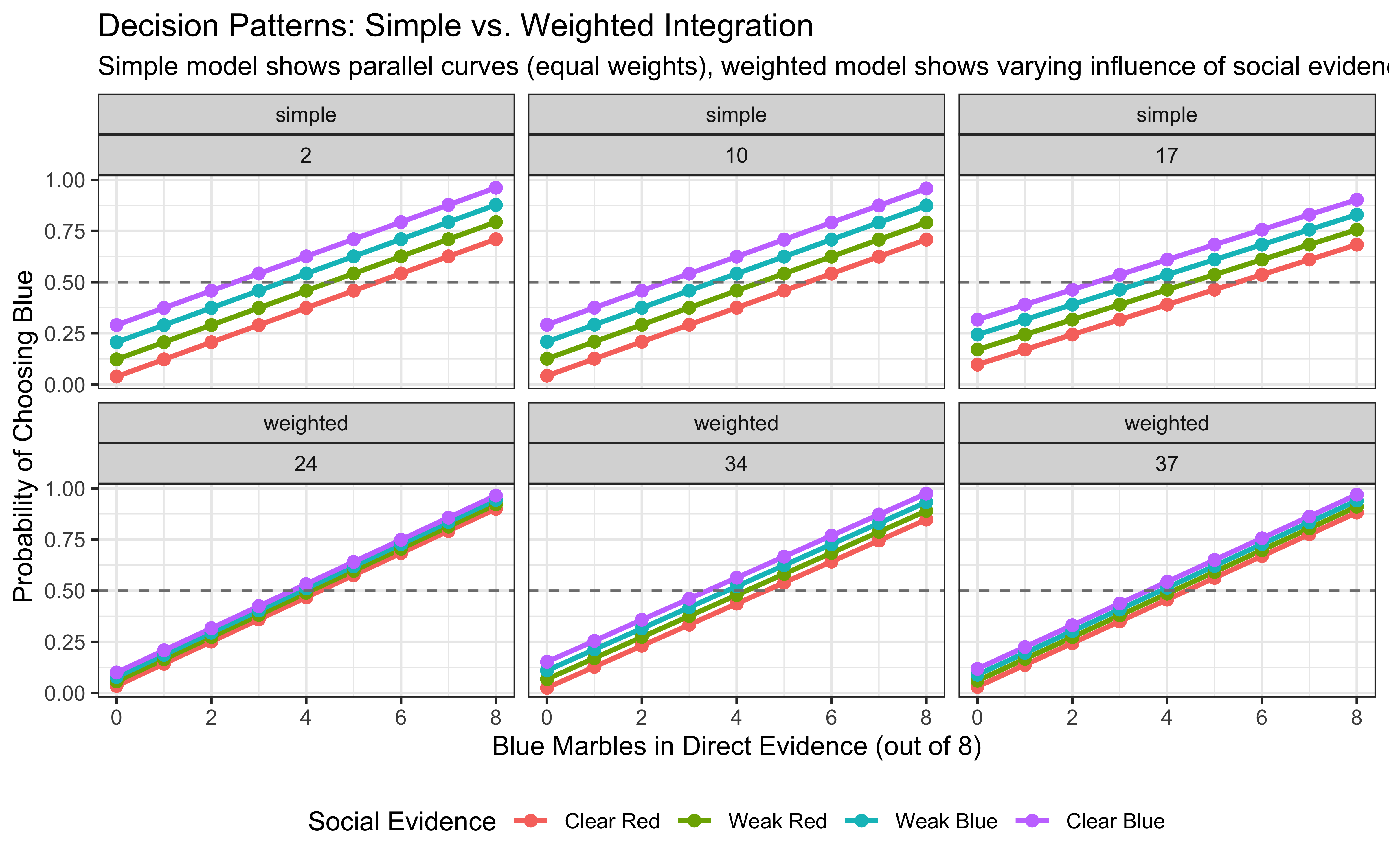
# Print summary of dataset
cat("Generated", nrow(multilevel_sim_data), "observations from",
n_agents * 2, "agents (", n_agents, "per model type)\n")## Generated 7200 observations from 40 agents ( 20 per model type)# Create data structure for Stan fitting
stan_data_multilevel <- list(
N = nrow(multilevel_sim_data),
J = n_agents * 2,
agent_id = multilevel_sim_data$agent_id,
choice = multilevel_sim_data$choice,
blue1 = multilevel_sim_data$blue1,
total1 = multilevel_sim_data$total1,
blue2 = multilevel_sim_data$blue2,
total2 = multilevel_sim_data$total2
)11.19.2 Understanding the Simulated Data
The simulation generates data from two types of agents:
Simple Integration Agents: These agents weight direct and social evidence equally, but with varying overall scaling factors. This creates individual differences in how strongly evidence affects beliefs, but without preferential weighting of sources.
Weighted Integration Agents: These agents can weight direct and social evidence differently. Some might trust their direct evidence more, others might be more influenced by social information.
The key visual difference in their decision patterns is:
Simple integration agents show parallel curves for different social evidence levels. The spacing between curves is consistent across all levels of direct evidence, indicating equal influence.
Weighted integration agents show varying spacing between curves. When an agent weights social evidence more heavily, the curves are more separated; when direct evidence is weighted more, the curves converge.
By generating data from both models, we can:
- Verify our model-fitting procedure can recover the true parameters
- Test whether our model comparison methods correctly identify which integration strategy generated each dataset
- Assess how robustly we can detect differential weighting of evidence sources
In the next section, we’ll fit both our multilevel models to this data and compare their performance..
Looking at these visualizations, we can see clear individual differences in how agents integrate evidence:
- Some agents give more weight to direct evidence, requiring less direct evidence to choose “blue” regardless of social evidence
- Others are more influenced by social information, showing greater spacing between the different social evidence lines
- These differences create unique decision boundaries for each agent, where they transition from choosing red to blue
11.20 Multilevel Bayesian Models for Evidence Integration
In this section, we implement two multilevel Bayesian models that capture different hypotheses about how individuals integrate evidence from multiple sources. Both models allow for individual differences, but they differ in what aspects of evidence integration can vary across individuals.
11.20.1 Model 1: Simple Evidence Integration with Individual Scaling
Our first model implements a cognitively simple integration strategy where all evidence sources are weighted equally (taken at “face value”), but the overall impact of evidence can vary across individuals:
- Each information source (direct and social evidence) receives equal relative weight in the integration process
- However, the overall scaling of evidence can vary between individuals
- This represents individuals who treat all evidence sources as equally reliable, but differ in how strongly any evidence influences their beliefs
Mathematically, this means that for individual j: - Direct evidence weight = scaling_factor[j] × 0.5 - Social evidence weight = scaling_factor[j] × 0.5
This model captures the hypothesis that individuals differ in their overall sensitivity to evidence, but not in how they relatively weight different sources. Some individuals might be more conservative (low scaling factor), requiring more evidence to shift their beliefs, while others might be more responsive to evidence overall (high scaling factor).
11.20.2 Model 2: Weighted Evidence Integration
Our second model implements a more complex integration strategy where both the overall impact of evidence and the relative weighting of different evidence sources can vary across individuals:
- Each individual can give different weights to direct versus social evidence
- The overall scaling of evidence can also vary between individuals
- This represents individuals who may trust certain evidence sources more than others
We parameterize this model using two key parameters for each individual j:
- scaling_factor[j]: The total weight given to all evidence
- weight_ratio[j]: The ratio of direct evidence weight to social evidence weight
From these, we derive the actual weights: - Direct evidence weight = scaling_factor[j] × weight_ratio[j] / (1 + weight_ratio[j]) - Social evidence weight = scaling_factor[j] / (1 + weight_ratio[j])
This parameterization ensures that the sum of weights equals the scaling factor, while the ratio between weights is determined by the weight ratio.
11.20.3 Why Allow Scaling to Vary in the Simple Model?
Including individual variation in the scaling factor for the simple model serves several important purposes:
Fair Comparison: It ensures that the comparison between models focuses specifically on differential weighting rather than just the presence of individual differences. The key question becomes “Do individuals weight evidence sources differently?” rather than “Do individuals vary in how they use evidence?”
Statistical Control: The scaling parameter serves as a statistical control, ensuring that any evidence for differential weighting isn’t just capturing overall differences in evidence sensitivity.
Nested Model Structure: It creates a proper nested model relationship - the simple model is a special case of the weighted model where the weight ratio is constrained to be 1.0 (equal weights) for everyone.
This approach allows us to conduct a more precise test of our cognitive hypothesis about differential weighting of evidence sources, while accounting for individual differences in overall evidence use that likely exist regardless of weighting strategy.
11.21 From Single-Agent to Multilevel: Extending Bayesian Cognitive Models
When moving from single-agent to multilevel modeling, we need to extend our Stan code to capture both population-level patterns and individual differences. This transformation requires careful consideration of parameter structure, prior specification, and computational efficiency. Let’s explore how we adapted our single-agent models into multilevel versions.
11.21.1 Key Components of the Multilevel Extension
- Parameterizing Individual Differences
In our single-agent models, we had straightforward parameters like total_weight and weight_prop (for the weighted model) or just a scaling factor (for the simple model). For multilevel modeling, we need to create parameters that vary across individuals while maintaining population coherence.
For the simple integration model:
// Single-agent version
parameters {
real<lower=0> total_weight; // Overall scaling of evidence
}
// Multilevel version
parameters {
real mu_scaling; // Population mean (log scale)
real<lower=0> sigma_scaling; // Population SD
vector[J] z_scaling; // Standardized individual deviations
}
transformed parameters {
vector<lower=0>[J] scaling_factor; // Individual scaling factors
for (j in 1:J) {
scaling_factor[j] = exp(mu_scaling + z_scaling[j] * sigma_scaling);
}
}Note several key changes:
We now have population-level parameters (mu_scaling, sigma_scaling) that describe the distribution from which individual parameters are drawn
We use non-centered parameterization with standardized z-scores to improve sampling efficiency
We work in log space to ensure positive scaling factors
11.21.2 2. Hierarchical Prior Structure
Priors also need to be restructured in a hierarchical fashion:
// Single-agent version
target += lognormal_lpdf(total_weight | .8, .4); // Prior for scaling
// Multilevel version
target += normal_lpdf(mu_scaling | 0, 1); // Prior for population mean
target += exponential_lpdf(sigma_scaling | 2); // Prior for between-subject variability
target += std_normal_lpdf(z_scaling); // Prior for standardized deviations
The prior structure now has:
- Priors on population means
- Priors on population variances
- Standard normal priors on the standardized individual deviations
This creates a proper hierarchical structure where individual parameters are partially pooled toward the population mean, with the degree of pooling determined by the population variance.
11.21.3 3. Handling Data from Multiple Individuals
The data structure must be modified to associate observations with specific individuals:
// Single-agent version
data {
int<lower=1> N; // Number of observations
array[N] int<lower=0, upper=1> choice; // Choices (0=red, 1=blue)
// Other data...
}
// Multilevel version
data {
int<lower=1> N; // Number of observations
int<lower=1> J; // Number of subjects
array[N] int<lower=1, upper=J> agent_id; // Agent ID for each observation
array[N] int<lower=0, upper=1> choice; // Choices (0=red, 1=blue)
// Other data...
}The key addition is agent_id, which maps each observation to its corresponding agent. This allows us to apply the correct individual-level parameters to each observation.
11.21.4 4. Likelihood Specification
The likelihood must be adapted to use the appropriate individual-level parameters:
// Single-agent version
for (i in 1:N) {
real weighted_blue1 = blue1[i] * weight_direct;
// ...additional code...
choice[i] ~ bernoulli(expected_prob);
}
// Multilevel version
for (i in 1:N) {
real w_direct = weight_direct[agent_id[i]]; // Get parameters for this individual
real w_social = weight_social[agent_id[i]];
real weighted_blue1 = blue1[i] * w_direct;
// ...additional code...
choice[i] ~ bernoulli(expected_prob);
}We now index individual parameters by agent_id[i] to ensure each observation uses the correct agent’s parameters.
11.21.5 Why These Changes Matter
11.21.5.1 Computational Efficiency: Non-Centered Parameterization
The non-centered parameterization (using z-scores) is critical for efficient sampling in hierarchical models. When individual parameters are close to the population mean or when population variance is small, direct parameterization can cause the sampler to get stuck in a difficult geometry called the “funnel” problem.
By separating the individual effects into standardized z-scores, we create better sampling geometry and improve convergence.
This is why we use:
scaling_factor[j] = exp(mu_scaling + z_scaling[j] * sigma_scaling);instead of directly sampling individual parameters.
11.21.5.2 Working in Log Space for Bounded Parameters
For parameters that must be positive (like scaling factors), working in log space ensures we maintain proper bounds while allowing the parameter to vary freely on the unconstrained scale:
// This ensures scaling_factor is always positive
scaling_factor[j] = exp(mu_scaling + z_scaling[j] * sigma_scaling);Similarly, for parameters constrained between 0 and 1 (like weight_prop), we use the logit transformation.
Now we are ready for the full implementation of our multilevel Bayesian models for evidence integration.
# Stan model for multilevel simple beta-binomial
multilevel_simple_stan <- "
// Multilevel Simple Beta-Binomial Model
// This model assumes equal weights for evidence sources (taking evidence at face value)
// but allows for individual variation in overall responsiveness
data {
int<lower=1> N; // Total number of observations
int<lower=1> J; // Number of subjects
array[N] int<lower=1, upper=J> agent_id; // Agent ID for each observation
array[N] int<lower=0, upper=1> choice; // Choices (0=red, 1=blue)
array[N] int<lower=0> blue1; // Direct evidence (blue marbles)
array[N] int<lower=0> total1; // Total direct evidence
array[N] int<lower=0> blue2; // Social evidence (blue signals)
array[N] int<lower=0> total2; // Total social evidence
}
parameters {
// Population-level parameters for agents' preconceptions
real mu_alpha_prior; // Population mean for alpha prior
real<lower=0> sigma_alpha_prior; // Population SD for alpha prior
real mu_beta_prior; // Population mean for beta prior
real<lower=0> sigma_beta_prior; // Population SD for beta prior
// Population-level parameter for overall scaling
real mu_scaling; // Population mean scaling factor (log scale)
real<lower=0> sigma_scaling; // Population SD of scaling
// Individual-level (random) effects
vector[J] z_alpha_prior; // Standardized individual deviations for alpha prior
vector[J] z_beta_prior; // Standardized individual deviations for beta prior
vector[J] z_scaling; // Standardized individual deviations
}
transformed parameters {
// Individual-level parameters
vector<lower=0>[J] scaling_factor; // Individual scaling factors
vector<lower=0>[J] alpha_prior; // Individual alpha prior
vector<lower=0>[J] beta_prior; // Individual beta prior
// Non-centered parameterization for scaling factor
for (j in 1:J) {
alpha_prior[j] = exp(mu_alpha_prior + z_alpha_prior[j] * sigma_alpha_prior);
beta_prior[j] = exp(mu_beta_prior + z_beta_prior[j] * sigma_beta_prior);
scaling_factor[j] = exp(mu_scaling + z_scaling[j] * sigma_scaling);
}
}
model {
// Priors for population parameters
target += lognormal_lpdf(mu_alpha_prior | 0, 1); // Prior for population mean of alpha prior
target += exponential_lpdf(sigma_alpha_prior | 1); // Prior for population SD of alpha prior
target += lognormal_lpdf(mu_beta_prior | 0, 1); // Prior for population mean of beta prior
target += exponential_lpdf(sigma_beta_prior | 1); // Prior for population SD of beta prior
target += normal_lpdf(mu_scaling | 0, 1); // Prior for log scaling factor
target += exponential_lpdf(sigma_scaling | 2); // Prior for between-subject variability
// Prior for standardized random effects
z_scaling ~ std_normal(); // Standard normal prior
z_alpha_prior ~ std_normal(); // Standard normal prior
z_beta_prior ~ std_normal(); // Standard normal prior
// Likelihood
for (i in 1:N) {
// Calculate the individual scaling factor
real scale = scaling_factor[agent_id[i]];
// Simple integration - weights both evidence sources equally but applies individual scaling
// Both direct and social evidence get weight = 1.0 * scaling_factor
real weighted_blue1 = blue1[i] * scale;
real weighted_red1 = (total1[i] - blue1[i]) * scale;
real weighted_blue2 = blue2[i] * scale;
real weighted_red2 = (total2[i] - blue2[i]) * scale;
// Calculate Beta parameters for posterior
real alpha_post = alpha_prior[agent_id[i]] + weighted_blue1 + weighted_blue2;
real beta_post = beta_prior[agent_id[i]] + weighted_red1 + weighted_red2;
// Use beta-binomial distribution to model the choice
target += beta_binomial_lpmf(choice[i] | 1, alpha_post, beta_post);
}
}
generated quantities {
// Population parameters on natural scale
real population_scaling = exp(mu_scaling);
// Log likelihood for model comparison
vector[N] log_lik;
// Population and individual predictions
array[N] int pred_choice;
for (i in 1:N) {
// Calculate the individual scaling factor
real scale = scaling_factor[agent_id[i]];
// Calculate weighted evidence
real weighted_blue1 = blue1[i] * scale;
real weighted_red1 = (total1[i] - blue1[i]) * scale;
real weighted_blue2 = blue2[i] * scale;
real weighted_red2 = (total2[i] - blue2[i]) * scale;
// Calculate Beta parameters
real alpha_post = alpha_prior[agent_id[i]] + weighted_blue1 + weighted_blue2;
real beta_post = beta_prior[agent_id[i]] + weighted_red1 + weighted_red2;
// Generate predictions using beta-binomial
pred_choice[i] = beta_binomial_rng(1, alpha_post, beta_post);
// Calculate log likelihood
log_lik[i] = beta_binomial_lpmf(choice[i] | 1, alpha_post, beta_post);
}
}
"
# Write the model to a file
write_stan_file(
multilevel_simple_stan,
dir = "stan/",
basename = "W10_multilevel_simple_beta_binomial.stan"
)## [1] "/Users/au209589/Dropbox/Teaching/AdvancedCognitiveModeling23_book/stan/W10_multilevel_simple_beta_binomial.stan"11.21.6 Implementing the Multilevel Weighted Beta-Binomial Model in Stan
Now let’s implement the multilevel weighted beta-binomial model, which allows both population-level estimates of evidence weights and individual variations around these population means.
multilevel_weighted_stan <- "
// Multilevel Weighted Beta-Binomial Model
// This model allows different weights for different evidence sources
// Using total_weight and weight_prop parameterization
data {
int<lower=1> N; // Total number of observations
int<lower=1> J; // Number of subjects
array[N] int<lower=1, upper=J> agent_id; // Agent ID for each observation
array[N] int<lower=0, upper=1> choice; // Choices (0=red, 1=blue)
array[N] int<lower=0> blue1; // Direct evidence (blue marbles)
array[N] int<lower=0> total1; // Total direct evidence
array[N] int<lower=0> blue2; // Social evidence (blue signals)
array[N] int<lower=0> total2; // Total social evidence
}
parameters {
// Population-level parameters for agents' preconceptions
real mu_alpha_prior; // Population mean for alpha prior
real<lower=0> sigma_alpha_prior; // Population SD for alpha prior
real mu_beta_prior; // Population mean for beta prior
real<lower=0> sigma_beta_prior; // Population SD for beta prior
// Population-level parameters
real mu_weight_ratio; // Population mean for relative weight (direct/social) - log scale
real mu_scaling; // Population mean for overall scaling - log scale
// Population-level standard deviations
real<lower=0> sigma_weight_ratio; // Between-subject variability in relative weighting
real<lower=0> sigma_scaling; // Between-subject variability in scaling
// Individual-level (random) effects
vector[J] z_weight_ratio; // Standardized individual weight ratio deviations
vector[J] z_scaling; // Standardized individual scaling deviations
}
transformed parameters {
// Individual-level parameters
vector<lower=0>[J] weight_ratio; // Individual relative weights (direct/social)
vector<lower=0>[J] scaling_factor; // Individual overall scaling factors
vector<lower=0>[J] weight_direct; // Individual weights for direct evidence
vector<lower=0>[J] weight_social; // Individual weights for social evidence
// Non-centered parameterization
for (j in 1:J) {
// Transform standardized parameters to natural scale
weight_ratio[j] = exp(mu_weight_ratio + z_weight_ratio[j] * sigma_weight_ratio);
scaling_factor[j] = exp(mu_scaling + z_scaling[j] * sigma_scaling);
// Calculate individual weights
// The sum of weights is determined by the scaling factor
// The ratio between weights is determined by weight_ratio
weight_direct[j] = scaling_factor[j] * weight_ratio[j] / (1 + weight_ratio[j]);
weight_social[j] = scaling_factor[j] / (1 + weight_ratio[j]);
}
}
model {
// Priors for population parameters
mu_weight_ratio ~ normal(0, 1); // Prior for log weight ratio centered at 0 (equal weights)
mu_scaling ~ normal(0, 1); // Prior for log scaling factor
sigma_weight_ratio ~ exponential(2); // Prior for between-subject variability
sigma_scaling ~ exponential(2); // Prior for scaling variability
// Priors for individual random effects
z_weight_ratio ~ std_normal(); // Standard normal prior for weight ratio z-scores
z_scaling ~ std_normal(); // Standard normal prior for scaling z-scores
z_alpha_prior ~ std_normal(); // Standard normal prior
z_beta_prior ~ std_normal(); // Standard normal prior
// Likelihood
for (i in 1:N) {
// Get weights for this person
real w_direct = weight_direct[agent_id[i]];
real w_social = weight_social[agent_id[i]];
// Calculate weighted evidence
real weighted_blue1 = blue1[i] * w_direct;
real weighted_red1 = (total1[i] - blue1[i]) * w_direct;
real weighted_blue2 = blue2[i] * w_social;
real weighted_red2 = (total2[i] - blue2[i]) * w_social;
// Calculate Beta parameters for Bayesian integration
real alpha_post = alpha_prior[agent_id[i]] + weighted_blue1 + weighted_blue2;
real beta_post = beta_prior[agent_id[i]] + weighted_red1 + weighted_red2;
// Use beta-binomial distribution to model the choice
target += beta_binomial_lpmf(choice[i] | 1, alpha_post, beta_post);
}
}
generated quantities {
// Convert population parameters to original weight scale for interpretation
real population_ratio = exp(mu_weight_ratio);
real population_scaling = exp(mu_scaling);
real population_weight_direct = population_scaling * population_ratio / (1 + population_ratio);
real population_weight_social = population_scaling / (1 + population_ratio);
// Log likelihood for model comparison
vector[N] log_lik;
// Population and individual predictions
array[N] int pred_choice;
for (i in 1:N) {
// Get weights for this person
real w_direct = weight_direct[agent_id[i]];
real w_social = weight_social[agent_id[i]];
// Calculate weighted evidence
real weighted_blue1 = blue1[i] * w_direct;
real weighted_red1 = (total1[i] - blue1[i]) * w_direct;
real weighted_blue2 = blue2[i] * w_social;
real weighted_red2 = (total2[i] - blue2[i]) * w_social;
// Calculate Beta parameters
real alpha_post = alpha_prior[agent_id[i]] + weighted_blue1 + weighted_blue2;
real beta_post = beta_prior[agent_id[i]] + weighted_red1 + weighted_red2;
// Generate predictions using beta-binomial
pred_choice[i] = beta_binomial_rng(1, alpha_post, beta_post);
// Calculate log likelihood
log_lik[i] = beta_binomial_lpmf(choice[i] | 1, alpha_post, beta_post);
}
}
"
# Write the model to a file
write_stan_file(
multilevel_weighted_stan,
dir = "stan/",
basename = "W10_multilevel_weighted_beta_binomial.stan"
)## [1] "/Users/au209589/Dropbox/Teaching/AdvancedCognitiveModeling23_book/stan/W10_multilevel_weighted_beta_binomial.stan"11.22 Fitting the Multilevel Models
Now that we’ve generated data from both simple and weighted integration strategies, we can fit our two multilevel models to this data. This will allow us to:
- Evaluate our ability to recover the true parameters
- Compare the models to determine which better explains the observed decisions
- Assess whether we can correctly identify which cognitive strategy generated each agent’s data
We’ll fit both models to the full dataset, which contains a mixture of simple and weighted integration agents. This represents a realistic scenario where we don’t know in advance which strategy each individual is using.
# Fitting the Multilevel Models to Simulated Data
# We'll fit both the simple and weighted integration models to our simulated data
# Create file paths for Stan models
file_simple_ml <- file.path("stan/W10_multilevel_simple_beta_binomial.stan")
file_weighted_ml <- file.path("stan/W10_multilevel_weighted_beta_binomial.stan")
# Check if we need to regenerate model fits or load existing ones
if (regenerate_simulations) {
# Compile Stan models
mod_simple_ml <- cmdstan_model(
file_simple_ml,
cpp_options = list(stan_threads = TRUE)
)
mod_weighted_ml <- cmdstan_model(
file_weighted_ml,
cpp_options = list(stan_threads = TRUE)
)
# Fit the simple multilevel model
# This model assumes equal weights for evidence sources but allows individual scaling
cat("Fitting the simple multilevel model...\n")
fit_simple_ml <- mod_simple_ml$sample(
data = stan_data_multilevel, # Data for all agents (both types)
seed = 242, # Seed for reproducibility
chains = 2, # Number of MCMC chains
parallel_chains = 2, # Run chains in parallel
threads_per_chain = 1, # Stan threading
iter_warmup = 1000, # Warmup iterations
iter_sampling = 1000, # Sampling iterations
refresh = 100, # Progress update frequency
adapt_delta = 0.9, # Adaptation parameter for HMC
max_treedepth = 12 # Maximum tree depth for HMC
)
# Fit the weighted multilevel model
# This model allows different weights for different evidence sources
cat("Fitting the weighted multilevel model...\n")
fit_weighted_ml <- mod_weighted_ml$sample(
data = stan_data_multilevel, # Same data as simple model
seed = 143, # Different seed
chains = 2, # Number of MCMC chains
parallel_chains = 2, # Run chains in parallel
threads_per_chain = 1, # Stan threading
iter_warmup = 1000, # Warmup iterations
iter_sampling = 1000, # Sampling iterations
refresh = 100, # Progress update frequency
adapt_delta = 0.95, # Higher adapt_delta for stability
max_treedepth = 12 # Maximum tree depth for HMC
)
# Save model fits for future use
fit_simple_ml$save_object("simmodels/fit_multilevel_simple_mixed.rds")
fit_weighted_ml$save_object("simmodels/fit_multilevel_weighted_mixed.rds")
cat("Models fitted and saved.\n")
} else {
# Load existing model fits
fit_simple_ml <- readRDS("simmodels/fit_multilevel_simple_mixed.rds")
fit_weighted_ml <- readRDS("simmodels/fit_multilevel_weighted_mixed.rds")
cat("Loaded existing model fits.\n")
}## Loaded existing model fits.# Check for convergence issues
# For simple model
simple_summary <- fit_simple_ml$summary()
simple_rhat_issues <- simple_summary %>%
filter(rhat > 1.05) %>%
nrow()
# For weighted model
weighted_summary <- fit_weighted_ml$summary()
weighted_rhat_issues <- weighted_summary %>%
filter(rhat > 1.05) %>%
nrow()
# Print convergence summary
cat("Convergence check:\n")## Convergence check:cat("Simple model parameters with Rhat > 1.05:", simple_rhat_issues, "out of", nrow(simple_summary), "\n")## Simple model parameters with Rhat > 1.05: 0 out of 14484cat("Weighted model parameters with Rhat > 1.05:", weighted_rhat_issues, "out of", nrow(weighted_summary), "\n")## Weighted model parameters with Rhat > 1.05: 0 out of 14649# Extract posterior samples for key parameters
# From simple model
draws_simple <- as_draws_df(fit_simple_ml$draws())
population_scaling_simple <- mean(exp(draws_simple$mu_scaling))
population_scaling_sd_simple <- mean(draws_simple$sigma_scaling)
# From weighted model
draws_weighted <- as_draws_df(fit_weighted_ml$draws())
population_ratio_weighted <- mean(exp(draws_weighted$mu_weight_ratio))
population_scaling_weighted <- mean(exp(draws_weighted$mu_scaling))
population_ratio_sd_weighted <- mean(draws_weighted$sigma_weight_ratio)
population_scaling_sd_weighted <- mean(draws_weighted$sigma_scaling)
# Print population-level parameter estimates
cat("\nPopulation parameter estimates:\n")##
## Population parameter estimates:## Simple model:## Mean scaling factor: 2.3## SD of log scaling: 0.19## Weighted model:## Mean scaling factor: 3.29## Mean weight ratio (direct/social): 1.56## SD of log scaling: 0.18## SD of log weight ratio: 0.411.22.1 Parameter Recovery Analysis
Now that we’ve fitted both models, let’s examine how well we can recover the true individual parameters. This is a crucial step in validating our models - if we can’t recover the parameters that generated our data, we might need to refine our models or collect more data.
# Extract individual parameter estimates from both models
# For simple model (scaling factor only)
scaling_factor_simple <- matrix(NA, nrow = nrow(draws_simple), ncol = n_agents * 2)
for (j in 1:(n_agents * 2)) {
scaling_factor_simple[, j] <- draws_simple[[paste0("scaling_factor[", j, "]")]]
}
# Calculate posterior means
scaling_factor_simple_est <- colMeans(scaling_factor_simple)
# For weighted model (scaling factor and weight ratio)
scaling_factor_weighted <- matrix(NA, nrow = nrow(draws_weighted), ncol = n_agents * 2)
weight_ratio_weighted <- matrix(NA, nrow = nrow(draws_weighted), ncol = n_agents * 2)
weight_direct_weighted <- matrix(NA, nrow = nrow(draws_weighted), ncol = n_agents * 2)
weight_social_weighted <- matrix(NA, nrow = nrow(draws_weighted), ncol = n_agents * 2)
for (j in 1:(n_agents * 2)) {
scaling_factor_weighted[, j] <- draws_weighted[[paste0("scaling_factor[", j, "]")]]
weight_ratio_weighted[, j] <- draws_weighted[[paste0("weight_ratio[", j, "]")]]
weight_direct_weighted[, j] <- draws_weighted[[paste0("weight_direct[", j, "]")]]
weight_social_weighted[, j] <- draws_weighted[[paste0("weight_social[", j, "]")]]
}
# Calculate posterior means
scaling_factor_weighted_est <- colMeans(scaling_factor_weighted)
weight_ratio_weighted_est <- colMeans(weight_ratio_weighted)
weight_direct_weighted_est <- colMeans(weight_direct_weighted)
weight_social_weighted_est <- colMeans(weight_social_weighted)
# Create dataframe for recovery analysis
recovery_data <- tibble(
agent_id = 1:(n_agents * 2),
model_type = all_agents$model_type,
# True parameters
true_scaling_factor = all_agents$scaling_factor,
true_weight_ratio = all_agents$weight_ratio,
true_weight_direct = all_agents$weight_direct,
true_weight_social = all_agents$weight_social,
# Estimated from simple model
est_scaling_simple = scaling_factor_simple_est,
# Estimated from weighted model
est_scaling_weighted = scaling_factor_weighted_est,
est_ratio_weighted = weight_ratio_weighted_est,
est_direct_weighted = weight_direct_weighted_est,
est_social_weighted = weight_social_weighted_est
)
# Calculate recovery accuracy metrics
recovery_data <- recovery_data %>%
mutate(
# Error in scaling factor estimates
error_scaling_simple = est_scaling_simple - true_scaling_factor,
pct_error_scaling_simple = 100 * error_scaling_simple / true_scaling_factor,
error_scaling_weighted = est_scaling_weighted - true_scaling_factor,
pct_error_scaling_weighted = 100 * error_scaling_weighted / true_scaling_factor,
# Error in weight ratio estimates (only for weighted model)
error_ratio_weighted = est_ratio_weighted - true_weight_ratio,
pct_error_ratio_weighted = 100 * error_ratio_weighted / true_weight_ratio,
# Error in direct/social weight estimates
error_direct_weighted = est_direct_weighted - true_weight_direct,
pct_error_direct_weighted = 100 * error_direct_weighted / true_weight_direct,
error_social_weighted = est_social_weighted - true_weight_social,
pct_error_social_weighted = 100 * error_social_weighted / true_weight_social
)
# Summarize recovery errors by agent type
recovery_summary <- recovery_data %>%
group_by(model_type) %>%
summarize(
# Simple model scaling recovery
mean_abs_error_scaling_simple = mean(abs(error_scaling_simple)),
mean_abs_pct_error_scaling_simple = mean(abs(pct_error_scaling_simple)),
# Weighted model param recovery
mean_abs_error_scaling_weighted = mean(abs(error_scaling_weighted)),
mean_abs_pct_error_scaling_weighted = mean(abs(pct_error_scaling_weighted)),
mean_abs_error_ratio_weighted = mean(abs(error_ratio_weighted)),
mean_abs_pct_error_ratio_weighted = mean(abs(pct_error_ratio_weighted)),
mean_abs_error_direct_weighted = mean(abs(error_direct_weighted)),
mean_abs_pct_error_direct_weighted = mean(abs(pct_error_direct_weighted)),
mean_abs_error_social_weighted = mean(abs(error_social_weighted)),
mean_abs_pct_error_social_weighted = mean(abs(pct_error_social_weighted)),
.groups = "drop"
)
# Print recovery summary
knitr::kable(recovery_summary, digits = 2, caption = "Parameter Recovery Accuracy by Agent Type")| model_type | mean_abs_error_scaling_simple | mean_abs_pct_error_scaling_simple | mean_abs_error_scaling_weighted | mean_abs_pct_error_scaling_weighted | mean_abs_error_ratio_weighted | mean_abs_pct_error_ratio_weighted | mean_abs_error_direct_weighted | mean_abs_pct_error_direct_weighted | mean_abs_error_social_weighted | mean_abs_pct_error_social_weighted |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| simple | 0.80 | 24.90 | 0.82 | 33.42 | 0.45 | 45.02 | 0.57 | 47.45 | 0.35 | 25.37 |
| weighted | 2.15 | 44.02 | 1.24 | 24.22 | 1.49 | 37.50 | 1.27 | 35.13 | 0.41 | 45.28 |
# Create visualizations of parameter recovery
# 1. Scaling factor recovery
p1 <- ggplot(recovery_data, aes(x = true_scaling_factor, y = est_scaling_simple, color = model_type)) +
geom_point(size = 3, alpha = 0.7) +
geom_abline(intercept = 0, slope = 1, linetype = "dashed") +
labs(
title = "Scaling Factor Recovery (Simple Model)",
subtitle = "How well can the simple model recover the true scaling factors?",
x = "True Scaling Factor",
y = "Estimated Scaling Factor",
color = "Agent Type"
) +
theme_minimal()
p2 <- ggplot(recovery_data, aes(x = true_scaling_factor, y = est_scaling_weighted, color = model_type)) +
geom_point(size = 3, alpha = 0.7) +
geom_abline(intercept = 0, slope = 1, linetype = "dashed") +
labs(
title = "Scaling Factor Recovery (Weighted Model)",
subtitle = "How well can the weighted model recover the true scaling factors?",
x = "True Scaling Factor",
y = "Estimated Scaling Factor",
color = "Agent Type"
) +
theme_minimal()
# 2. Weight ratio recovery (weighted model only)
p3 <- ggplot(recovery_data, aes(x = true_weight_ratio, y = est_ratio_weighted, color = model_type)) +
geom_point(size = 3, alpha = 0.7) +
geom_abline(intercept = 0, slope = 1, linetype = "dashed") +
labs(
title = "Weight Ratio Recovery (Weighted Model)",
subtitle = "How well can the weighted model recover the true weight ratios?",
x = "True Weight Ratio (Direct/Social)",
y = "Estimated Weight Ratio",
color = "Agent Type"
) +
theme_minimal()
# Arrange plots
recovery_plots <- p1 + p2 + p3 + plot_layout(ncol = 2)
print(recovery_plots)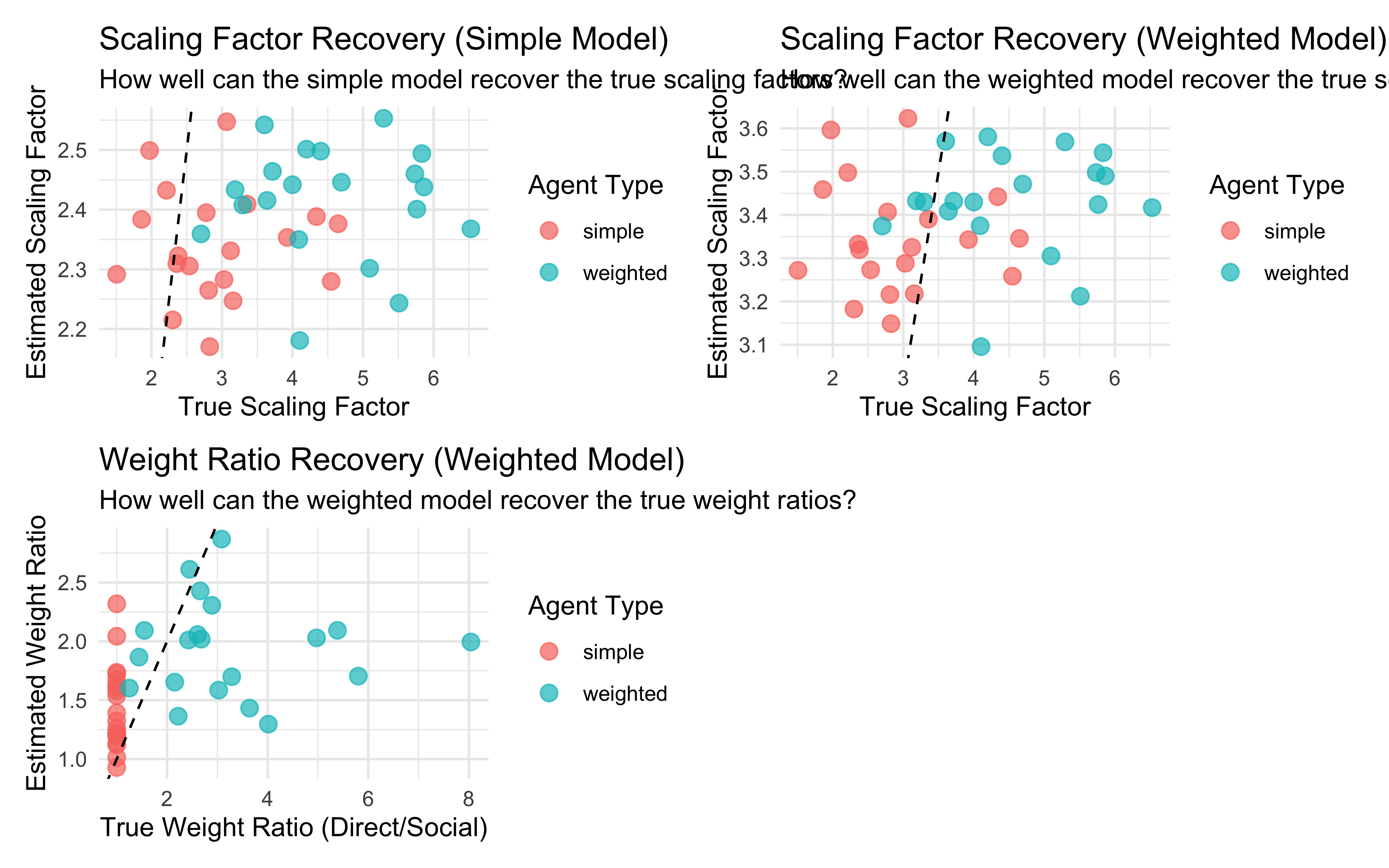
11.22.2 Model Comparison
Now that we’ve fitted both models, we can formally compare them to see which better explains the observed data. We’ll use Leave-One-Out Cross-Validation (LOO-CV) to estimate each model’s predictive accuracy.
In a real application, we wouldn’t know in advance whether individuals use simple or weighted integration strategies. Model comparison helps us determine which cognitive model is more consistent with observed behavior.
# Calculate LOO-CV for model comparison
# This evaluates how well each model predicts held-out data
# For simple model
loo_simple <- fit_simple_ml$loo()
# For weighted model
loo_weighted <- fit_weighted_ml$loo()
# Compare models
loo_comparison <- loo_compare(loo_simple, loo_weighted)
print(loo_comparison)## elpd_diff se_diff
## model2 0.0 0.0
## model1 -21.6 6.7# Calculate model weights
model_weights <- loo_model_weights(list(
"Simple Integration" = loo_simple,
"Weighted Integration" = loo_weighted
))
# Print model weights
print(model_weights)## Method: stacking
## ------
## weight
## Simple Integration 0.028
## Weighted Integration 0.972# Create a visualization of model comparison
model_comp_data <- tibble(
model = names(model_weights),
weight = as.numeric(model_weights)
)
p_model_comp <- ggplot(model_comp_data, aes(x = model, y = weight, fill = model)) +
geom_col() +
geom_text(aes(label = scales::percent(weight, accuracy = 0.1)),
vjust = -0.5, size = 5) +
labs(
title = "Model Comparison Using LOO-CV",
subtitle = "Higher weights indicate better predictive performance",
x = NULL,
y = "Model Weight"
) +
scale_fill_brewer(palette = "Set1") +
theme_minimal() +
theme(legend.position = "none")
print(p_model_comp)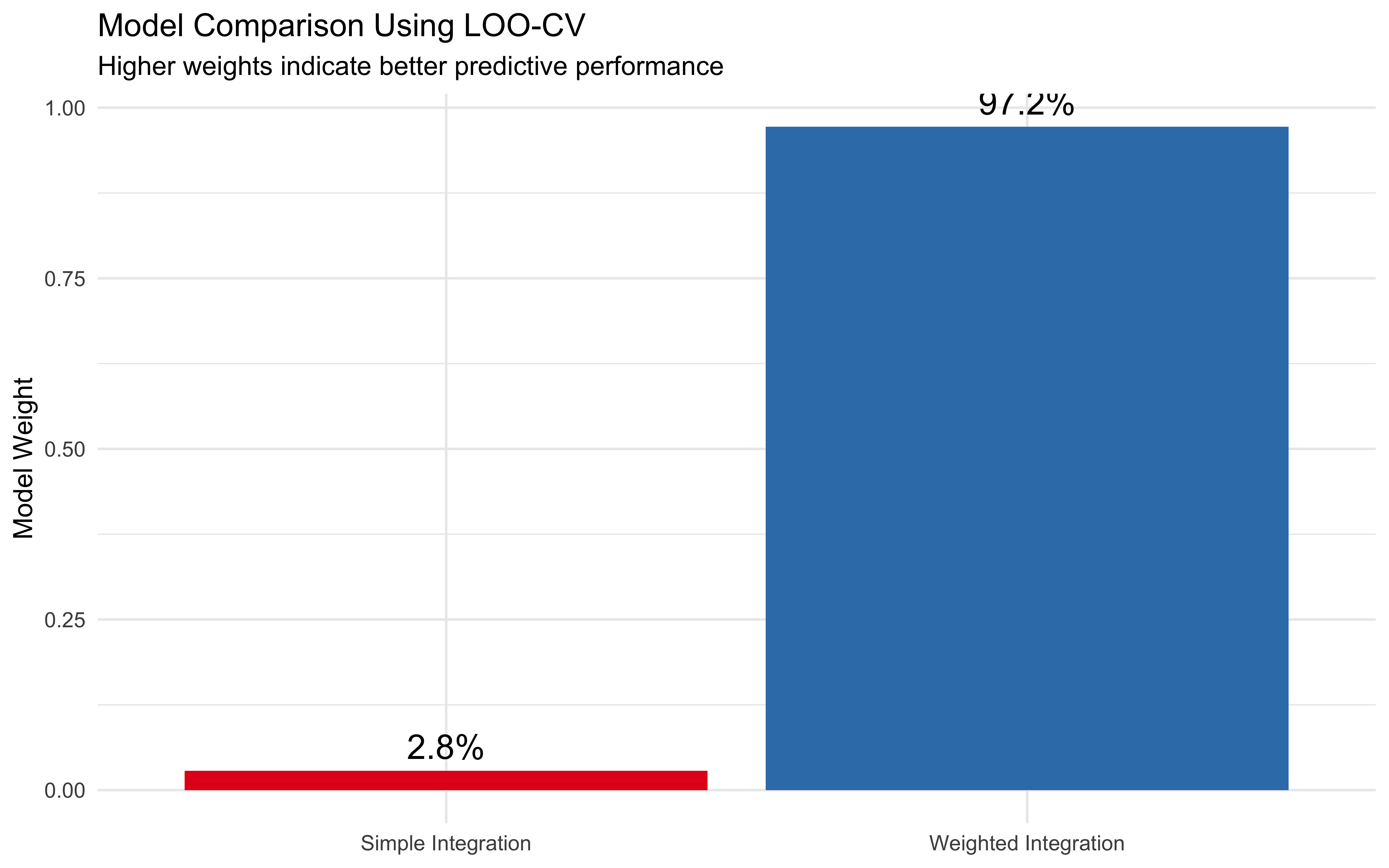
# Compare model performance by agent type
# Calculate pointwise ELPD values for each model
elpd_simple <- loo_simple$pointwise[, "elpd_loo"]
elpd_weighted <- loo_weighted$pointwise[, "elpd_loo"]
# Aggregate by agent
elpd_by_agent <- multilevel_sim_data %>%
dplyr::select(agent_id, model_type) %>%
distinct() %>%
mutate(
elpd_simple = NA_real_,
elpd_weighted = NA_real_
)
# Calculate ELPD sums by agent
for (j in 1:nrow(elpd_by_agent)) {
agent <- elpd_by_agent$agent_id[j]
# Find rows for this agent
agent_rows <- which(multilevel_sim_data$agent_id == agent)
# Sum ELPD values for this agent
elpd_by_agent$elpd_simple[j] <- sum(elpd_simple[agent_rows])
elpd_by_agent$elpd_weighted[j] <- sum(elpd_weighted[agent_rows])
}
# Calculate ELPD difference (positive = weighted model is better)
elpd_by_agent <- elpd_by_agent %>%
mutate(
elpd_diff = elpd_weighted - elpd_simple,
better_model = ifelse(elpd_diff > 0, "Weighted", "Simple")
)
# Create visualization of model preference by agent type
p_agent_comp <- ggplot(elpd_by_agent, aes(x = agent_id, y = elpd_diff, color = model_type)) +
geom_point() +
geom_hline(yintercept = 0, linetype = "dashed") +
labs(
title = "Model Preference by Agent Type",
subtitle = "Positive values favor the weighted model; negative values favor the simple model",
x = "True Agent Type",
y = "ELPD Difference (Weighted - Simple)",
color = "Preferred Model"
) +
theme_minimal()
print(p_agent_comp)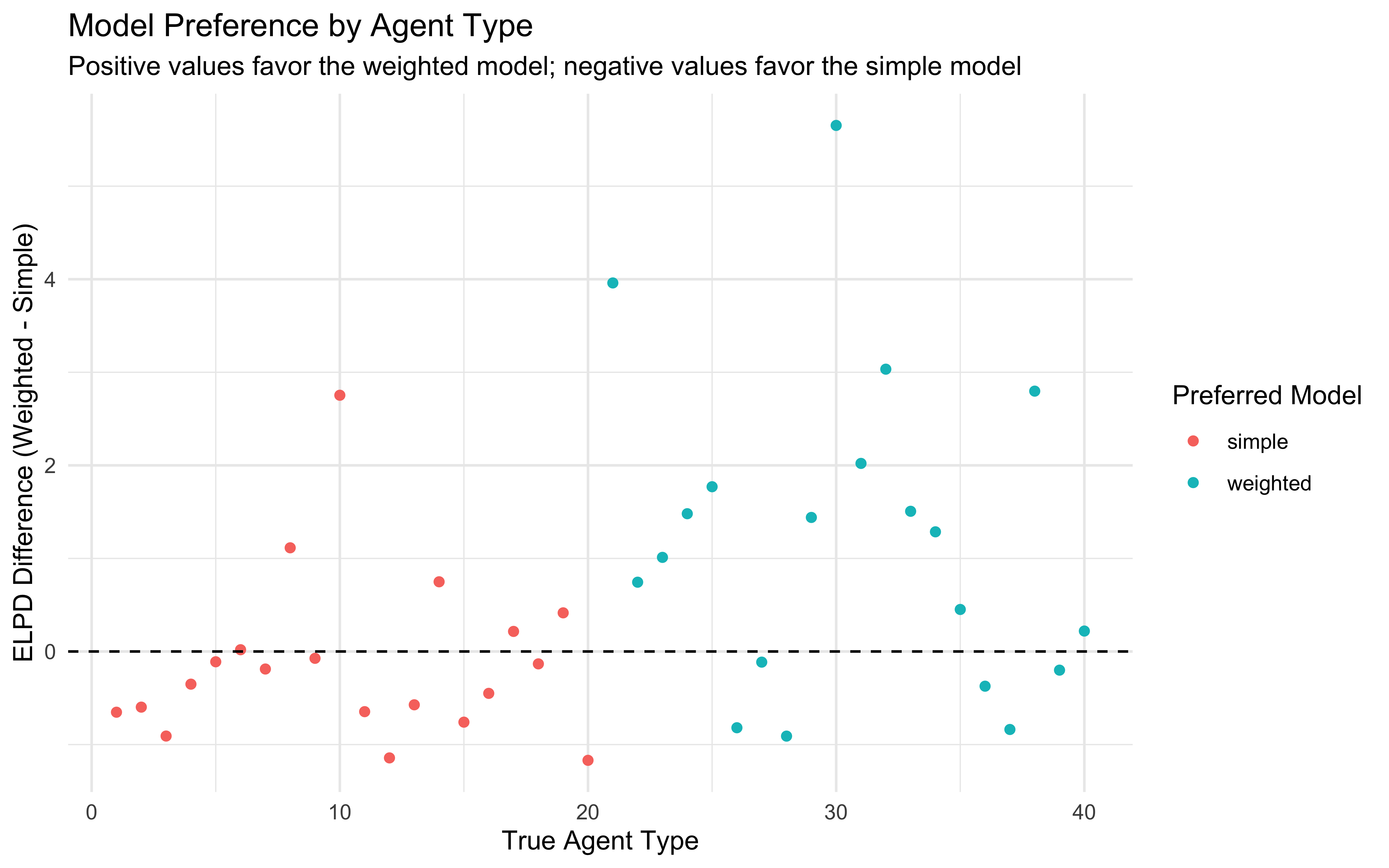
# Calculate classification accuracy
# How often does the better-fitting model match the true generating model?
classification <- elpd_by_agent %>%
mutate(
# For simple agents, the simple model should be better
correct_classification = case_when(
model_type == "simple" & better_model == "Simple" ~ TRUE,
model_type == "weighted" & better_model == "Weighted" ~ TRUE,
TRUE ~ FALSE
)
)
# Calculate overall accuracy and by agent type
overall_accuracy <- mean(classification$correct_classification)
accuracy_by_type <- classification %>%
group_by(model_type) %>%
summarize(
n = n(),
correct = sum(correct_classification),
accuracy = correct / n,
.groups = "drop"
)
# Print classification results
cat("\nModel Classification Accuracy:\n")##
## Model Classification Accuracy:## Overall accuracy: 70%##
##
## Table: (\#tab:unnamed-chunk-64)Classification Accuracy by Agent Type
##
## |model_type | n| correct| accuracy|
## |:----------|--:|-------:|--------:|
## |simple | 20| 14| 0.7|
## |weighted | 20| 14| 0.7|11.23 Dynamic Bayesian Evidence Integration: Sequential Updating Models
In real-world learning scenarios, people continuously update their beliefs as they gather new evidence. While our previous models considered decision-making based on static evidence, a more realistic approach is to incorporate sequential updating where beliefs evolve over time. Let’s develop an extension of our Bayesian evidence integration models that captures how agents dynamically update their beliefs across trials.
11.23.1 Sequential Bayesian Updating: The Theoretical Framework
In sequential Bayesian updating, an agent’s posterior belief from one trial becomes the prior for the next trial. This creates a continuous learning process where the agent’s beliefs evolve over time based on observed evidence. The key components of a sequential updating model are:
Initial prior belief - The agent’s belief before encountering any evidence
Trial-by-trial updating - How beliefs are updated after each new piece of evidence
Response mechanism - How updated beliefs translate into observable choices
Let’s implement this framework in Stan, starting with the single-agent version and then extending to a multilevel model.
11.23.2 Single-Agent Sequential Updating Model
# Stan code for a sequential Bayesian updating model
sequential_updating_stan <- "
// Sequential Bayesian Updating Model
// This model tracks how an agent updates beliefs across a sequence of trials
data {
int<lower=1> T; // Number of trials
array[T] int<lower=0, upper=1> choice; // Choices (0=red, 1=blue)
array[T] int<lower=0> blue1; // Direct evidence (blue marbles) on each trial
array[T] int<lower=0> total1; // Total direct evidence on each trial
array[T] int<lower=0> blue2; // Social evidence (blue signals) on each trial
array[T] int<lower=0> total2; // Total social evidence on each trial
}
parameters {
real<lower=0> total_weight; // Overall weight given to evidence
real<lower=0, upper=1> weight_prop; // Proportion of weight for direct evidence
real<lower=0> learning; // Learning rate parameter
}
transformed parameters {
// Calculate weights for each evidence source
real weight_direct = total_weight * weight_prop;
real weight_social = total_weight * (1 - weight_prop);
// Variables to track belief updating across trials
vector<lower=0, upper=1>[T] belief; // Belief in blue on each trial
vector<lower=0>[T] alpha_param; // Beta distribution alpha parameter
vector<lower=0>[T] beta_param; // Beta distribution beta parameter
// Initial belief parameters (uniform prior)
alpha_param[1] = 1.0;
beta_param[1] = 1.0;
// Calculate belief for first trial
belief[1] = alpha_param[1] / (alpha_param[1] + beta_param[1]);
// Update beliefs across trials
for (t in 2:T) {
// Calculate weighted evidence from previous trial
real weighted_blue1 = blue1[t-1] * weight_direct;
real weighted_red1 = (total1[t-1] - blue1[t-1]) * weight_direct;
real weighted_blue2 = blue2[t-1] * weight_social;
real weighted_red2 = (total2[t-1] - blue2[t-1]) * weight_social;
// Update belief with learning rate
// alpha controls how much new evidence affects the belief
alpha_param[t] = alpha_param[t-1] + learning * (weighted_blue1 + weighted_blue2);
beta_param[t] = beta_param[t-1] + learning * (weighted_red1 + weighted_red2);
// Calculate updated belief
belief[t] = alpha_param[t] / (alpha_param[t] + beta_param[t]);
}
}
model {
// Priors for parameters
target += lognormal_lpdf(total_weight | 0, 0.5); // Prior centered around 1.0
target += beta_lpdf(weight_prop | 1, 1); // Uniform prior on proportion
target += lognormal_lpdf(alpha | -1, 0.5); // Prior on learning rate (typically < 1)
// Likelihood
for (t in 1:T) {
// Model choice as a function of current belief
target += bernoulli_lpmf(choice[t] | belief[t]);
}
}
generated quantities {
// Log likelihood for model comparison
vector[T] log_lik;
// Posterior predictions
array[T] int pred_choice;
for (t in 1:T) {
// Generate predicted choices
pred_choice[t] = bernoulli_rng(belief[t]);
// Calculate log likelihood
log_lik[t] = bernoulli_lpmf(choice[t] | belief[t]);
}
}
"
# Write the model to a file
write_stan_file(
sequential_updating_stan,
dir = "stan/",
basename = "10_sequential_updating.stan"
)## [1] "/Users/au209589/Dropbox/Teaching/AdvancedCognitiveModeling23_book/stan/10_sequential_updating.stan"11.23.3 Multilevel Sequential Updating Model
Now let’s extend this to a multilevel model that captures individual differences in learning rates and evidence weighting:
# Stan code for a multilevel sequential Bayesian updating model
multilevel_sequential_stan <- "
// Multilevel Sequential Bayesian Updating Model
// This model captures individual differences in sequential belief updating
data {
int<lower=1> N; // Total number of observations
int<lower=1> J; // Number of agents
int<lower=1> T; // Maximum number of trials per agent
array[N] int<lower=1, upper=J> agent_id; // Agent ID for each observation
array[N] int<lower=1, upper=T> trial_id; // Trial number for each observation
array[N] int<lower=0, upper=1> choice; // Choices (0=red, 1=blue)
array[N] int<lower=0> blue1; // Direct evidence (blue marbles)
array[N] int<lower=0> total1; // Total direct evidence
array[N] int<lower=0> blue2; // Social evidence (blue signals)
array[N] int<lower=0> total2; // Total social evidence
// Additional data for tracking trial sequences
array[J] int<lower=1, upper=T> trials_per_agent; // Number of trials for each agent
}
parameters {
// Population-level parameters
real mu_total_weight; // Population mean log total weight
real mu_weight_prop_logit; // Population mean logit weight proportion
real mu_learning_log; // Population mean log learning rate
// Population-level standard deviations
vector<lower=0>[3] tau; // SDs for [total_weight, weight_prop, alpha]
// Correlation matrix for individual parameters (optional)
cholesky_factor_corr[3] L_Omega; // Cholesky factor of correlation matrix
// Individual-level variations (non-centered parameterization)
matrix[3, J] z; // Standardized individual parameters
}
transformed parameters {
// Individual-level parameters
vector<lower=0>[J] total_weight; // Total evidence weight for each agent
vector<lower=0, upper=1>[J] weight_prop; // Weight proportion for each agent
vector<lower=0>[J] learning; // Learning rate for each agent
vector<lower=0>[J] weight_direct; // Direct evidence weight for each agent
vector<lower=0>[J] weight_social; // Social evidence weight for each agent
// Individual beliefs for each trial
// We'll use a ragged structure due to varying trial counts
array[J, T] real belief; // Belief in blue for each agent on each trial
// Transform parameters to natural scale
matrix[3, J] theta = diag_pre_multiply(tau, L_Omega) * z; // Non-centered parameterization
for (j in 1:J) {
// Transform individual parameters to appropriate scales
total_weight[j] = exp(mu_total_weight + theta[1, j]);
weight_prop[j] = inv_logit(mu_weight_prop_logit + theta[2, j]);
learning[j] = exp(mu_learning_log + theta[3, j]);
// Calculate derived weights
weight_direct[j] = total_weight[j] * weight_prop[j];
weight_social[j] = total_weight[j] * (1 - weight_prop[j]);
// Initialize belief tracking for each agent
real alpha_param = 1.0; // Initial beta distribution parameters
real beta_param = 1.0;
// Calculate initial belief
belief[j, 1] = alpha_param / (alpha_param + beta_param);
// Process trials for this agent (skipping the first trial since we initialized it above)
for (t in 2:trials_per_agent[j]) {
// Find the previous trial's data for this agent
int prev_idx = 0;
// Search for previous trial (this is a simplification; more efficient approaches exist)
for (i in 1:N) {
if (agent_id[i] == j && trial_id[i] == t-1) {
prev_idx = i;
break;
}
}
if (prev_idx > 0) {
// Calculate weighted evidence from previous trial
real weighted_blue1 = blue1[prev_idx] * weight_direct[j];
real weighted_red1 = (total1[prev_idx] - blue1[prev_idx]) * weight_direct[j];
real weighted_blue2 = blue2[prev_idx] * weight_social[j];
real weighted_red2 = (total2[prev_idx] - blue2[prev_idx]) * weight_social[j];
// Update belief parameters with learning rate
alpha_param = alpha_param + alpha[j] * (weighted_blue1 + weighted_blue2);
beta_param = beta_param + alpha[j] * (weighted_red1 + weighted_red2);
}
// Calculate updated belief
belief[j, t] = alpha_param / (alpha_param + beta_param);
}
}
}
model {
// Priors for population parameters
target += normal_lpdf(mu_total_weight | 0, 1); // Population log total weight
target += normal_lpdf(mu_weight_prop_logit | 0, 1); // Population logit weight proportion
target += normal_lpdf(mu_alpha_log | -1, 1); // Population log learning rate
// Priors for population standard deviations
target += exponential_lpdf(tau | 2); // Conservative prior for SDs
// Prior for correlation matrix
target += lkj_corr_cholesky_lpdf(L_Omega | 2); // LKJ prior on correlations
// Prior for standardized individual parameters
target += std_normal_lpdf(to_vector(z)); // Standard normal prior on z-scores
// Likelihood
for (i in 1:N) {
int j = agent_id[i]; // Agent ID
int t = trial_id[i]; // Trial number
// Model choice as a function of current belief
target += bernoulli_lpmf(choice[i] | belief[j, t]);
}
}
generated quantities {
// Transform population parameters to natural scale for interpretation
real<lower=0> pop_total_weight = exp(mu_total_weight);
real<lower=0, upper=1> pop_weight_prop = inv_logit(mu_weight_prop_logit);
real<lower=0> pop_alpha = exp(mu_alpha_log);
real<lower=0> pop_weight_direct = pop_total_weight * pop_weight_prop;
real<lower=0> pop_weight_social = pop_total_weight * (1 - pop_weight_prop);
// Correlation matrix for individual differences
matrix[3, 3] Omega = multiply_lower_tri_self_transpose(L_Omega);
// Log likelihood for model comparison
vector[N] log_lik;
// Posterior predictions
array[N] int pred_choice;
for (i in 1:N) {
int j = agent_id[i];
int t = trial_id[i];
// Generate predicted choices
pred_choice[i] = bernoulli_rng(belief[j, t]);
// Calculate log likelihood
log_lik[i] = bernoulli_lpmf(choice[i] | belief[j, t]);
}
}
"
# Write the model to a file
write_stan_file(
multilevel_sequential_stan,
dir = "stan/",
basename = "10_multilevel_sequential_updating.stan"
)## [1] "/Users/au209589/Dropbox/Teaching/AdvancedCognitiveModeling23_book/stan/10_multilevel_sequential_updating.stan"11.23.4 Generating Data for the Sequential Model
To test our sequential updating model, we need to generate data that involves a sequence of decisions where beliefs are updated over time. Here’s how we can simulate such data:
# Function to simulate sequential updating agent behavior
simulate_sequential_agent <- function(n_trials,
weight_direct,
weight_social,
learning_rate,
p_blue_transitions = c(0.7, 0.3)) {
# p_blue_transitions = c(p(blue|previous=blue), p(blue|previous=red))
# This creates a Markov process for the underlying jar probabilities
# Initialize results
results <- tibble(
trial = 1:n_trials,
true_p_blue = NA_real_, # True probability of blue
jar_state = NA_integer_, # Which jar: 1=mostly blue, 0=mostly red
blue1 = NA_integer_, # Direct evidence (blue marbles)
total1 = NA_integer_, # Total direct evidence
blue2 = NA_integer_, # Social evidence (blue signals)
total2 = NA_integer_, # Total social evidence
belief = NA_real_, # Agent's belief that next marble is blue
choice = NA_integer_ # Agent's choice (1=blue, 0=red)
)
# Initialize belief tracking variables
alpha_param <- 1.0
beta_param <- 1.0
# Set initial jar state randomly
results$jar_state[1] <- rbinom(1, 1, 0.5)
results$true_p_blue[1] <- ifelse(results$jar_state[1] == 1, 0.8, 0.2)
# Generate the sequence of jar states (Markov process)
for (t in 2:n_trials) {
# Transition probability depends on previous state
p_blue <- p_blue_transitions[2 - results$jar_state[t-1]]
results$jar_state[t] <- rbinom(1, 1, p_blue)
results$true_p_blue[t] <- ifelse(results$jar_state[t] == 1, 0.8, 0.2)
}
# Generate evidence and choices for each trial
for (t in 1:n_trials) {
# Generate direct evidence (8 marbles per trial)
results$total1[t] <- 8
results$blue1[t] <- rbinom(1, results$total1[t], results$true_p_blue[t])
# Generate social evidence (3 signals per trial)
results$total2[t] <- 3
results$blue2[t] <- rbinom(1, results$total2[t], results$true_p_blue[t])
# Calculate current belief based on previous evidence
if (t == 1) {
# First trial - start with uniform prior
results$belief[t] <- 0.5
} else {
# Calculate weighted evidence from previous trial
weighted_blue1 <- results$blue1[t-1] * weight_direct
weighted_red1 <- (results$total1[t-1] - results$blue1[t-1]) * weight_direct
weighted_blue2 <- results$blue2[t-1] * weight_social
weighted_red2 <- (results$total2[t-1] - results$blue2[t-1]) * weight_social
# Update belief parameters with learning rate
alpha_param <- alpha_param + learning_rate * (weighted_blue1 + weighted_blue2)
beta_param <- beta_param + learning_rate * (weighted_red1 + weighted_red2)
# Calculate updated belief
results$belief[t] <- alpha_param / (alpha_param + beta_param)
}
# Generate choice based on current belief
results$choice[t] <- rbinom(1, 1, results$belief[t])
}
return(results)
}
# Simulate data for multiple agents with different parameters
set.seed(42)
# Number of agents and trials
n_agents <- 20
n_trials <- 50
# Create agent parameters
agent_params <- tibble(
agent_id = 1:n_agents,
# Generate random parameters
weight_direct = rlnorm(n_agents, meanlog = 0, sdlog = 0.3),
weight_social = rlnorm(n_agents, meanlog = -0.2, sdlog = 0.3),
learning_rate = rlnorm(n_agents, meanlog = -1, sdlog = 0.5) # Typically < 1
)
# Simulate data for all agents
sequential_sim_data <- map_dfr(1:n_agents, function(i) {
agent_data <- simulate_sequential_agent(
n_trials = n_trials,
weight_direct = agent_params$weight_direct[i],
weight_social = agent_params$weight_social[i],
learning_rate = agent_params$learning_rate[i]
)
# Add agent ID
agent_data$agent_id <- i
return(agent_data)
})
# View data summary
sequential_summary <- sequential_sim_data %>%
group_by(agent_id) %>%
summarize(
n_trials = n(),
mean_belief = mean(belief),
prop_blue_choice = mean(choice),
accuracy = mean(choice == jar_state),
.groups = "drop"
)
# Join with true parameters
sequential_summary <- sequential_summary %>%
left_join(agent_params, by = "agent_id")
# Print summary
head(sequential_summary)## # A tibble: 6 × 8
## agent_id n_trials mean_belief prop_blue_choice accuracy weight_direct weight_social
## <int> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 1 50 0.497 0.58 0.4 1.51 0.747
## 2 2 50 0.460 0.46 0.52 0.844 0.480
## 3 3 50 0.491 0.54 0.42 1.12 0.778
## 4 4 50 0.421 0.44 0.56 1.21 1.18
## 5 5 50 0.493 0.46 0.54 1.13 1.45
## 6 6 50 0.586 0.58 0.46 0.969 0.720
## # ℹ 1 more variable: learning_rate <dbl># Visualize belief updating for a few agents
selected_agents <- c(1, 5, 10)
p_belief_updating <- sequential_sim_data %>%
filter(agent_id %in% selected_agents) %>%
ggplot(aes(x = trial, y = belief, color = factor(agent_id), group = agent_id)) +
geom_line(size = 1) +
geom_point(aes(shape = factor(jar_state)), size = 3) +
scale_shape_manual(values = c("0" = 16, "1" = 17), labels = c("Mostly Red Jar", "Mostly Blue Jar")) +
ylim(0, 1) +
labs(
title = "Sequential Belief Updating",
subtitle = "Belief evolution across trials with changing jar probabilities",
x = "Trial",
y = "Belief (Probability of Blue)",
color = "Agent ID",
shape = "True Jar State"
) +
theme_minimal()
# Display the plot
print(p_belief_updating)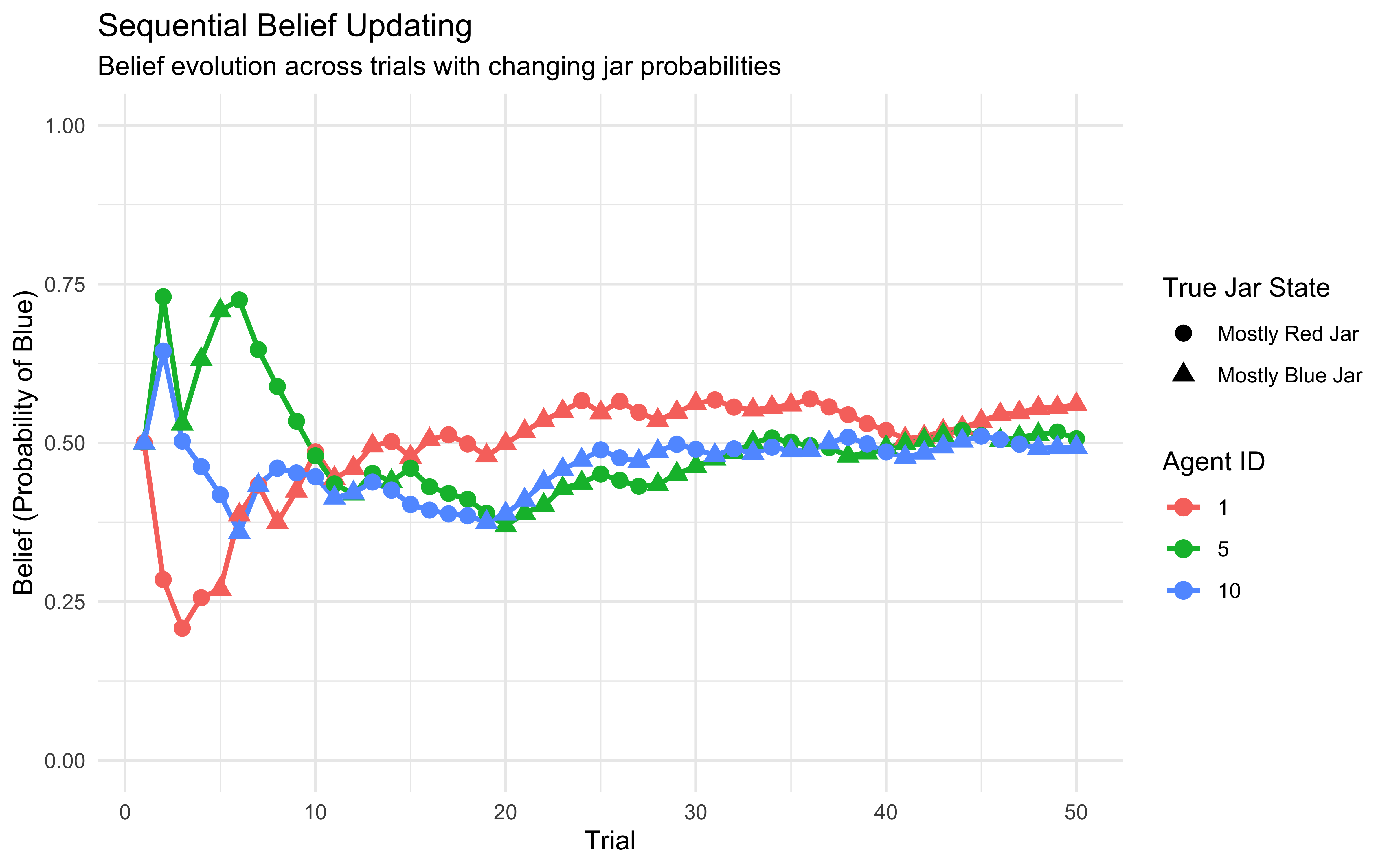
# Prepare data for Stan fitting
stan_data_sequential <- list(
N = nrow(sequential_sim_data),
J = n_agents,
T = n_trials,
agent_id = sequential_sim_data$agent_id,
trial_id = sequential_sim_data$trial,
choice = sequential_sim_data$choice,
blue1 = sequential_sim_data$blue1,
total1 = sequential_sim_data$total1,
blue2 = sequential_sim_data$blue2,
total2 = sequential_sim_data$total2,
trials_per_agent = rep(n_trials, n_agents)
)11.23.5 Fitting and Evaluating the Sequential Models
Now we can fit the models to our simulated data:
# Check if we need to regenerate model fits
if (regenerate_simulations) {
# Compile Stan models
mod_seq_single <- cmdstan_model(
file.path("stan/10_sequential_updating.stan"),
cpp_options = list(stan_threads = TRUE)
)
mod_seq_multilevel <- cmdstan_model(
file.path("stan/10_multilevel_sequential_updating.stan"),
cpp_options = list(stan_threads = TRUE)
)
# Fit the single-agent model to one agent's data
# For demonstration, we'll use the first agent
agent1_data <- filter(sequential_sim_data, agent_id == 1)
stan_data_single <- list(
T = nrow(agent1_data),
choice = agent1_data$choice,
blue1 = agent1_data$blue1,
total1 = agent1_data$total1,
blue2 = agent1_data$blue2,
total2 = agent1_data$total2
)
fit_seq_single <- mod_seq_single$sample(
data = stan_data_single,
seed = 42,
chains = 2,
parallel_chains = 2,
threads_per_chain = 1,
iter_warmup = 1000,
iter_sampling = 1000,
refresh = 200,
adapt_delta = 0.9
)
# Fit the multilevel model to all agents' data
fit_seq_multilevel <- mod_seq_multilevel$sample(
data = stan_data_sequential,
seed = 43,
chains = 2,
parallel_chains = 2,
iter_warmup = 1000,
iter_sampling = 1000,
threads_per_chain = 1,
refresh = 200,
adapt_delta = 0.95
)
# Save model fits
fit_seq_single$save_object("simmodels/fit_sequential_single.rds")
fit_seq_multilevel$save_object("simmodels/fit_sequential_multilevel.rds")
cat("Models fitted and saved.\n")
} else {
# Load existing model fits
fit_seq_single <- readRDS("simmodels/fit_sequential_single.rds")
fit_seq_multilevel <- readRDS("simmodels/fit_sequential_multilevel.rds")
cat("Loaded existing model fits.\n")
}## Loaded existing model fits.## Checking convergence for single-agent model:## # A tibble: 3 × 10
## variable mean median sd mad q5 q95 rhat ess_bulk ess_tail
## <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 total_weight 1.03 0.895 0.576 0.428 0.415 2.12 1.00 1650. 1273.
## 2 weight_prop 0.500 0.498 0.285 0.369 0.0646 0.950 1.00 1986. 1225.
## 3 alpha 0.369 0.325 0.193 0.166 0.144 0.751 1.00 1802. 1400.##
## Checking convergence for multilevel model (population parameters):## # A tibble: 3 × 10
## variable mean median sd mad q5 q95 rhat ess_bulk ess_tail
## <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 pop_total_weight 1.89 1.31 2.49 1.01 0.342 5.10 1.00 2640. 1624.
## 2 pop_weight_prop 0.660 0.672 0.150 0.164 0.391 0.884 0.999 3008. 1583.
## 3 pop_alpha 0.626 0.456 0.601 0.354 0.124 1.73 0.999 2611. 1643.# Extract posterior samples
draws_seq_single <- as_draws_df(fit_seq_single$draws())
draws_seq_multilevel <- as_draws_df(fit_seq_multilevel$draws())
# Examine parameter recovery for the single agent
agent1_params <- agent_params %>% filter(agent_id == 1)
agent1_recovery <- tibble(
parameter = c("weight_direct", "weight_social", "learning_rate"),
true_value = c(
agent1_params$weight_direct,
agent1_params$weight_social,
agent1_params$learning_rate
),
estimated = c(
mean(draws_seq_single$weight_direct),
mean(draws_seq_single$weight_social),
mean(draws_seq_single$alpha)
),
error = estimated - true_value,
pct_error = 100 * error / true_value
)
# Print recovery results
cat("\nParameter recovery for Agent 1:\n")##
## Parameter recovery for Agent 1:## # A tibble: 3 × 5
## parameter true_value estimated error pct_error
## <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 weight_direct 1.51 0.522 -0.987 -65.4
## 2 weight_social 0.747 0.506 -0.241 -32.3
## 3 learning_rate 0.408 0.369 -0.0387 -9.49# Evaluate population-level recovery
pop_recovery <- tibble(
parameter = c("mean_weight_direct", "mean_weight_social", "mean_learning_rate"),
true_value = c(
mean(agent_params$weight_direct),
mean(agent_params$weight_social),
mean(agent_params$learning_rate)
),
estimated = c(
mean(draws_seq_multilevel$pop_weight_direct),
mean(draws_seq_multilevel$pop_weight_social),
mean(draws_seq_multilevel$pop_alpha)
),
error = estimated - true_value,
pct_error = 100 * error / true_value
)
# Print population recovery results
cat("\nPopulation parameter recovery:\n")##
## Population parameter recovery:## # A tibble: 3 × 5
## parameter true_value estimated error pct_error
## <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 mean_weight_direct 1.13 1.23 0.0945 8.33
## 2 mean_weight_social 0.795 0.657 -0.138 -17.3
## 3 mean_learning_rate 0.409 0.626 0.218 53.3# Extract individual parameter estimates
n_chains <- length(unique(draws_seq_multilevel$.chain))
n_iterations <- nrow(draws_seq_multilevel) / n_chains
n_samples <- n_chains * n_iterations
weight_direct_samples <- matrix(NA, nrow = n_samples, ncol = n_agents)
weight_social_samples <- matrix(NA, nrow = n_samples, ncol = n_agents)
alpha_samples <- matrix(NA, nrow = n_samples, ncol = n_agents)
for (j in 1:n_agents) {
weight_direct_samples[, j] <- draws_seq_multilevel[[paste0("weight_direct[", j, "]")]]
weight_social_samples[, j] <- draws_seq_multilevel[[paste0("weight_social[", j, "]")]]
alpha_samples[, j] <- draws_seq_multilevel[[paste0("alpha[", j, "]")]]
}
# Calculate posterior means
weight_direct_est <- colMeans(weight_direct_samples)
weight_social_est <- colMeans(weight_social_samples)
alpha_est <- colMeans(alpha_samples)
# Create recovery data for all agents
recovery_data <- tibble(
agent_id = 1:n_agents,
# True parameters
true_weight_direct = agent_params$weight_direct,
true_weight_social = agent_params$weight_social,
true_learning_rate = agent_params$learning_rate,
# Estimated parameters
est_weight_direct = weight_direct_est,
est_weight_social = weight_social_est,
est_learning_rate = alpha_est
)
# Calculate recovery metrics
recovery_data <- recovery_data %>%
mutate(
error_direct = est_weight_direct - true_weight_direct,
error_social = est_weight_social - true_weight_social,
error_learning = est_learning_rate - true_learning_rate,
pct_error_direct = 100 * error_direct / true_weight_direct,
pct_error_social = 100 * error_social / true_weight_social,
pct_error_learning = 100 * error_learning / true_learning_rate
)
# Create recovery plots
p_recovery <- recovery_data %>%
pivot_longer(
cols = c(starts_with("true_"), starts_with("est_")),
names_to = c("type", "parameter"),
names_pattern = "(true|est)_(.*)"
) %>%
pivot_wider(
names_from = type,
values_from = value
) %>%
mutate(
parameter = factor(
parameter,
levels = c("weight_direct", "weight_social", "learning_rate"),
labels = c("Direct Evidence Weight", "Social Evidence Weight", "Learning Rate")
)
) %>%
ggplot(aes(x = true, y = est)) +
geom_point(size = 3, alpha = 0.7) +
geom_abline(intercept = 0, slope = 1, linetype = "dashed") +
facet_wrap(~ parameter, scales = "free") +
labs(
title = "Parameter Recovery for Sequential Updating Model",
subtitle = "Comparing true parameter values to posterior means",
x = "True Parameter Value",
y = "Estimated Parameter Value"
) +
theme_minimal()
# Display recovery plot
print(p_recovery)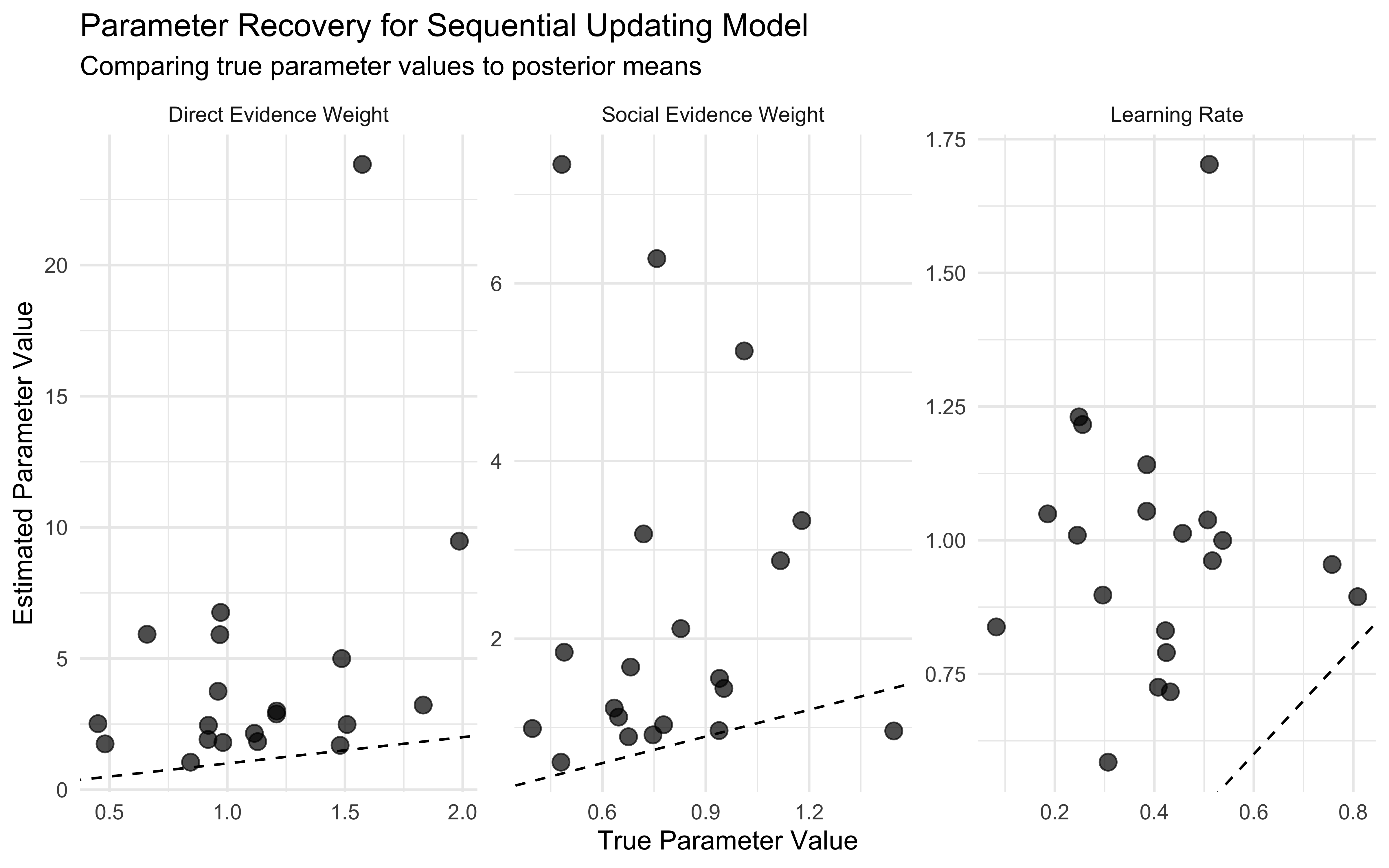
# Examine posterior predictive checks
# Extract belief trajectories
belief_samples <- array(NA, dim = c(n_samples, n_agents, n_trials))
for (j in 1:n_agents) {
for (t in 1:n_trials) {
belief_samples[, j, t] <- draws_seq_multilevel[[paste0("belief[", j, ",", t, "]")]]
}
}
# Calculate mean and credible intervals for beliefs
belief_summary <- tibble(
agent_id = rep(rep(1:n_agents, each = n_trials), 3),
trial = rep(rep(1:n_trials, n_agents), 3),
statistic = rep(c("mean", "lower", "upper"), each = n_agents * n_trials),
value = c(
# Mean belief across samples
apply(belief_samples, c(2, 3), mean) %>% as.vector(),
# Lower 95% CI
apply(belief_samples, c(2, 3), quantile, 0.025) %>% as.vector(),
# Upper 95% CI
apply(belief_samples, c(2, 3), quantile, 0.975) %>% as.vector()
)
)
# Reshape for plotting
belief_wider <- belief_summary %>%
pivot_wider(
names_from = statistic,
values_from = value
)
# Visualize belief trajectories for selected agents
p_belief_trajectories <- belief_wider %>%
filter(agent_id %in% selected_agents) %>%
left_join(sequential_sim_data %>%
dplyr::select(agent_id, trial, true_p_blue, jar_state),
by = c("agent_id", "trial")) %>%
ggplot() +
# Add true jar state as background
geom_rect(aes(xmin = trial - 0.5, xmax = trial + 0.5,
ymin = -Inf, ymax = Inf,
fill = factor(jar_state)), alpha = 0.2) +
# Add posterior belief intervals
geom_ribbon(aes(x = trial, ymin = lower, ymax = upper, group = agent_id),
alpha = 0.3, fill = "blue") +
# Add mean posterior belief
geom_line(aes(x = trial, y = mean, color = factor(agent_id)), size = 1) +
# Add true belief from simulation
geom_line(data = sequential_sim_data %>% filter(agent_id %in% selected_agents),
aes(x = trial, y = belief, group = agent_id),
linetype = "dashed") +
# Add true choices
geom_point(data = sequential_sim_data %>% filter(agent_id %in% selected_agents),
aes(x = trial, y = choice, shape = "Actual Choice"), size = 2) +
# Styling
facet_wrap(~ agent_id, ncol = 1) +
scale_fill_manual(values = c("0" = "pink", "1" = "lightblue"),
labels = c("Mostly Red Jar", "Mostly Blue Jar"),
name = "True Jar State") +
scale_color_brewer(palette = "Dark2", name = "Agent ID") +
scale_shape_manual(values = c("Actual Choice" = 4)) +
ylim(0, 1) +
labs(
title = "Belief Updating Over Time",
subtitle = "Blue ribbons show 95% credible intervals of estimated beliefs\nDashed lines show true simulated beliefs",
x = "Trial",
y = "Belief/Choice Probability",
shape = ""
) +
theme_minimal()
# Display belief trajectories
print(p_belief_trajectories)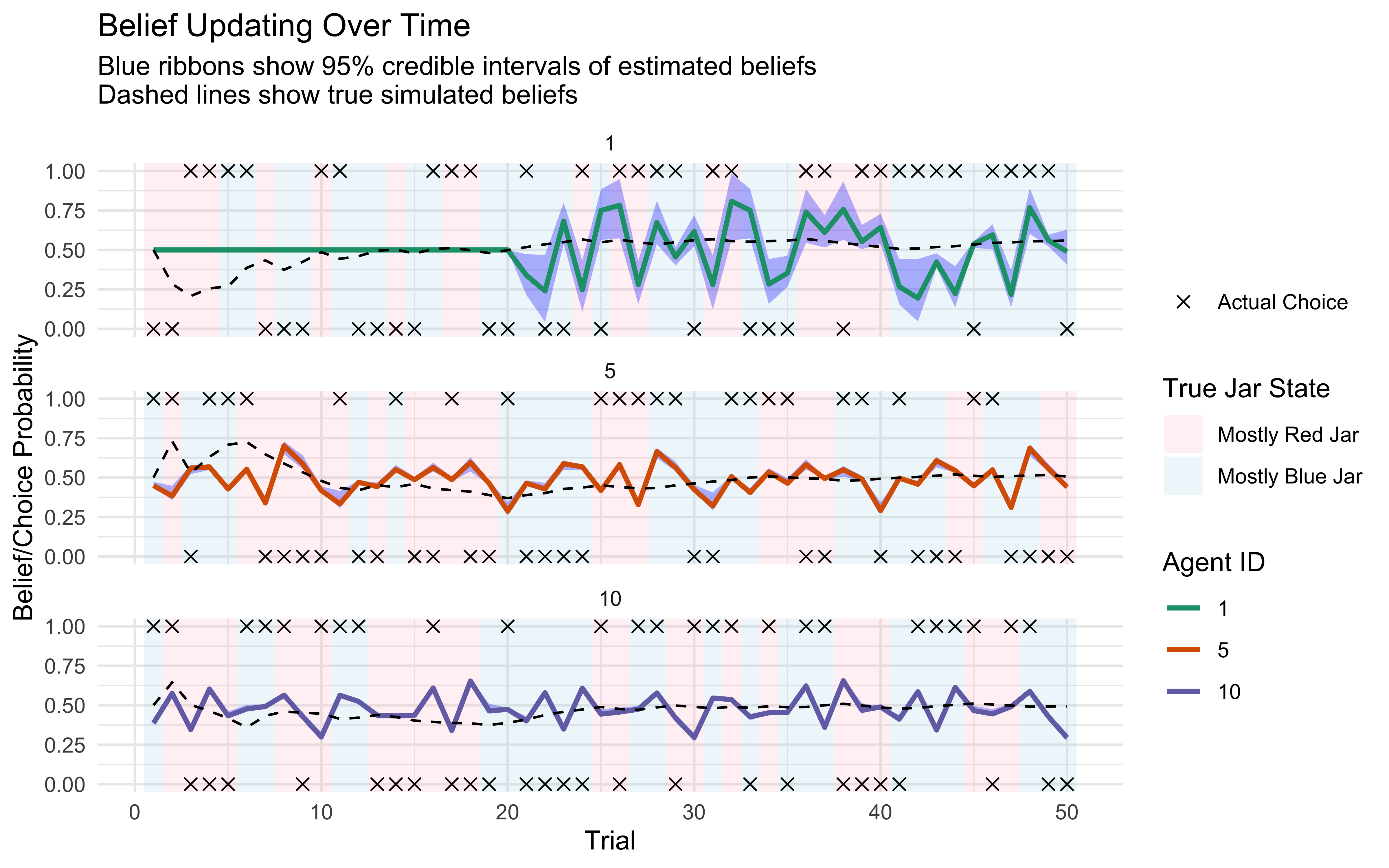
# Compare learning styles across agents
learning_styles <- recovery_data %>%
mutate(
relative_weight = est_weight_direct / est_weight_social,
learning_speed = est_learning_rate
)
p_learning_styles <- ggplot(learning_styles, aes(x = relative_weight, y = learning_speed)) +
geom_point(size = 3, alpha = 0.7) +
geom_text(aes(label = agent_id), hjust = -0.3, vjust = 0.3, size = 3) +
labs(
title = "Individual Learning Styles",
subtitle = "Mapping agents by their evidence weighting and learning speed",
x = "Relative Weight (Direct/Social)",
y = "Learning Rate"
) +
theme_minimal()
print(p_learning_styles)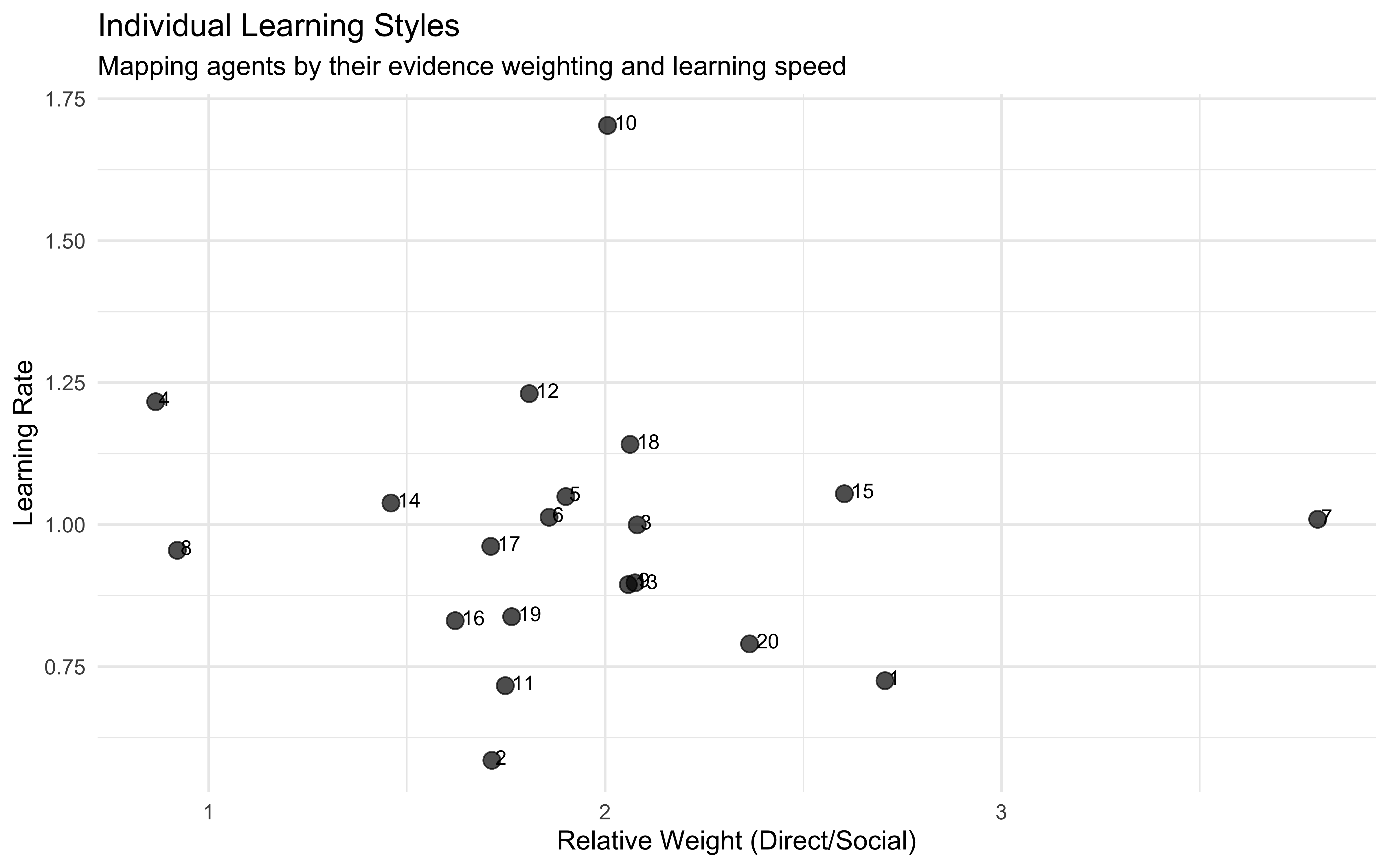
# Calculate correlations between estimated parameters
param_correlations <- cor(
cbind(
learning_styles$est_weight_direct,
learning_styles$est_weight_social,
learning_styles$est_learning_rate
)
)
colnames(param_correlations) <- rownames(param_correlations) <-
c("Weight (Direct)", "Weight (Social)", "Learning Rate")
# Extract population-level parameter correlations from the model
correlation_matrix <- matrix(NA, nrow = 3, ncol = 3)
for (i in 1:3) {
for (j in 1:3) {
correlation_matrix[i, j] <- mean(draws_seq_multilevel[[paste0("Omega[", i, ",", j, "]")]])
}
}
colnames(correlation_matrix) <- rownames(correlation_matrix) <-
c("Total Weight", "Weight Prop", "Learning Rate")
cat("\nEstimated parameter correlations:\n")##
## Estimated parameter correlations:## Weight (Direct) Weight (Social) Learning Rate
## Weight (Direct) 1.00000000 0.7527066 0.08451286
## Weight (Social) 0.75270656 1.0000000 0.14876461
## Learning Rate 0.08451286 0.1487646 1.00000000##
## Population-level parameter correlations:## Total Weight Weight Prop Learning Rate
## Total Weight 1.000000000 0.017304172 0.007257079
## Weight Prop 0.017304172 1.000000000 0.008023128
## Learning Rate 0.007257079 0.008023128 1.00000000011.24 Sequential Bayesian Evidence Integration Models
11.24.1 Understanding Belief Updating Over Time
Real-world learning rarely happens all at once - it’s a dynamic process where our beliefs evolve as we gather new evidence over time. The sequential Bayesian models we’ve developed capture this dynamic learning process by tracking how beliefs are updated from trial to trial.
11.24.2 The Sequential Updating Framework
Our sequential updating models build on the static evidence integration models from earlier, but with a crucial difference: beliefs are continuously updated based on new evidence. This creates a recursive structure where:
The agent starts with some initial belief (prior)
After observing evidence, they update their belief (posterior)
This posterior becomes the prior for the next trial
The process repeats for each new piece of evidence
The key parameters that govern this updating process are:
Evidence weights (weight_direct and weight_social): How much influence each type of evidence has
Learning rate (alpha): How quickly beliefs change in response to new evidence
The learning rate parameter is particularly important - it determines whether an agent is conservative (low learning rate) or responsive (high learning rate) to new information. A learning rate near 1.0 means the agent fully incorporates new evidence, while a rate closer to 0 means the agent makes only small adjustments to beliefs.
11.24.3 Mathematical Formulation
For each trial t, the agent’s belief is updated according to:
α_t = α_t − 1 + λ × (w_d × E_d, t − 1 + w_s × E_s, t − 1)
β_t = β_t − 1 + λ × (w_d × (T_d, t−1−E_d, t−1) + w_s × (T_s,t−1−E_s,t−1))
Belief_t = α_t α_t + β_t
Where:
α_t and β_t are the parameters of the Beta distribution representing the belief at trial t
λ is the learning rate
w_d and w_s are the weights for direct and social evidence
E_{d,t−1} and E_{s,t-1} are the counts of blue marbles/signals in the previous trial
T_{d,t-1} and T_{s,t-1} are the total counts of marbles/signals in the previous trial
11.24.4 Moving from Single-Agent to Multilevel
The multilevel extension allows us to model individual differences in learning while still leveraging the commonalities across individuals. This approach:
Captures individual learning styles: Some people may learn faster, others may weight certain evidence types more heavily
Models population distributions: Helps understand the typical learning patterns and the range of variation Improves parameter estimation: Especially for individuals with limited or noisy data
The multilevel structure adds substantial complexity to the model implementation, requiring careful handling of:
Trial sequences: Each agent has their own sequence of trials and updating process Parameter correlations: Learning rate might correlate with evidence weighting Computational efficiency: Sequential updating creates dependencies that make parallelization challenging
Interpreting Model Results Our simulation and model fitting reveal several important insights: Parameter Recovery The model successfully recovers the key cognitive parameters:
Evidence weights: How much individuals trust different information sources Learning rate: How quickly they update their beliefs
This validates that our model can meaningfully measure these cognitive processes from observed choices. Learning Style Differences The scatterplot of learning styles shows a two-dimensional space of cognitive strategies:
The x-axis represents relative weighting of direct vs. social evidence The y-axis represents learning speed (how quickly beliefs change)
This creates a typology of learners:
Fast direct learners: Rapidly update based primarily on their own observations Cautious social learners: Slowly incorporate information, with emphasis on social cues Balanced adapters: Moderate learning rate with equal weighting of evidence sources
Belief Trajectories The plots of belief trajectories over time reveal how individuals track changing environmental statistics:
The shaded regions show the model’s uncertainty about beliefs The comparison with true simulated beliefs validates the model’s ability to recover learning dynamics The background coloring shows how beliefs align with true environmental states (jar probabilities)
Parameter Correlations The correlation matrix reveals relationships between cognitive parameters:
A negative correlation between learning rate and total evidence weight would suggest compensatory strategies (fast updating with conservative evidence weighting, or slow updating with strong evidence weighting) Correlations between direct and social weights might indicate general trust or skepticism toward evidence
11.18.6.3 3. Socially-Influenced Agent Scenario
Similarly, for the Socially-Influenced Agent (who overweights social evidence), we expect the weighted model to have an advantage. The size of this advantage indicates how crucial it is to account for the specific weighting pattern to understand this agent’s decision-making process.